|
Wilhelm Abraham Teller
Wilhelm Abraham Teller (9 January 17349 December 1804) was a German Protestant theologian who championed a rational approach to Christianity. Life and career Teller was born in Leipzig. His father, Romanus Teller (1703–1750), was a pastor at Leipzig, and afterwards became professor of theology in the University of Leipzig. He edited the earlier volumes of a ("Bible Book", 19 volumes, 1749–1770) which was designed as an adaptation for German readers of the exegetical works of Andrew Willet, Henry Ainsworth, Simon Patrick, Matthew Poole, Matthew Henry and others. Wilhelm Abraham studied philosophy and theology in the university of his native town. Amongst the men whose influence mainly determined his theological position and line of work was Johann August Ernesti. Teller's writings presented rationalism in its course of development from biblical supernaturalism to the borders of deistical naturalism. His first learned production was a Latin translation of Benjamin Kennico ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benjamin Kennicott
Benjamin Kennicott (4 April 171818 September 1783) was an English churchman and Hebrew scholar. Life Kennicott was born at Totnes, Devon where he attended Totnes Grammar School. He succeeded his father as master of a charity school, but the generosity of some friends enabled him to go to Wadham College, Oxford, in 1744, and he distinguished himself in Hebrew and divinity. While an undergraduate he published two dissertations, ''On the Tree of Life in Paradise, with some Observations on the Fall of Man'', and ''On the Oblations of Cain and Abel'', which obtained him a B.A. before the statutory time. In 1747 Kennicott was elected a fellow of Exeter College, Oxford, and in 1750 he took his degree of M.A. In 1764 he was made a fellow of the Royal Society, and in 1767 keeper of the Radcliffe Library. He was also a canon of Christ Church, Oxford (1770), and rector of Culham (1753) in Oxfordshire, and was subsequently given the living of Menheniot, Cornwall, which he was unable to vi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Illuminism
The Illuminati (; plural of Latin ''illuminatus'', 'enlightened') is a name given to several groups, both real and fictitious. Historically, the name usually refers to the Bavarian Illuminati, an Enlightenment-era secret society founded on 1 May 1776 in Bavaria, today part of Germany. The society's goals were to oppose superstition, obscurantism, religious influence over public life and abuses of state power. "The order of the day," they wrote in their general statutes, "is to put an end to the machinations of the purveyors of injustice, to control them without dominating them." The Illuminati—along with Freemasonry and other secret societies—were outlawed through edict by Charles Theodore, Elector of Bavaria, with the encouragement of the Catholic Church, in 1784, 1785, 1787 and 1790. During subsequent years, the group was generally vilified by conservative and religious critics who claimed that the Illuminati continued underground and were responsible for the French Re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Testament
The New Testament grc, Ἡ Καινὴ Διαθήκη, transl. ; la, Novum Testamentum. (NT) is the second division of the Christian biblical canon. It discusses the teachings and person of Jesus, as well as events in first-century Christianity. The New Testament's background, the first division of the Christian Bible, is called the Old Testament, which is based primarily upon the Hebrew Bible; together they are regarded as sacred scripture by Christians. The New Testament is a collection of Christian texts originally written in the Koine Greek language, at different times by various authors. While the Old Testament canon varies somewhat between different Christian denominations, the 27-book canon of the New Testament has been almost universally recognized within Christianity since at least Late Antiquity. Thus, in almost all Christian traditions today, the New Testament consists of 27 books: * 4 canonical gospels ( Matthew, Mark, Luke, and John) * The Acts of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christoph Friedrich Nicolai
Christoph Friedrich Nicolai (18 March 1733 – 11 January 1811) was a German writer and bookseller. Life Nicolai was born in Berlin, where his father, Christoph Gottlieb Nicolai (d. 1752), was the founder of the bookseller ''Nicolaische Buchhandlung''. He received a good education, and in 1749 went to Frankfurt (Oder) to learn his father's business, finding time also to become acquainted with English literature. In 1752 Nicolai returned to Berlin, and began to take part in literary controversy by defending John Milton against the attacks of JC Gottsched. His ''Briefe über den jetzigen Zustand der schönen Wissenschaften in Deutschland'', published anonymously in 1755 and reprinted by G Ellinger in 1894, were directed against both Gottsched and Gottsched's Swiss opponents, Johann Jakob Bodmer and Johann Jakob Breitinger; his enthusiasm for English literature won for him the friendship of Gotthold Ephraim Lessing and Moses Mendelssohn. In association with Mendelssohn he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Joachim Spalding
Johann Joachim Spalding (1 November 1714 – 25 May 1804) was a German Protestant theologian and philosopher of Scottish ancestry who was a native of Tribsees, Swedish Pomerania. He was the father of Georg Ludwig Spalding (1762–1811), a professor at Grauen Kloster in Berlin. He grew up as a son of the parish priest in Tribsees and studied himself philosophy and theology at the Universities of Rostock and Greifswald, afterwards working as an auxiliary preacher in his hometown of Tribsees. In 1755 he became a pastor in Lassan, then two years later served as a minister in the town of Barth. In 1764 he received the titles of provost and ''Oberkonsistorialrat'', and gained recognition for his sermons at St. Nicolai-Kirche and at Marienkirche in Berlin. He was a highly influential minister who had as friends, renowned personalities that included Ewald Christian von Kleist and Johann Wilhelm Ludwig Gleim. As a protest against the ''Wöllnersche Religionsedikt'' ( Wöllner Edic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friedrich Samuel Gottfried Sack
Friedrich Samuel Gottfried Sack (1738–1817) was Prussian theologian, court preacher, and Church governor.Lacroix 1880, p. 210. Life Friedrich Samuel Gottfried Sack was born in Magdeburg on 4 September 1738, the eldest son of August Friedrich Wilhelm Sack by his second wife. His mother was descended of a French refugee family, which explains a fondness which Sack had for the French language and literature. He studied at the University of Frankfort-on-the-Oder from 1755 to 1757. The next two years he studied in England, coming into contact with Secker, the Archbishop of Canterbury, Kennicott, Lardner, and others. On his return to Germany he acted as tutor to a young nobleman, whom he accompanied to Frankfort-on-the-Oder, and where he again heard lectures. He now associated much with Tollner. After preaching at Magdeburg (1769–1777), he was called by Frederick II as fifth court preacher to Berlin. Gradually he rose to the first place. In 1786 he became a member of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
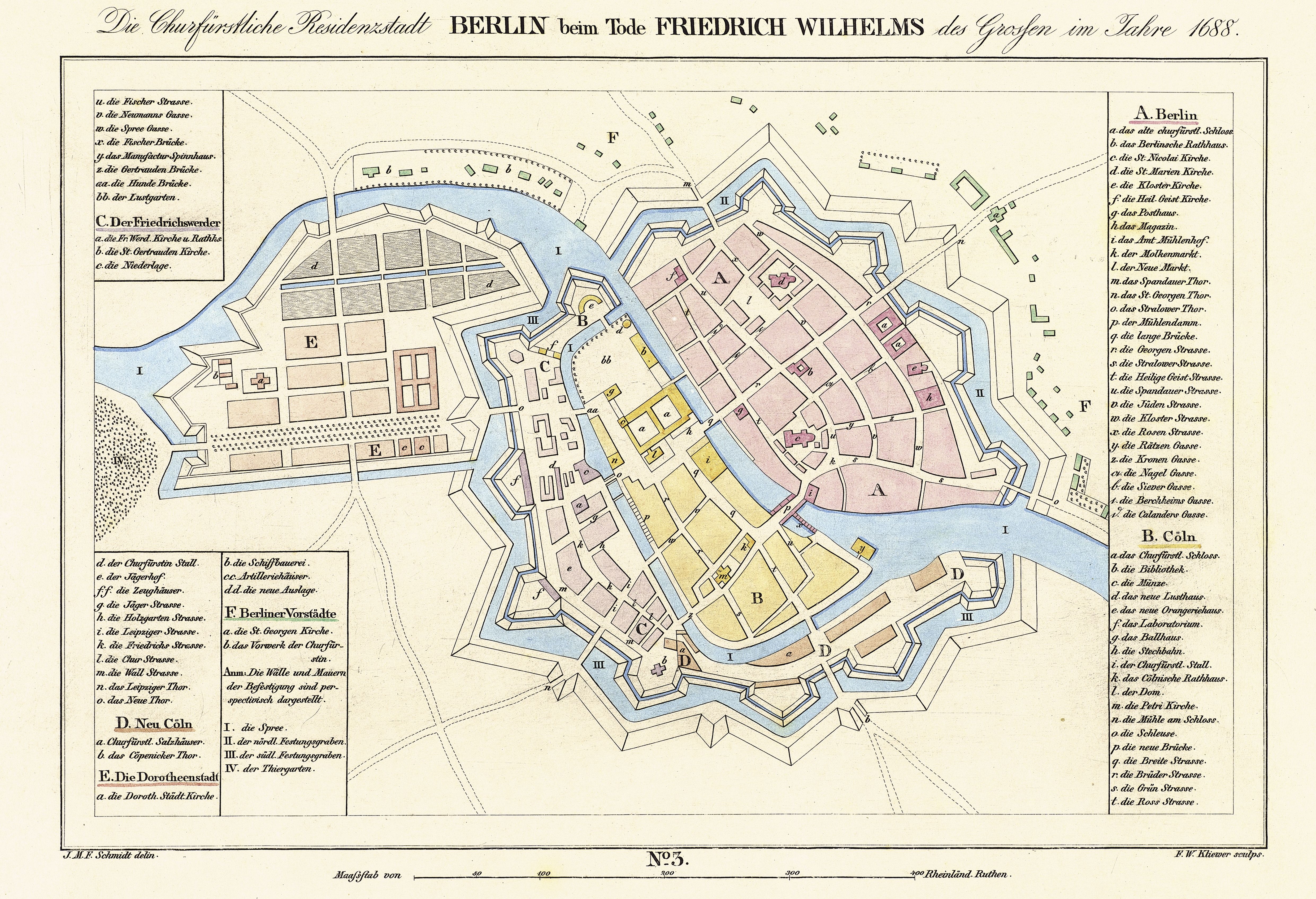
Berlin
Berlin ( , ) is the capital and List of cities in Germany by population, largest city of Germany by both area and population. Its 3.7 million inhabitants make it the European Union's List of cities in the European Union by population within city limits, most populous city, according to population within city limits. One of Germany's States of Germany, sixteen constituent states, Berlin is surrounded by the Brandenburg, State of Brandenburg and contiguous with Potsdam, Brandenburg's capital. Berlin's urban area, which has a population of around 4.5 million, is the second most populous urban area in Germany after the Ruhr. The Berlin/Brandenburg Metropolitan Region, Berlin-Brandenburg capital region has around 6.2 million inhabitants and is Metropolitan regions in Germany, Germany's third-largest metropolitan region after the Rhine-Ruhr and Frankfurt Rhine-Main, Rhine-Main regions. Berlin straddles the banks of the Spree (river), Spree, which flows into the Havel (a tributary of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consistory (Protestantism)
In Protestant usage, a consistory designates certain ruling bodies in various churches.''Encyclopedia of Protestantism'', J. Gordon Melton (ed.), New York: Facts On File, c2005, p. 162. The meaning and the scope of functions varies strongly, also along the separating lines of the Protestant denominations and church bodies. History Starting in 1539 the term was used for a body taking over the jurisdiction in marital matters, and later also church discipline, so that Protestant consistories can be regarded as successors not to the papal consistory in Rome but rather to the courts of Roman Catholic bishops.''The encyclopedia of Protestantism'', Hans J. Hillerbrand (ed.), New York: Routledge, 2004, . In the Lutheran or Reformed states of imperial immediacy in the Holy Roman Empire episcopal offices were not staffed any more and the secular government assumed the function of the bishop (summepiscopate, summus episcopus), looked after by the consistories. Not all Protestant churches ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cölln
Cölln () was the twin city of Old Berlin ( Altberlin) from the 13th century to the 18th century. Cölln was located on the Fisher Island section of Spree Island, opposite Altberlin on the western bank of the River Spree, until the cities were merged by Frederick I of Prussia to form Berlin in 1710. Today, the former site of Cölln is the historic core of the modern Mitte locality of the Berlin-Mitte borough in central Berlin. History Cölln is first mentioned in a 1237 deed, denoting a priest Symeon of Cölln's (Symeon de Colonia) Saint Peter's Church as a witness. This date is commonly regarded as the origin of Berlin, though Altberlin on the eastern bank of the Spree river was not mentioned before 1244 and parts of modern Greater Berlin, such as Spandau and Köpenick, are even older. Cölln and Altberlin were separated only by the river Spree, linked by the ''Mühlendamm'' causeway, hence there was a close connection right from the start. Since the trade route from Magd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Provost (religion)
A provost is a senior official in a number of Christian Churches. Historical development The word ''praepositus'' (Latin: "set over", from ''praeponere'', "to place in front") was originally applied to any ecclesiastical ruler or dignitary. It was soon more specifically applied to the immediate subordinate to the abbot of a monastery, or to the superior of a single cell, and it was defined as such in the Rule of St Benedict. The dean (''decanus'') was a similarly ranked official. Chrodegang of Metz adopted this usage from the Benedictines when he introduced the monastic organization of canon-law colleges, especially cathedral capitular colleges. The provostship (''praepositura'') was normally held by the archdeacon, while the office of dean was held by the archpriest. In many colleges, the temporal duties of the archdeacons made it impossible for them to fulfil those of the provostship, and the headship of the chapter thus fell to the dean. The title became ''prevost' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an emergency decree transferring powers of the Prussian government to German Chancellor Franz von Papen in 1932 and ''de jure'' by an Allied decree in 1947. For centuries, the House of Hohenzollern ruled Prussia, expanding its size with the Prussian Army. Prussia, with its capital at Königsberg and then, when it became the Kingdom of Prussia in 1701, Berlin, decisively shaped the history of Germany. In 1871, Prussian Minister-President Otto von Bismarck united most German principalities into the German Empire under his leadership, although this was considered to be a " Lesser Germany" because Austria and Switzerland were not included. In November 1918, the monarchies were abolished and the nobility lost its political power during ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)