|
Western Rufous Bristlebird
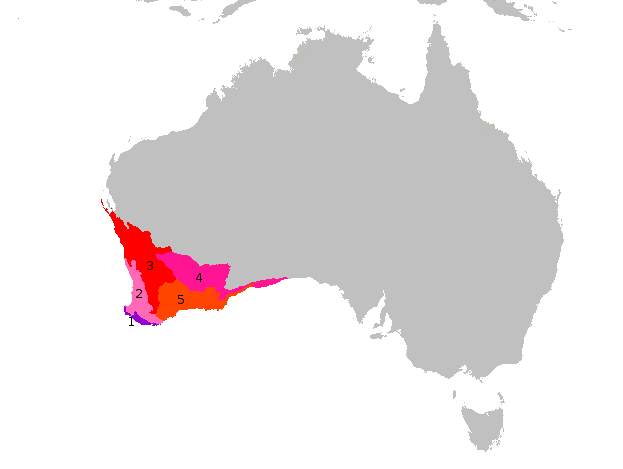
The western rufous bristlebird (''Dasyornis broadbenti litoralis''), also known as the rufous bristlebird (western), the south-western rufous bristlebird or the lesser rufous bristle bird, is an extinct and little-known subspecies of the rufous bristlebird that was endemic to Western Australia. History and status The bristlebird was discovered on 12 October 1901 at Ellensbrook near the Margaret River by Alexander William Milligan. He shot an adult female, describing it the following year in ''The Emu'' as a new species, ''Sphenura litoralis''. It was last reliably recorded in 1908 when a specimen was again collected. Since then there have been some unconfirmed sightings, which are not considered to be accurate, and the taxon is listed as extinct under Australia's Environment Protection and Biodiversity Conservation Act 1999. The reason for its extinction is thought to be the destruction of its shrubland habitat which was repeatedly burnt in the early 20th century to create p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extinction
Extinction is the termination of a kind of organism or of a group of kinds (taxon), usually a species. The moment of extinction is generally considered to be the death of the last individual of the species, although the capacity to breed and recover may have been lost before this point. Because a species' potential range may be very large, determining this moment is difficult, and is usually done retrospectively. This difficulty leads to phenomena such as Lazarus taxa, where a species presumed extinct abruptly "reappears" (typically in the fossil record) after a period of apparent absence. More than 99% of all species that ever lived on Earth, amounting to over five billion species, are estimated to have died out. It is estimated that there are currently around 8.7 million species of eukaryote globally, and possibly many times more if microorganisms, like bacteria, are included. Notable extinct animal species include non-avian dinosaurs, saber-toothed cats, dodos, m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cape Mentelle
Cape Mentelle is a limestone headland on the Indian Ocean coast of south-western Western Australia. It is within the Leeuwin-Naturaliste National Park, just north of the mouth of the Margaret River and west of the town of Margaret River. It lies on the Leeuwin-Naturaliste Ridge, halfway between Cape Naturaliste to the north, and Cape Leeuwin to the south, on the route of the Cape to Cape walking track. History The cape was named on 4 February 1803 by French navigator Nicolas Baudin, on his expedition to Australia, after Edme Mentelle (1730-1815), a French geographer, historian and cartographer. It has given its name to a well known Margaret River winery, Cape Mentelle Vineyards. See also * Cape Clairault * Cape Freycinet Cape Freycinet is a point on the coast between Cape Leeuwin and Cape Naturaliste in the south west of Western Australia. It is within the Shire of Augusta-Margaret River local government area, and the Leeuwin-Naturaliste National Park. It is n ... ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bird Extinctions Since 1500
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweight skeleton. Birds live worldwide and range in size from the bee hummingbird to the ostrich. There are about ten thousand living species, more than half of which are passerine, or "perching" birds. Birds have whose development varies according to species; the only known groups without wings are the extinct moa and elephant birds. Wings, which are modified forelimbs, gave birds the ability to fly, although further evolution has led to the loss of flight in some birds, including ratites, penguins, and diverse endemic island species. The digestive and respiratory systems of birds are also uniquely adapted for flight. Some bird species of aquatic environments, particularly seabirds and some waterbirds, have further evolved for swimming. Bird ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endemic Birds Of Southwest Australia
Endemism is the state of a species being found in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found elsewhere. For example, the Cape sugarbird is found exclusively in southwestern South Africa and is therefore said to be ''endemic'' to that particular part of the world. An endemic species can be also be referred to as an ''endemism'' or in scientific literature as an ''endemite''. For example '' Cytisus aeolicus'' is an endemite of the Italian flora. '' Adzharia renschi'' was once believed to be an endemite of the Caucasus, but it was later discovered to be a non-indigenous species from South America belonging to a different genus. The extreme opposite of an endemic species is one with a cosmopolitan distribution, having a global or widespread range. A rare alternative term for a species that is endemic is "precinctive", which applies to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dasyornis
The bristlebirds are a family of passerine birds, Dasyornithidae. There are three species in one genus, ''Dasyornis''. The family is endemic to the south-east coast and south-west corner of Australia.Del Hoyo, J.; Elliot, A. & Christie D. (editors). (2006). ''Handbook of the Birds of the World. Volume 12: Picathartes to Tits and Chickadees''. Lynx Edicions. The genus ''Dasyornis'' was sometimes placed in the Acanthizidae or, as a subfamily, Dasyornithinae, along with the Acanthizinae and Pardalotinae, within an expanded Pardalotidae, before being elevated to full family level by Christidis & Boles (2008).Higgins, P.J.; & Peter, J.M. (eds). (2003). ''Handbook of Australian, New Zealand and Antarctic Birds. Volume 6: Pardalotes to Shrike-thrushes''. Oxford University Press: Melbourne. Christidis, Les; & Boles, Walter E. (2008). ''Systematics and taxonomy of Australian birds''. CSIRO Publishing: Melbourne. Taxonomy and systematics Taxa accepted or described by Schodde & Maso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alarm Signal
In animal communication, an alarm signal is an antipredator adaptation in the form of signals emitted by social animals in response to danger. Many primates and birds have elaborate alarm calls for warning conspecifics of approaching predators. For example, the alarm call of the blackbird is a familiar sound in many gardens. Other animals, like fish and insects, may use non-auditory signals, such as chemical messages. Visual signs such as the white tail flashes of many deer have been suggested as alarm signals; they are less likely to be received by conspecifics, so have tended to be treated as a signal to the predator instead. Different calls may be used for predators on the ground or from the air. Often, the animals can tell which member of the group is making the call, so that they can disregard those of little reliability. Evidently, alarm signals promote survival by allowing the receivers of the alarm to escape from the source of peril; this can evolve by kin selection, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Land Snail
A land snail is any of the numerous species of snail that live on land, as opposed to the sea snails and freshwater snails. ''Land snail'' is the common name for terrestrial gastropod mollusks that have shells (those without shells are known as slugs). However, it is not always easy to say which species are terrestrial, because some are more or less amphibious between land and fresh water, and others are relatively amphibious between land and salt water. Land snails are a polyphyletic group comprising at least ten independent evolutionary transitions to terrestrial life (the last common ancestor of all gastropods was marine). The majority of land snails are pulmonates that have a lung and breathe air. Most of the non-pulmonate land snails belong to lineages in the Caenogastropoda, and tend to have a gill and an operculum. The largest clade of land snails is the Cyclophoroidea, with more than 7,000 species. Many of these operculate land snails live in habitats or microhabitats ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holotype
A holotype is a single physical example (or illustration) of an organism, known to have been used when the species (or lower-ranked taxon) was formally described. It is either the single such physical example (or illustration) or one of several examples, but explicitly designated as the holotype. Under the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN), a holotype is one of several kinds of name-bearing types. In the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants (ICN) and ICZN, the definitions of types are similar in intent but not identical in terminology or underlying concept. For example, the holotype for the butterfly '' Plebejus idas longinus'' is a preserved specimen of that subspecies, held by the Museum of Comparative Zoology at Harvard University. In botany, an isotype is a duplicate of the holotype, where holotype and isotypes are often pieces from the same individual plant or samples from the same gathering. A holotype is not necessarily "typ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shrubland
Shrubland, scrubland, scrub, brush, or bush is a plant community characterized by vegetation dominated by shrubs, often also including grasses, herbs, and geophytes. Shrubland may either occur naturally or be the result of human activity. It may be the mature vegetation type in a particular region and remain stable over time, or a transitional community that occurs temporarily as the result of a disturbance, such as fire. A stable state may be maintained by regular natural disturbance such as fire or browsing. Shrubland may be unsuitable for human habitation because of the danger of fire. The term was coined in 1903. Shrubland species generally show a wide range of adaptations to fire, such as heavy seed production, lignotubers, and fire-induced germination. Botanical structural form In botany and ecology a shrub is defined as a much-branched woody plant less than 8 m high and usually with many stems. Tall shrubs are mostly 2–8 m high, small shrubs 1–2 m high and su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southwest Australia
Southwest Australia is a biogeographic region in Western Australia. It includes the Mediterranean-climate area of southwestern Australia, which is home to a diverse and distinctive flora and fauna. The region is also known as the Southwest Australia Global Diversity Hotspot, as well as Kwongan. Geography The region includes the Mediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrub ecoregions of Western Australia. The region covers 356,717 km2, consisting of a broad coastal plain 20-120 kilometres wide, transitioning to gently undulating uplands made up of weathered granite, gneiss and laterite. Bluff Knoll in the Stirling Range is the highest peak in the region, at 1,099 metres (3,606 ft) elevation. Desert and xeric shrublands lie to the north and east across the centre of Australia, separating Southwest Australia from the other Mediterranean and humid-climate regions of the continent. Climate The region has a wet-winter, dry-summer Mediterranean climate, one of five such regio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cape Naturaliste
Cape Naturaliste is a headland in the south western region of Western Australia at the western edge of the Geographe Bay. It is the northernmost point of the Leeuwin-Naturaliste Ridge which was named after the cape. Also the Leeuwin-Naturaliste National Park, Cape Naturaliste Lighthouse and the Cape to Cape hiking track were named after this location. Settlements The nearest settlement is Bunker Bay – a community that evolved from holiday shacks to very expensive housing for wealthy residents as well as featuring a popular beach resort. Further east, across the Bay, is Dunsborough, a much older settlement. Busselton is located still further east from there. History The first peoples in Cape Naturaliste were the Wardandi Aboriginals, who called it "Kwirreejeenungup", meaning "the place with the beautiful view". In 1801, the French navigator Nicolas Baudin stopped here on 30 May during his exploration of Australia. The French were mapping the coast of New Holland (Australia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subspecies
In biological classification, subspecies is a rank below species, used for populations that live in different areas and vary in size, shape, or other physical characteristics (morphology), but that can successfully interbreed. Not all species have subspecies, but for those that do there must be at least two. Subspecies is abbreviated subsp. or ssp. and the singular and plural forms are the same ("the subspecies is" or "the subspecies are"). In zoology, under the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature, the subspecies is the only taxonomic rank below that of species that can receive a name. In botany and mycology, under the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants, other infraspecific ranks, such as variety, may be named. In bacteriology and virology, under standard bacterial nomenclature and virus nomenclature, there are recommendations but not strict requirements for recognizing other important infraspecific ranks. A taxonomist decides whether ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)