|
Wind River Indian Reservation
The Wind River Indian Reservation, in the west-central portion of the U.S. state of Wyoming, is shared by two Native American tribes, the Eastern Shoshone ( shh, Gweechoon Deka, ''meaning: "buffalo eaters"'') and the Northern Arapaho ( arp, hoteiniiciihehe'). Roughly east to west by north to south, the Indian reservation is located in the Wind River Basin, and includes portions of the Wind River Range, Owl Creek Mountains, and Absaroka Range. The Wind River Indian Reservation is the seventh-largest American Indian reservation in the United States by area and the fifth-largest by population. The land area is approximately , and the total area (land and water) is . The reservation constitutes just over one-third of Fremont County and over one-fifth of Hot Springs County. The 2000 census reported the population of Fremont County as 40,237. According to the 2010 census, only 26,490 people now live on the reservation, with about 15,000 of the residents being non-Indians on ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Reservation
An Indian reservation is an area of land held and governed by a federally recognized Native American tribal nation whose government is accountable to the United States Bureau of Indian Affairs and not to the state government in which it is located. Some of the country's 574 federally recognized tribes govern more than one of the 326 Indian reservations in the United States, while some share reservations, and others have no reservation at all. Historical piecemeal land allocations under the Dawes Act facilitated sales to non–Native Americans, resulting in some reservations becoming severely fragmented, with pieces of tribal and privately held land being treated as separate enclaves. This jumble of private and public real estate creates significant administrative, political and legal difficulties. The total area of all reservations is , approximately 2.3% of the total area of the United States and about the size of the state of Idaho. While most reservations are small c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Casino
A casino is a facility for certain types of gambling. Casinos are often built near or combined with hotels, resorts, restaurants, retail shopping, cruise ships, and other tourist attractions. Some casinos are also known for hosting live entertainment, such as stand-up comedy, concerts, and sports. and usage ''Casino'' is of Italian origin; the root means a house. The term ''casino'' may mean a small country villa, summerhouse, or social club. During the 19th century, ''casino'' came to include other public buildings where pleasurable activities took place; such edifices were usually built on the grounds of a larger Italian villa or palazzo, and were used to host civic town functions, including dancing, gambling, music listening, and sports. Examples in Italy include Villa Farnese and Villa Giulia, and in the US the Newport Casino in Newport, Rhode Island. In modern-day Italian, a is a brothel (also called , literally "closed house"), a mess (confusing situation), or a noisy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bison
Bison are large bovines in the genus ''Bison'' (Greek: "wild ox" (bison)) within the tribe Bovini. Two extant and numerous extinct species are recognised. Of the two surviving species, the American bison, ''B. bison'', found only in North America, is the more numerous. Although colloquially referred to as a buffalo in the United States and Canada, it is only distantly related to the true buffalo. The North American species is composed of two subspecies, the Plains bison, ''B. b. bison'', and the wood bison, ''B. b. athabascae'', which is the namesake of Wood Buffalo National Park in Canada. A third subspecies, the eastern bison (''B. b. pennsylvanicus'') is no longer considered a valid taxon, being a junior synonym of ''B. b. bison''. References to "woods bison" or "wood bison" from the eastern United States refer to this subspecies, not ''B. b. athabascae'', which was not found in the region. The European bison, ''B. bonasus'', or wisent, or zubr, or colloquially European buff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blackfoot Confederacy
The Blackfoot Confederacy, ''Niitsitapi'' or ''Siksikaitsitapi'' (ᖹᐟᒧᐧᒣᑯ, meaning "the people" or " Blackfoot-speaking real people"), is a historic collective name for linguistically related groups that make up the Blackfoot or Blackfeet people: the ''Siksika'' ("Blackfoot"), the '' Kainai or Blood'' ("Many Chiefs"), and two sections of the Peigan or Piikani ("Splotchy Robe") – the Northern Piikani (''Aapátohsipikáni'') and the Southern Piikani (''Amskapi Piikani'' or ''Pikuni''). Broader definitions include groups such as the ''Tsúùtínà'' ( Sarcee) and ''A'aninin'' (Gros Ventre) who spoke quite different languages but allied with or joined the Blackfoot Confederacy. Historically, the member peoples of the Confederacy were nomadic bison hunters and trout fishermen, who ranged across large areas of the northern Great Plains of western North America, specifically the semi-arid shortgrass prairie ecological region. They followed the bison herds as they mig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cheyenne
The Cheyenne ( ) are an Indigenous people of the Great Plains. Their Cheyenne language belongs to the Algonquian language family. Today, the Cheyenne people are split into two federally recognized nations: the Southern Cheyenne, who are enrolled in the Cheyenne and Arapaho Tribes in Oklahoma, and the Northern Cheyenne, who are enrolled in the Northern Cheyenne Tribe of the Northern Cheyenne Indian Reservation in Montana. The Cheyenne comprise two Native American tribes, the Só'taeo'o or Só'taétaneo'o (more commonly spelled as Suhtai or Sutaio) and the Tsétsêhéstâhese (also spelled Tsitsistas, The term for the Cheyenne homeland is ''Tsiihistano''. Language The Cheyenne of Montana and Oklahoma speak the Cheyenne language, known as ''Tsêhésenêstsestôtse'' (common spelling: Tsisinstsistots). Approximately 800 people speak Cheyenne in Oklahoma. There are only a handful of vocabulary differences between the two locations. The Cheyenne alphabet contains 14 letters. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crow People
The Crow, whose autonym is Apsáalooke (), also spelled Absaroka, are Native Americans living primarily in southern Montana. Today, the Crow people have a federally recognized tribe, the Crow Tribe of Montana, with an Indian reservation located in the south-central part of the state. Crow Indians are a Plains tribe, who speak the Crow language, part of the Missouri River Valley branch of Siouan languages. Of the 14,000 enrolled tribal members, an estimated 3,000 spoke the Crow language in 2007. During the expansion into the West, the Crow Nation was allied with the United States against its neighbors and rivals, the Sioux and Cheyenne. In historical times, the Crow lived in the Yellowstone River valley, which extends from present-day Wyoming, through Montana and into North Dakota, where it joins the Missouri River. Since the 19th century, Crow people have been concentrated on their reservation established south of Billings, Montana. Today, they live in several major, mai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Plains
The Great Plains (french: Grandes Plaines), sometimes simply "the Plains", is a broad expanse of flatland in North America. It is located west of the Mississippi River and east of the Rocky Mountains, much of it covered in prairie, steppe, and grassland. It is the southern and main part of the Interior Plains, which also include the tallgrass prairie between the Great Lakes and Appalachian Plateau, and the Taiga Plains and Boreal Plains ecozones in Northern Canada. The term Western Plains is used to describe the ecoregion of the Great Plains, or alternatively the western portion of the Great Plains. The Great Plains lies across both Central United States and Western Canada, encompassing: * The entirety of the U.S. states of Kansas, Nebraska, North Dakota and South Dakota; * Parts of the U.S. states of Colorado, Iowa, Minnesota, Missouri, Montana, New Mexico, Oklahoma, Texas and Wyoming; * The southern portions of the Canadian provinces of Alberta, Saskatchewan and Manitoba. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
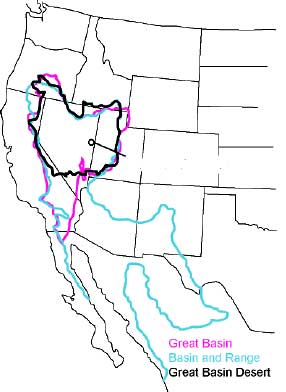
Great Basin
The Great Basin is the largest area of contiguous endorheic basin, endorheic watersheds, those with no outlets, in North America. It spans nearly all of Nevada, much of Utah, and portions of California, Idaho, Oregon, Wyoming, and Baja California. It is noted for both its arid climate and the basin and range topography that varies from the North American low point at Badwater Basin in Death Valley to the highest point of the contiguous United States, less than away at the summit of Mount Whitney. The region spans several physical geography, physiographic divisions, biomes, ecoregions, and deserts. Definition The term "Great Basin" is applied to hydrography, hydrographic, ecology, biological, floristic province, floristic, physiographic, topography, topographic, and Ethnography, ethnographic geographic areas. The name was originally coined by John C. Frémont, who, based on information gleaned from Joseph R. Walker as well as his own travels, recognized the hydrographic nature o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legend Rock
Legend Rock Petroglyph Site is located in Hot Springs County, Wyoming, 20 miles northwest of Hot Springs State Park (which is located in Thermopolis, Wyoming). Legend Rock is a petroglyph site which features hundreds of individual petroglyphs spread across the face of the rock. Although a handful of the rock's etchings have variously been eroded and defaced, a wide majority have been preserved for public viewing. The nearly 300 individual petroglyphs feature some of the oldest and best examples of Dinwoody rock art in the world.Legend Rock. Arts. Parks. History. Wyoming State Parks & Cultural Resources, Web. 27 Mar 2011. . The origins of the petroglyphs are still subject to debate. The site was listed on the National Register of Historic Places on July 5, 1973. and it is preserved by the state of Wyoming as a state historic site. References External links Legend Rock Wyoming Division of State Parks and Historic Sites * https://web.archive.org/web/20120324034208/http://wyopark ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torrey Lake Petroglyph District
The Torrey Lake Petroglyph District extends for about along Torrey Creek in Fremont County, Wyoming. The site includes about 175 petroglyphs, as well as eleven lithic scatters and a sheep trap. The petroglyphs are in the Interior Line Style, or Dinwoody style, consistent with other rock art in central Wyoming. Site investigations have uncovered a number of petroglyphs that had previously been hidden under lichen. The site was placed on the National Register of Historic Places The National Register of Historic Places (NRHP) is the United States federal government's official list of districts, sites, buildings, structures and objects deemed worthy of preservation for their historical significance or "great artistic ... on October 4, 1993. References External links Torrey Lake Petroglyph Districtat the Wyoming State Historic Preservation Office Torrey Valley Petroglyph Recording Projectat the American Rock Art Research Association {{NRHP in Fremont County, Wyoming Natio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bighorn Basin
The Bighorn Basin is a plateau region and intermontane basin, approximately 100 miles (160 km) wide, in north-central Wyoming in the United States. It is bounded by the Absaroka Range on the west, the Pryor Mountains on the north, the Bighorn Mountains on the east, and the Owl Creek Mountains and Bridger Mountains on the south. It is drained to the north by tributaries of the Bighorn River, which enters the basin from the south, through a gap between the Owl Creek and Bridger Mountains, as the Wind River, and becomes the Bighorn as it enters the basin. The region is semi-arid, receiving only 6–10 in (15–25 cm) of rain annually. The largest cities in the basin include the Wyoming towns of Cody, Thermopolis, Worland, and Powell. Sugar beets, pinto beans, sunflowers, barley, oats, corn and alfalfa hay are grown on irrigated farms in the region. History The basin was explored by John Colter in 1807. Just west of Cody, he discovered geothermal features that were la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |







.jpg)