|
Winston Price
Winston Harvey Price (1923 – April 30, 1981) was an American scientist and professor of epidemiology with a special interest in infectious diseases, who made media headlines in 1957, when he reported details of a vaccine for the common cold after isolating the first rhinovirus. He was acknowledged by the director of the Public Health Research Institute at the time. However, other specialists in the field of vaccine research have disputed his methods and data. Earlier in his career, he had detailed how ticks of the genus ''Dermacentor'' were the main vectors of ''Rickettsia rickettsii'' that caused Rocky mountain spotted fever in humans. Early life and education Price was born in New York City in 1923. He had one older brother, Ira, and his father was a wealthy physician. According to the 1925 New York State Census, his mother was Canadian-born Florence, who had emigrated to the United States. His family lived at 1565 Grand Concourse in the Bronx. In 1942 he earned a B.A. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baltimore, Maryland
Baltimore ( , locally: or ) is the most populous city in the U.S. state of Maryland, fourth most populous city in the Mid-Atlantic, and the 30th most populous city in the United States with a population of 585,708 in 2020. Baltimore was designated an independent city by the Constitution of Maryland in 1851, and today is the most populous independent city in the United States. As of 2021, the population of the Baltimore metropolitan area was estimated to be 2,838,327, making it the 20th largest metropolitan area in the country. Baltimore is located about north northeast of Washington, D.C., making it a principal city in the Washington–Baltimore combined statistical area (CSA), the third-largest CSA in the nation, with a 2021 estimated population of 9,946,526. Prior to European colonization, the Baltimore region was used as hunting grounds by the Susquehannock Native Americans, who were primarily settled further northwest than where the city was later built. Colonis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rickettsia Rickettsii
''Rickettsia rickettsii'' (abbreviated as ''R. rickettsii'') is a gram-negative, intracellular, coccobacillus bacterium that is around 0.8 to 2.0 μm long. ''R. rickettsii'' is the causative agent of Rocky Mountain spotted fever. ''R. rickettsii'' is one of the most pathogenic ''Rickettsia'' strains. It affects a large majority of the Western Hemisphere and small portions of the Eastern Hemisphere. History Rocky Mountain spotted fever (RMSF) first emerged in the Idaho Valley in 1896. At that time, not much information was known about the disease; it was originally called Black Measles because patients had a characteristic spotted rash appearance throughout their body. The first clinical description of Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever was reported in 1899 by Edward E. Maxey. Howard Ricketts (1871–1910), an associate professor of pathology at the University of Chicago in 1902, was the first to identify and study ''R. rickettsii''. At this time, the trademark rash now began to slowl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Offit
Paul Allan Offit (born March 27, 1951) is an American pediatrician specializing in infectious diseases, vaccines, immunology, and virology. He is the co-inventor of a rotavirus vaccine. Offit is the Maurice R. Hilleman Professor of Vaccinology, professor of pediatrics at the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, former chief of the Division of Infectious Diseases (1992–2014), and the director of the Vaccine Education Center at The Children's Hospital of Philadelphia. He has been a member of the Centers for Disease Control (CDC) Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices. Offit is a board member of Every Child By Two and a Founding Board Member of the Autism Science Foundation (ASF). Offit has published more than 130 papers in medical and scientific journals in the areas of rotavirus-specific immune responses and vaccine safety, and is the author or co-author of books on vaccines, vaccination, the rejection of medicine by some religious groups, and an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4-Aminobenzoic Acid
4-Aminobenzoic acid (also known as ''para''-aminobenzoic acid or PABA because the two functional groups are attached to the benzene ring across from one another in the ''para'' position) is an organic compound with the formula H2NC6H4CO2H. PABA is a white solid, although commercial samples can appear gray. It is slightly soluble in water. It consists of a benzene ring substituted with amino and carboxyl groups. The compound occurs extensively in the natural world. Production and occurrence In industry, PABA is prepared mainly by two routes: * Reduction of 4-nitrobenzoic acid * Hoffman degradation of the monoamide derived from terephthalic acid. Food sources of PABA include liver, brewer's yeast (and unfiltered beer), kidney, molasses, mushrooms, and whole grains. A review on this compound. Biology Biochemistry PABA is an intermediate in the synthesis of folate by bacteria, plants, and fungi. Many bacteria, including those found in the human intestinal tract such as ''E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haemaphysalis
''Haemaphysalis'' is a genus of ticks, containing these species: *'' Haemaphysalis aborensis'' Warburton, 1913 *'' Haemaphysalis aciculifer'' Warburton, 1913 *'' Haemaphysalis aculeata'' Lavarra, 1904 *'' Haemaphysalis adleri'' Feldman-Muhsam, 1951 *'' Haemaphysalis anomala'' Warburton, 1913 *'' Haemaphysalis anomaloceraea'' Teng & Cui, 1984 *'' Haemaphysalis anoplos'' Hoogstraal, Uilenberg & Klein, 1967 *'' Haemaphysalis aponommoides'' Warburton, 1913 *'' Haemaphysalis asiatica'' (Supino, 1897) *'' Haemaphysalis atheruri'' Hoogstraal, Trapido & Kohls, 1965 *'' Haemaphysalis bancrofti'' Nuttall & Warburton, 1915 *'' Haemaphysalis bandicota'' Hoogstraal & Kohls, 1965 *'' Haemaphysalis bartelsi'' Schulze, 1938 *'' Haemaphysalis bequaerti'' Hoogstraal, 1956 *'' Haemaphysalis birmaniae'' Supino, 1897 *'' Haemaphysalis bispinosa'' Neumann, 1897 *'' Haemaphysalis bochkovi'' Apanaskevich & Tomlinson, 2019Dmitry Apanaskevich and Jackson A. Tomlinson. 2019. Description of four new species ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
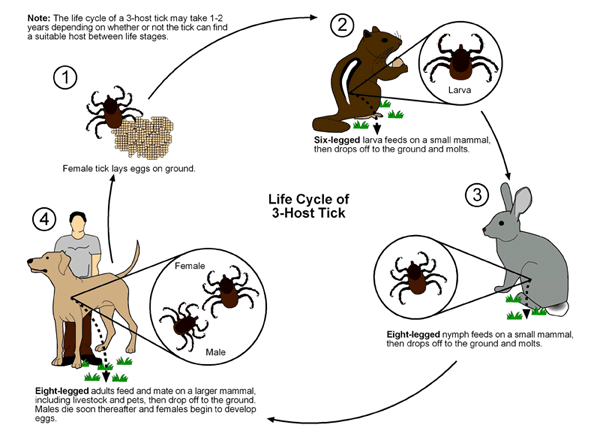
American Dog Tick (Dermacentor Variabilis)
''Dermacentor variabilis'', also known as the American dog tick or wood tick, is a species of tick that is known to carry bacteria responsible for several diseases in humans, including Rocky Mountain spotted fever and tularemia (''Francisella tularensis''). It is one of the best-known hard ticks. Diseases are spread when it sucks blood from the host. It may take several days for the host to experience symptoms. Though ''D. variabilis'' may be exposed to ''Borrelia burgdorferi'', the causative agent of Lyme disease, these ticks are not competent vectors for the transmission of this disease. The primary vectors for ''B. burgdorferi'' are the deer ticks ''Ixodes scapularis'' in eastern parts of the United States, ''Ixodes pacificus'' in California and Oregon, and ''Ixodes ricinus'' in Europe. ''D. variabilis'' may also carry ''Anaplasma phagocytophilum'', the causative agent of human granulocytic anaplasmosis, and ''Ehrlichia chaffeensis'', the causative agent of human monocytic ehr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteriophage
A bacteriophage (), also known informally as a ''phage'' (), is a duplodnaviria virus that infects and replicates within bacteria and archaea. The term was derived from "bacteria" and the Greek φαγεῖν ('), meaning "to devour". Bacteriophages are composed of proteins that encapsulate a DNA or RNA genome, and may have structures that are either simple or elaborate. Their genomes may encode as few as four genes (e.g. MS2) and as many as hundreds of genes. Phages replicate within the bacterium following the injection of their genome into its cytoplasm. Bacteriophages are among the most common and diverse entities in the biosphere. Bacteriophages are ubiquitous viruses, found wherever bacteria exist. It is estimated there are more than 1031 bacteriophages on the planet, more than every other organism on Earth, including bacteria, combined. Viruses are the most abundant biological entity in the water column of the world's oceans, and the second largest component of biom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biochemistry
Biochemistry or biological chemistry is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. A sub-discipline of both chemistry and biology, biochemistry may be divided into three fields: structural biology, enzymology and metabolism. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become successful at explaining living processes through these three disciplines. Almost all areas of the life sciences are being uncovered and developed through biochemical methodology and research. Voet (2005), p. 3. Biochemistry focuses on understanding the chemical basis which allows biological molecules to give rise to the processes that occur within living cells and between cells,Karp (2009), p. 2. in turn relating greatly to the understanding of tissues and organs, as well as organism structure and function.Miller (2012). p. 62. Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, which is the study of the molecular mechanisms of biological phenomena.As ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rockefeller University
The Rockefeller University is a private biomedical research and graduate-only university in New York City, New York. It focuses primarily on the biological and medical sciences and provides doctoral and postdoctoral education. It is classified among "R2: Doctoral Universities – High research activity." Rockefeller is the oldest biomedical research institute in the United States. In 2018, the faculty included 82 tenured and tenure-track members, including 37 members of the National Academy of Sciences, 17 members of the National Academy of Medicine, seven Lasker Award recipients, and five Nobel laureates. As of March 2022, a total of 26 Nobel laureates have been affiliated with Rockefeller University. The university is located on the Upper East Side of Manhattan, between 63rd and 68th streets on York Avenue. Richard P. Lifton became the university's eleventh president on September 1, 2016. The Rockefeller University Press publishes the ''Journal of Experimental Medicine' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million personnel from more than 30 countries. The major participants in the war threw their entire economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities behind the war effort, blurring the distinction between civilian and military resources. Aircraft played a major role in the conflict, enabling the strategic bombing of population centres and deploying the only two nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II was by far the deadliest conflict in human history; it resulted in 70 to 85 million fatalities, mostly among civilians. Tens of millions died due to genocides (including the Holocaust), starvation, ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arrowsmith (novel)
''Arrowsmith'' is a novel by American author Sinclair Lewis, first published in 1925. It won the 1926 Pulitzer Prize (which Lewis declined). Lewis was greatly assisted in its preparation by science writer Paul de Kruif, who received 25% of the royalties on sales, although Lewis was listed as the sole author. ''Arrowsmith'' is an early major novel dealing with the culture of science. It was written in the period after the reforms of medical education flowing from the Flexner Report on ''Medical Education in the United States and Canada: A Report to the Carnegie Foundation for the Advancement of Teaching'', 1910, which had called on medical schools in the United States to adhere to mainstream science in their teaching and research. The book was adapted by Hollywood as '' Arrowsmith'' in 1931, starring Ronald Colman and Helen Hayes. It was nominated for four Academy Awards, including Best Adapted Screenplay. Plot ''Arrowsmith'' tells the story of bright and scientifically minded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinclair Lewis
Harry Sinclair Lewis (February 7, 1885 – January 10, 1951) was an American writer and playwright. In 1930, he became the first writer from the United States (and the first from the Americas) to receive the Nobel Prize in Literature, which was awarded "for his vigorous and graphic art of description and his ability to create, with wit and humor, new types of characters." He is best known for his novels '' Main Street'' (1920), ''Babbitt'' (1922), '' Arrowsmith'' (1925), ''Elmer Gantry'' (1927), '' Dodsworth'' (1929), and ''It Can't Happen Here'' (1935). His works are known for their critical views of American capitalism and materialism in the interwar period. He is also respected for his strong characterizations of modern working women. H. L. Mencken wrote of him, " fthere was ever a novelist among us with an authentic call to the trade ... it is this red-haired tornado from the Minnesota wilds." Early life Born February 7, 1885, in the village of Sauk Centre, Minnesota, Le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)