Land snail on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]


 A land snail is any of the numerous species of snail that live on land, as opposed to the
A land snail is any of the numerous species of snail that live on land, as opposed to the

 Land snails move by gliding along on their muscular foot, which is lubricated with
Land snails move by gliding along on their muscular foot, which is lubricated with

 A snail breaks up its food using the
A snail breaks up its food using the
File:Snail 9881.JPG, Snail with a rightwardly spiraling shell
File:Samsoncj snail 07.jpg, Sinistral (left-handed) species of snail from western



 The great majority of land snails are hermaphrodites with a full set of reproductive organs of both sexes, able to produce both
The great majority of land snails are hermaphrodites with a full set of reproductive organs of both sexes, able to produce both
 In an attempt to protect themselves against predators, land snails retract their soft parts into their shell when they are resting; some bury themselves. Land snails have many natural predators, including members of all the land
In an attempt to protect themselves against predators, land snails retract their soft parts into their shell when they are resting; some bury themselves. Land snails have many natural predators, including members of all the land
 Land snails have been eaten for thousands of years, going back at least as far as the Pleistocene. Archaeological evidence of snail consumption is especially abundant in Capsian sites in
Land snails have been eaten for thousands of years, going back at least as far as the Pleistocene. Archaeological evidence of snail consumption is especially abundant in Capsian sites in
 Snails are also popular in
Snails are also popular in 
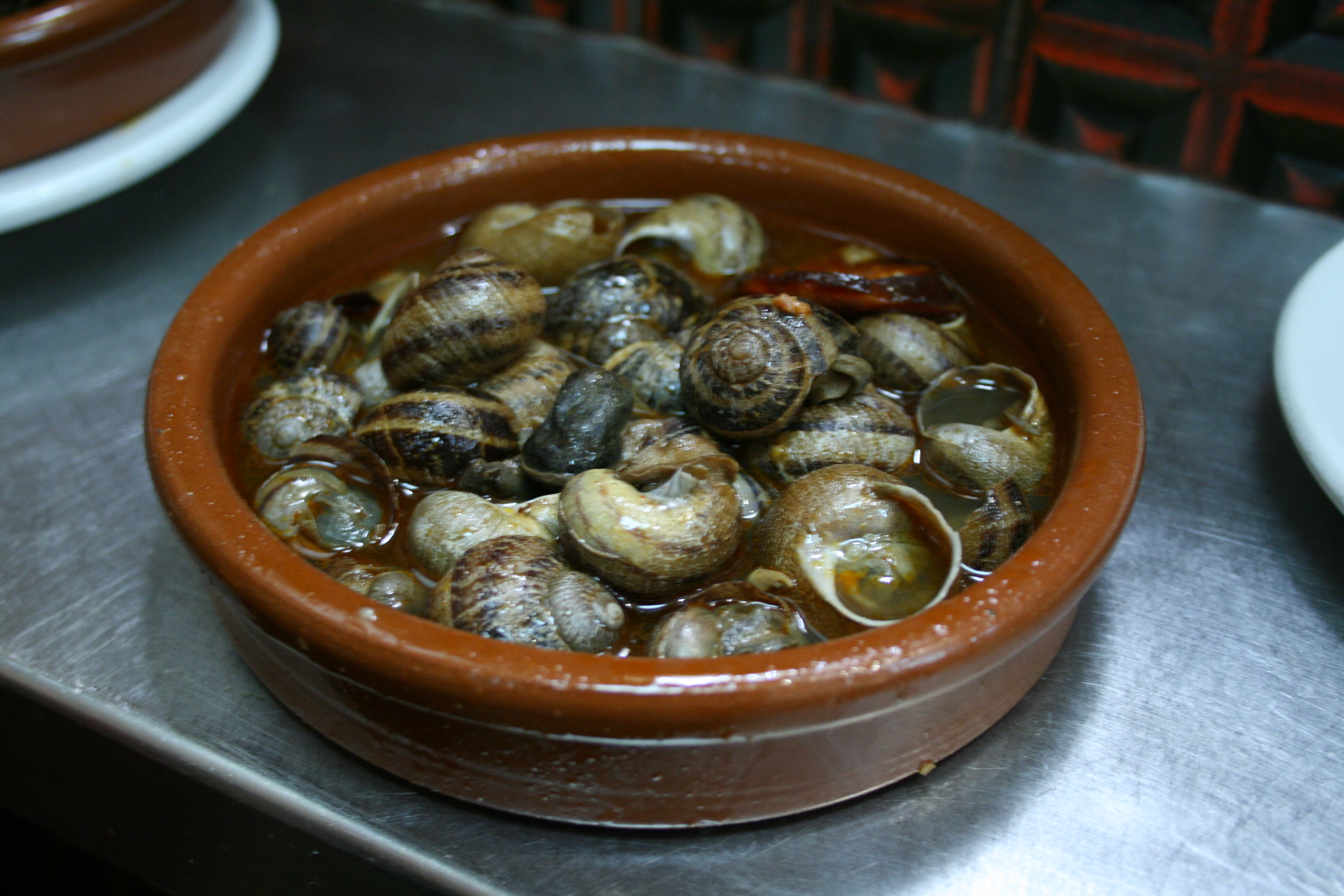 Traditional Spanish cuisine also uses snails ("caracoles" in Spanish; "caragols" or "cargols" in Catalan), consuming several species such as ''Cornu aspersum'', ''
Traditional Spanish cuisine also uses snails ("caracoles" in Spanish; "caragols" or "cargols" in Catalan), consuming several species such as ''Cornu aspersum'', ''
 In
In
Recipes for snails
on the UF /
Site with many photographs
Mollusc common names


 A land snail is any of the numerous species of snail that live on land, as opposed to the
A land snail is any of the numerous species of snail that live on land, as opposed to the sea snail
Sea snail is a common name for slow-moving marine gastropod molluscs, usually with visible external shells, such as whelk or abalone. They share the taxonomic class Gastropoda with slugs, which are distinguished from snails primarily by the ...
s and freshwater snails. ''Land snail'' is the common name
In biology, a common name of a taxon or organism (also known as a vernacular name, English name, colloquial name, country name, popular name, or farmer's name) is a name that is based on the normal language of everyday life; and is often contra ...
for terrestrial gastropod mollusk
Mollusca is the second-largest phylum of invertebrate animals after the Arthropoda, the members of which are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 85,000 extant species of molluscs are recognized. The number of fossil species is es ...
s that have shells (those without shells are known as slug
Slug, or land slug, is a common name for any apparently shell-less terrestrial gastropod mollusc. The word ''slug'' is also often used as part of the common name of any gastropod mollusc that has no shell, a very reduced shell, or only a sm ...
s). However, it is not always easy to say which species are terrestrial, because some are more or less amphibious between land and fresh water, and others are relatively amphibious between land and salt water.
Land snails are a polyphyletic
A polyphyletic group is an assemblage of organisms or other evolving elements that is of mixed evolutionary origin. The term is often applied to groups that share similar features known as homoplasies, which are explained as a result of conver ...
group comprising at least ten independent evolutionary transitions to terrestrial life (the last common ancestor of all gastropods was marine). The majority of land snails are pulmonate
Pulmonata or pulmonates, is an informal group (previously an order, and before that a subclass) of snails and slugs characterized by the ability to breathe air, by virtue of having a pallial lung instead of a gill, or gills. The group includ ...
s that have a lung and breathe air. Most of the non-pulmonate land snails belong to lineages in the Caenogastropoda, and tend to have a gill and an operculum. The largest clade of land snails is the Cyclophoroidea, with more than 7,000 species. Many of these operculate land snails live in habitats or microhabitats that are sometimes (or often) damp or wet, such as in moss
Mosses are small, non-vascular flowerless plants in the taxonomic division Bryophyta (, ) '' sensu stricto''. Bryophyta (''sensu lato'', Schimp. 1879) may also refer to the parent group bryophytes, which comprise liverworts, mosses, and hor ...
.
Land snails have a strong muscular foot; they use mucus
Mucus ( ) is a slippery aqueous secretion produced by, and covering, mucous membranes. It is typically produced from cells found in mucous glands, although it may also originate from mixed glands, which contain both serous and mucous cells. It ...
to enable them to crawl over rough surfaces and to keep their soft bodies from drying out. Like other mollusks, land snails have a mantle
A mantle is a piece of clothing, a type of cloak. Several other meanings are derived from that.
Mantle may refer to:
*Mantle (clothing), a cloak-like garment worn mainly by women as fashionable outerwear
**Mantle (vesture), an Eastern Orthodox ve ...
, and they have one or two pairs of tentacles on their head. Their internal anatomy includes a radula
The radula (, ; plural radulae or radulas) is an anatomical structure used by molluscs for feeding, sometimes compared to a tongue. It is a minutely toothed, chitinous ribbon, which is typically used for scraping or cutting food before the food ...
and a primitive brain.
In terms of reproduction, many caenogastropod land snails (e.g., diplommatinids) are dioecious, but pulmonate land snails are hermaphrodites (they have a full set of organs of both sexes) and most lay clutches of eggs in the soil. Tiny snails hatch out of the egg with a small shell in place, and the shell grows spirally as the soft parts gradually increase in size. Most land snails have shells that are right-handed in their coiling.
A wide range of different vertebrate and invertebrate animals prey on land snails. They are used as food by humans in various cultures worldwide, and are raised on farms in some areas for use as food.
Biology
Physical characteristics


 Land snails move by gliding along on their muscular foot, which is lubricated with
Land snails move by gliding along on their muscular foot, which is lubricated with mucus
Mucus ( ) is a slippery aqueous secretion produced by, and covering, mucous membranes. It is typically produced from cells found in mucous glands, although it may also originate from mixed glands, which contain both serous and mucous cells. It ...
and covered with epithelial cilia. This motion is powered by succeeding waves of muscular contractions that move down the ventral of the foot. This muscular action is clearly visible when a snail is crawling on the glass of a window or aquarium. Snails move at a proverbially low speed (1 mm/s is a typical speed for adult '' Helix lucorum''). Snails secrete mucus externally to keep their soft bodies from drying out. They also secrete mucus from the foot to aid in locomotion by reducing friction, and to help reduce the risk of mechanical injury from sharp objects, meaning they can crawl over a sharp edge like a straight razor and not be injured. The mucus that land snails secrete with the foot leaves a slime trail
Snail slime (''mucopolysaccharide'') is a kind of mucus (an external bodily secretion) produced by snails, which are gastropod mollusks. Land snails and slugs both produce mucus, as does every other kind of gastropod, from marine, freshwater, ...
behind them, which is often visible for some hours afterwards as a shiny "path" on the surface over which they have crawled.
Snails (like all molluscs) also have a mantle
A mantle is a piece of clothing, a type of cloak. Several other meanings are derived from that.
Mantle may refer to:
*Mantle (clothing), a cloak-like garment worn mainly by women as fashionable outerwear
**Mantle (vesture), an Eastern Orthodox ve ...
, a specialized layer of tissue which covers all of the internal organs as they are grouped together in the visceral mass. The mantle also extends outward in flaps which reach to the edge of the shell and in some cases can cover the shell, and which are partially retractable. The mantle is attached to the shell, and creates the shell and makes shell growth possible by secretion.
Most molluscs, including land snails, have a shell which is part of their anatomy since the larval stage, and which grows with them in size by the process of secreting calcium carbonate along the open edge and on the inner side for extra strength. Although some land snails create shells that are almost entirely formed from the protein conchiolin, most land snails need a good supply of calcium
Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar t ...
in their diet and environment to produce a strong shell. A lack of calcium, or low pH in their surroundings, can result in thin, cracked, or perforated shells. Usually a snail can repair damage to its shell over time if its living conditions improve, but severe damage can be fatal.
When retracted into their shells, many snails with gills (including some terrestrial species) are able to protect themselves with a door-like anatomical structure called an '' operculum''.
Land snails range greatly in size. The largest living species is the Giant African Snail or Ghana Tiger Snail (''Achatina achatina
''Achatina achatina'', commonly known as the giant African snail, also known as the giant tiger land snail, and gigantocochlea, is a species of large, air-breathing land snail, a terrestrial pulmonate gastropod mollusk in the family Achatinidae. ...
''; Family Achatinidae), which can measure up to 30 cm. The largest land snails of non-tropical Eurasia are endemic Caucasian snails ''Helix buchi
A helix () is a shape like a corkscrew or spiral staircase. It is a type of smooth space curve with tangent lines at a constant angle to a fixed axis. Helices are important in biology, as the DNA molecule is formed as two intertwined helices, ...
'' and ''Helix goderdziana
''Helix goderdziana'' is a species of large air-breathing land snail, a terrestrial pulmonate gastropod mollusk in the family Helicidae, the typical snail.
This is the largest species in the genus ''Helix''.
Distribution
This species occu ...
'' from the south-eastern Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, ...
area in Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to t ...
and Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a list of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolia, Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with ...
; diameter of the shell of the latter may exceed 6 cm
Most land snails bear one or two pairs of tentacles on their heads. In most land snails
A land snail is any of the numerous species of snail that live on land, as opposed to the sea snails and freshwater snails. ''Land snail'' is the common name for terrestrial gastropod mollusks that have shells (those without shells are known ...
the eyes are carried on the first (upper) set of tentacles (called ommatophores
In anatomy, an eyestalk (sometimes spelled eye stalk and also known as an ommatophore) is a protrusion that extends an eye away from the body, giving the eye a better field of view. It is a common feature in nature and frequently appears in fict ...
or more informally 'eye stalks') which are usually roughly 75% of the width of the eyes. The second (lower) set of tentacles act as olfactory
The sense of smell, or olfaction, is the special sense through which smells (or odors) are perceived. The sense of smell has many functions, including detecting desirable foods, hazards, and pheromones, and plays a role in taste.
In humans, it ...
organs. Both sets of tentacles are retractable in land snails
A land snail is any of the numerous species of snail that live on land, as opposed to the sea snails and freshwater snails. ''Land snail'' is the common name for terrestrial gastropod mollusks that have shells (those without shells are known ...
.
Digestion and nervous system

 A snail breaks up its food using the
A snail breaks up its food using the radula
The radula (, ; plural radulae or radulas) is an anatomical structure used by molluscs for feeding, sometimes compared to a tongue. It is a minutely toothed, chitinous ribbon, which is typically used for scraping or cutting food before the food ...
inside its mouth. The radula is a chitinous ribbon-like structure containing rows of microscopic teeth. With this the snail scrapes at food, which is then transferred to the digestive tract. In a very quiet setting, a large land snail can be heard 'crunching' its food: the radula is tearing away at the surface of the food that the snail is eating.
The cerebral ganglia of the snail form a primitive brain
The brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It consists of nervous tissue and is typically located in the head ( cephalization), usually near organs for special ...
which is divided into four sections. This structure is very much simpler than the brains of mammal
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class (biology), class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in Female#Mammalian female, females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a ...
s, reptile
Reptiles, as most commonly defined are the animals in the class Reptilia ( ), a paraphyletic grouping comprising all sauropsids except birds. Living reptiles comprise turtles, crocodilians, squamates (lizards and snakes) and rhynchocephal ...
s and bird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweig ...
s, but nonetheless, snails are capable of associative learning.
Shell growth
As the snail grows, so does its calcium carbonate shell. The shell grows additively, by the addition of new calcium carbonate, which is secreted by glands located in the snail'smantle
A mantle is a piece of clothing, a type of cloak. Several other meanings are derived from that.
Mantle may refer to:
*Mantle (clothing), a cloak-like garment worn mainly by women as fashionable outerwear
**Mantle (vesture), an Eastern Orthodox ve ...
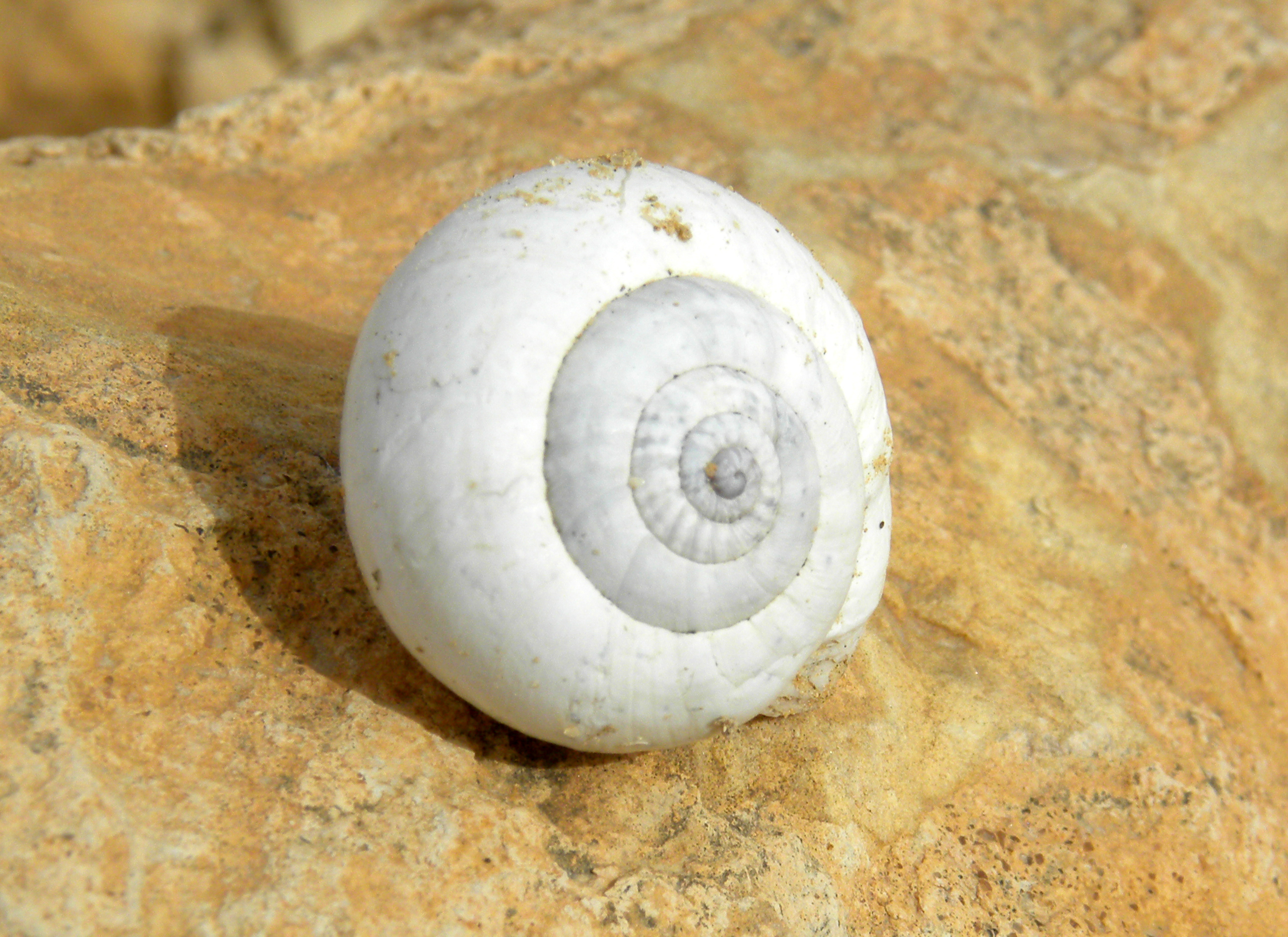
. The new material is added to the edge of the shell aperture (the opening of the shell). Therefore, the centre of the shell's spiral was made when the snail was younger, and the outer part when the snail was older. When the snail reaches full adult size, it may build a thickened lip around the shell aperture. At this point the snail stops growing, and begins reproducing.
A snail's shell forms a logarithmic spiral. Most snail shells are right-handed or dextral in coiling, meaning that if the shell is held with the apex (the tip, or the juvenile whorls) pointing towards the observer, the spiral proceeds in a clockwise direction from the apex to the opening.
India
India, officially the Republic of India ( Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the ...
Hibernation and estivation
Some snailshibernate
Hibernation is a state of minimal activity and metabolic depression undergone by some animal species. Hibernation is a seasonal heterothermy characterized by low body-temperature, slow breathing and heart-rate, and low metabolic rate. It most ...
during the winter (typically October through April in the Northern Hemisphere). They may also estivate
Aestivation ( la, aestas (summer); also spelled estivation in American English) is a state of animal dormancy, similar to hibernation, although taking place in the summer rather than the winter. Aestivation is characterized by inactivity and ...
in the summer in drought
A drought is defined as drier than normal conditions.Douville, H., K. Raghavan, J. Renwick, R.P. Allan, P.A. Arias, M. Barlow, R. Cerezo-Mota, A. Cherchi, T.Y. Gan, J. Gergis, D. Jiang, A. Khan, W. Pokam Mba, D. Rosenfeld, J. Tierney, an ...
conditions. To stay moist during hibernation, a snail seals its shell opening with a dry layer of mucus called an '' epiphragm''.
Reproduction



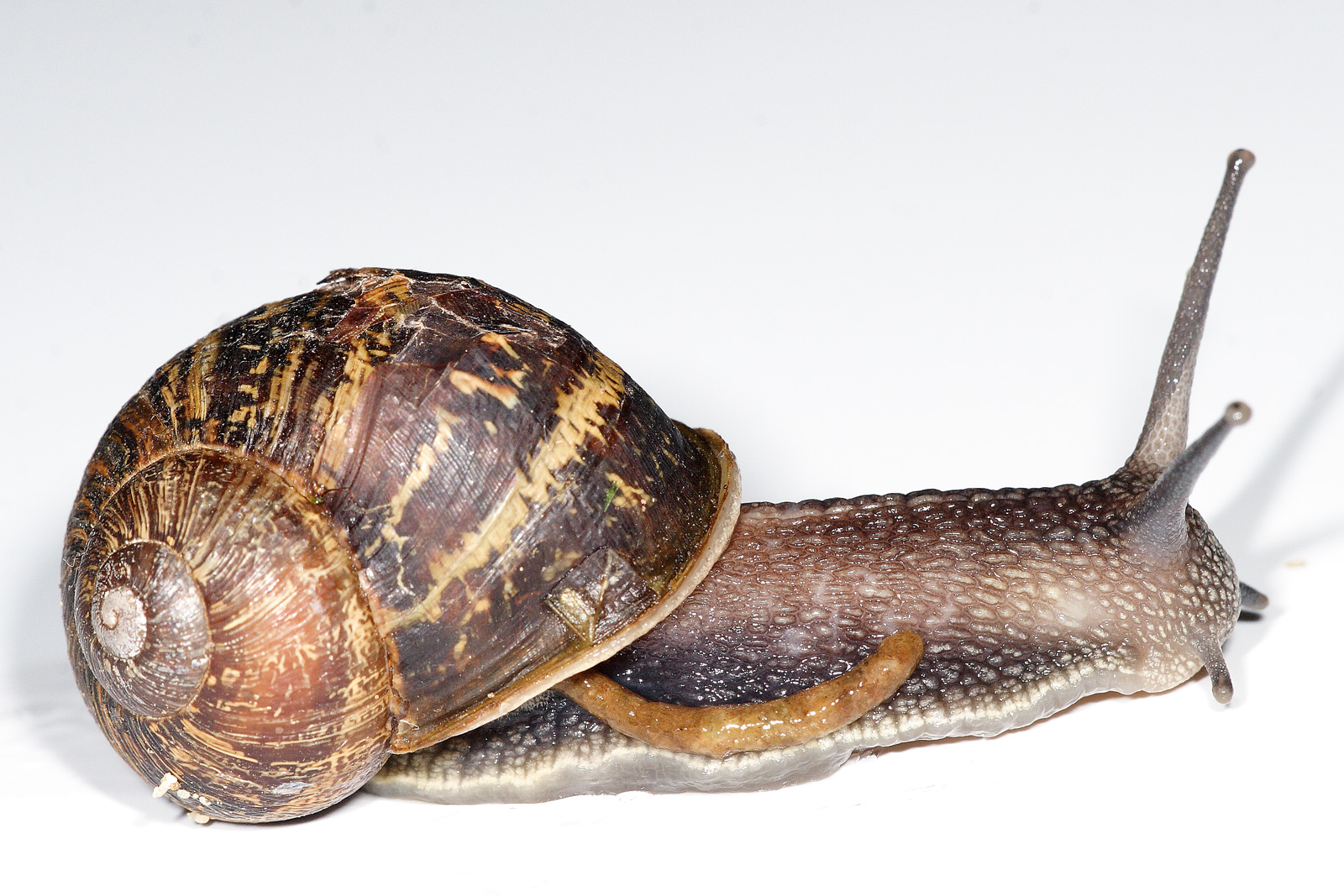
 The great majority of land snails are hermaphrodites with a full set of reproductive organs of both sexes, able to produce both
The great majority of land snails are hermaphrodites with a full set of reproductive organs of both sexes, able to produce both spermatozoa
A spermatozoon (; also spelled spermatozoön; ; ) is a motile sperm cell (biology), cell, or moving form of the ploidy, haploid cell (biology), cell that is the male gamete. A spermatozoon Fertilization, joins an ovum to form a zygote. (A zygote ...
and ova. A few groups of land snails such as the Pomatiidae, which are distantly related to periwinkles, have separate sexes: male and female. The age of sexual maturity varies depending on species of snail, ranging from as little as 6 weeks to 5 years. Adverse environmental conditions may delay sexual maturity in some snail species.
Most pulmonate
Pulmonata or pulmonates, is an informal group (previously an order, and before that a subclass) of snails and slugs characterized by the ability to breathe air, by virtue of having a pallial lung instead of a gill, or gills. The group includ ...
air-breathing land snails perform courtship
Courtship is the period wherein some couples get to know each other prior to a possible marriage. Courtship traditionally may begin after a betrothal and may conclude with the celebration of marriage. A courtship may be an informal and private ...
behaviors before mating. The courtship may last anywhere between two and twelve hours. In a number of different families of land snails and slugs, prior to mating one or more love darts are fired into the body of the partner.
Pulmonate land snails are prolific breeders and inseminate each other in pairs to internally fertilize their ova via a reproductive opening on one side of the body, near the front, through which the outer reproductive organs are extruded so that sperm can be exchanged. Fertilization then occurs and the eggs develop. Each brood may consist of up to 100 eggs.
Garden snails bury their eggs in shallow topsoil primarily while the weather is warm and damp, usually 5 to 10 cm down, digging with their foot. Egg sizes differ between species, from a 3 mm diameter in the grove snail
The grove snail, brown-lipped snail or Lemon snail (''Cepaea nemoralis'') is a species of air-breathing land snail, a terrestrial pulmonate gastropod mollusc. MolluscaBase eds. (2020). MolluscaBase. Cepaea nemoralis (Linnaeus, 1758). Accessed t ...
to a 6 mm diameter in the Giant African Land Snail. After 2 to 4 weeks of favorable weather, these eggs hatch and the young emerge. Snails may lay eggs as often as once a month.
There have been hybridizations of snail species; although these do not occur commonly in the wild, in captivity they can be coaxed into doing so.
Parthenogenesis
Parthenogenesis (; from the Greek grc, παρθένος, translit=parthénos, lit=virgin, label=none + grc, γένεσις, translit=génesis, lit=creation, label=none) is a natural form of asexual reproduction in which growth and developmen ...
has been reported only in one species of slug, but many species can self-fertilise.
Lifespan
Most species of land snail are annual, others are known to live 2 or 3 years, but some of the larger species may live over 10 years in the wild. For instance, 10-year old individuals of the Roman snail '' Helix pomatia'' are probably not uncommon in natural populations. Populations of some threatened species may be dependent on a pool of such long-lived adults. In captivity, the lifespan of snails can be much longer than in the wild, for instance up to 25 years in ''H. pomatia''.The Roman snail or escargot (''Helix pomatia'')Diet
In the wild, snails eat a variety of different foods. Terrestrial snails are usually herbivorous, however some species are predatory carnivores or omnivores, including the genus '' Powelliphanta'', which includes the largest carnivorous snails in the world, native to New Zealand. The diet of most land snails can include leaves, stems, soft bark, fruit, vegetables,fungi
A fungus (plural, : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of Eukaryote, eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and Mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified ...
and algae
Algae ( , ; : alga ) are any of a large and diverse group of photosynthetic, eukaryotic organisms. The name is an informal term for a polyphyletic grouping that includes species from multiple distinct clades. Included organisms range from ...
. Some species can cause damage to agricultural crops and garden
A garden is a planned space, usually outdoors, set aside for the cultivation, display, and enjoyment of plants and other forms of nature. The single feature identifying even the wildest wild garden is ''control''. The garden can incorporate bot ...
plants, and are therefore often regarded as pests
PESTS was an anonymous American activist group formed in 1986 to critique racism, tokenism, and exclusion in the art world. PESTS produced newsletters, posters, and other print material highlighting examples of discrimination in gallery represent ...
.
Predators
vertebrate
Vertebrates () comprise all animal taxon, taxa within the subphylum Vertebrata () (chordates with vertebral column, backbones), including all mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. Vertebrates represent the overwhelming majority of the ...
groups, three examples being thrushes, hedgehogs and '' Pareas'' snakes. Invertebrate predators include decollate snails, ground beetle
Ground beetles are a large, cosmopolitan family of beetles, the Carabidae, with more than 40,000 species worldwide, around 2,000 of which are found in North America and 2,700 in Europe. As of 2015, it is one of the 10 most species-rich animal fami ...
s, leech
Leeches are segmented parasitic or predatory worms that comprise the subclass Hirudinea within the phylum Annelida. They are closely related to the oligochaetes, which include the earthworm, and like them have soft, muscular segmented bodie ...
es, certain land flatworms such as ''Platydemus manokwari
''Platydemus manokwari'', also known as the New Guinea flatworm, is a species of large predatory land flatworm.
Native to New Guinea, it has been accidentally introduced to the soil of many countries, including the United States. It was al ...
'' and even the predatory caterpillar '' Hyposmocoma molluscivora''.
In the case of the marsh snail '' Succinea putris'', the snails can be parasitized
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson has ...
by a microscopic flatworm of the species '' Leucochloridium paradoxum'', which then reproduces within the snail's body. The flatworms invade the snail's eye stalks, causing them to become enlarged. Birds are attracted to and consume these eye stalks, consuming the flatworms in the process and becoming the final hosts of the flatworm.
Human activity poses great dangers to snails in the wild. Pollution and habitat destruction have caused the extinction of a considerable number of snail species in recent years.
Human food
 Land snails have been eaten for thousands of years, going back at least as far as the Pleistocene. Archaeological evidence of snail consumption is especially abundant in Capsian sites in
Land snails have been eaten for thousands of years, going back at least as far as the Pleistocene. Archaeological evidence of snail consumption is especially abundant in Capsian sites in North Africa
North Africa, or Northern Africa is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region, and it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of Mauritania in t ...
, but is also found throughout the Mediterranean region in archaeological sites dating between 12,000 and 6,000 years ago.
However, wild-caught land snails which are prepared for the table but are not thoroughly cooked, can harbor a parasite ('' Angiostrongylus cantonensis'') that can cause a rare kind of meningitis
Meningitis is acute or chronic inflammation of the protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord, collectively called the meninges. The most common symptoms are fever, headache, and neck stiffness. Other symptoms include confusion or ...
.
Snail eggs, sold as snail caviar, are a specialty food that is growing in popularity in European cuisine.
Africa
In parts ofWest Africa
West Africa or Western Africa is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, The Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Ivory Coast, Liberia, Mali, Mau ...
, specifically Ghana
Ghana (; tw, Gaana, ee, Gana), officially the Republic of Ghana, is a country in West Africa. It abuts the Gulf of Guinea and the Atlantic Ocean to the south, sharing borders with Ivory Coast in Ghana–Ivory Coast border, the west, Burkina ...
, snails are served as a delicacy. ''Achatina achatina
''Achatina achatina'', commonly known as the giant African snail, also known as the giant tiger land snail, and gigantocochlea, is a species of large, air-breathing land snail, a terrestrial pulmonate gastropod mollusk in the family Achatinidae. ...
'', Ghana tiger snails, are also known as some of the largest snails in the world.
Snail, called "igbin" in Yoruba language is a delicacy, widely eaten in Nigeria, especially among the Yorubas and Igbos.
In Cameroon
Cameroon (; french: Cameroun, ff, Kamerun), officially the Republic of Cameroon (french: République du Cameroun, links=no), is a country in west- central Africa. It is bordered by Nigeria to the west and north; Chad to the northeast; th ...
, snails, usually called 'nyamangoro' and 'slow boys' are a delicacy especially to natives of the South West region of Cameroon. The snails are either eaten cooked and spiced or with a favourite dish called 'eru'.
In North Morocco
Morocco (),, ) officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is the westernmost country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It overlooks the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria ...
, small snails are eaten as snacks in spicy soup. The recipe is identical to this prepared in Andalusia
Andalusia (, ; es, Andalucía ) is the southernmost autonomous community in Peninsular Spain. It is the most populous and the second-largest autonomous community in the country. It is officially recognised as a "historical nationality". The ...
(South Spain), showing the close cultural relationship between both kinds of cuisine.
Europe
Snails are eaten in severalEurope
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located enti ...
an countries, as they were in the past in the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post- Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Medite ...
. Mainly three species, all from the family Helicidae, are ordinarily eaten:
*'' Helix pomatia'', or ''edible snail'', generally prepared in its shell, with parsley
Parsley, or garden parsley (''Petroselinum crispum'') is a species of flowering plant in the family Apiaceae that is native to the central and eastern Mediterranean region (Sardinia, Lebanon, Israel, Cyprus, Turkey, southern Italy, Greece, Por ...
butter (size: 40 to 55 mm for an adult weight of 25 to 45 g; typically found in Burgundy, France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan ar ...
; known as ''l'Escargot de Bourgogne'').
*'' Helix lucorum'', found throughout the Eastern Mediterranean region are commonly eaten in Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders wit ...
and in some rural communities (ethnic Greeks and Georgian Catholics) in Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to t ...
.
*'' Cornu aspersum'', synonym
A synonym is a word, morpheme, or phrase that means exactly or nearly the same as another word, morpheme, or phrase in a given language. For example, in the English language, the words ''begin'', ''start'', ''commence'', and ''initiate'' are all ...
''Helix aspersa'':
**''Cornu aspersum'', better known as the European brown snail
''Cornu aspersum'' (syn. ''Cryptomphalus aspersus''), known by the common name garden snail, is a species of land snail in the family Helicidae, which includes some of the most familiar land snails. Of all terrestrial molluscs, this species may w ...
, is cooked in many different ways, according to different local traditions (size: 28 to 35 mm for an adult weight of 7 to 15 g; typically found in the Mediterranean countries of Europe and North Africa and the French Atlantic coast; ''Helix aspersa aspersa'' known as ''le Petit-gris'').
**''Cornu aspersum maxima'' (size 40 to 45 mm for an average weight of 20 to 30 g; typically found in North Africa).
Snails are a delicacy in French cuisine, where they are called '' escargots''. 191 farms produced escargots in France as of 2014. In an English-language menu, ''escargot'' is generally reserved for snails prepared with traditional French recipes (served in the shell with a garlic and parsley butter). Before preparing snails to eat, the snails should be fasting for three days with only water available. After three days of fasting, the snails should be fed flour and offered water for at least a week. This process is thought to cleanse the snails.
Portuguese cuisine
The oldest known book on Portuguese cuisine, entitled ''Livro de Cozinha da Infanta D. Maria de Portugal'', from the 16th century, describes many popular dishes of meat, fish, poultry and others.
''Culinária Portuguesa'', by António-Maria De O ...
where they are called in Portuguese ''caracóis'', and served in cheap snack houses and taverns, usually stew
A stew is a combination of solid food ingredients that have been cooked in liquid and served in the resultant gravy. A stew needs to have raw ingredients added to the gravy. Ingredients in a stew can include any combination of vegetables an ...
ed (with different mixtures of white wine, garlic, piri piri, oregano
Oregano (, ; ''Origanum vulgare'') is a species of flowering plant in the mint family Lamiaceae. It was native to the Mediterranean region, but widely naturalised elsewhere in the temperate Northern Hemisphere.
Oregano is a woody perennial pla ...
, coriander or parsley, and sometimes chouriço
Chorizo (, from Spanish ; similar to but distinct from Portuguese ) is a type of pork cured meat originating from the Iberian Peninsula.
In Europe, chorizo is a fermented, cured, smoked meat, which may be sliced and eaten without cooking ...
). Bigger varieties, called ''caracoletas'' (especially, ''Cornu aspersum''), are generally grilled and served with a butter sauce, but other dishes also exist such as '' feijoada de caracóis''. Overall, Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic, In recognized minority languages of Portugal:
:* mwl, República Pertuesa is a country located on the Iberian Peninsula, in Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes the Macaronesian ...
consumes about 4,000 tonnes of snails each year.
 Traditional Spanish cuisine also uses snails ("caracoles" in Spanish; "caragols" or "cargols" in Catalan), consuming several species such as ''Cornu aspersum'', ''
Traditional Spanish cuisine also uses snails ("caracoles" in Spanish; "caragols" or "cargols" in Catalan), consuming several species such as ''Cornu aspersum'', ''Otala lactea
''Otala lactea'', known as the milk snail or Spanish snail, is a large, edible species of air-breathing land snail, a terrestrial pulmonate gastropod mollusk, in the family Helicidae, the typical snails.MolluscaBase eds. (2021). MolluscaBase. Ota ...
'', '' Otala punctata'' and '' Theba pisana''. Snails are very popular in Andalusia
Andalusia (, ; es, Andalucía ) is the southernmost autonomous community in Peninsular Spain. It is the most populous and the second-largest autonomous community in the country. It is officially recognised as a "historical nationality". The ...
, Valencia
Valencia ( va, València) is the capital of the autonomous community of Valencia and the third-most populated municipality in Spain, with 791,413 inhabitants. It is also the capital of the province of the same name. The wider urban area al ...
and Catalonia
Catalonia (; ca, Catalunya ; Aranese Occitan: ''Catalonha'' ; es, Cataluña ) is an autonomous community of Spain, designated as a '' nationality'' by its Statute of Autonomy.
Most of the territory (except the Val d'Aran) lies on the no ...
. There are even snail celebrations, such as the "L'Aplec del Caragol
L'Aplec del Caragol is a meeting that is held annually, on a weekend in May, on the banks of the river Segre and the Champs Elysees in Lleida since 1980. It is a gastronomic event where snails are the protagonists and which incorporates music, b ...
", which takes place in Lleida
Lleida (, ; Spanish: Lérida ) is a city in the west of Catalonia, Spain. It is the capital city of the province of Lleida.
Geographically, it is located in the Catalan Central Depression. It is also the capital city of the Segrià comarca, ...
each May and draws more than 200,000 visitors from abroad.
Small to medium-sized varieties are usually cooked in one of several spicy sauces or even in soups, and eaten as an appetizer. The bigger ones may be reserved for more elaborate dishes, such as the "arroz con conejo y caracoles" (a paella-style rice with snails and rabbit
Rabbits, also known as bunnies or bunny rabbits, are small mammals in the family Leporidae (which also contains the hares) of the order Lagomorpha (which also contains the pikas). ''Oryctolagus cuniculus'' includes the European rabbit speci ...
meat, from the inner regions of south-eastern Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = '' Plus ultra'' ( Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, ...
), "cabrillas" (snails in spicy tomato sauce, typical of western Andalusia) and the Catalan '' caragols a la llauna'' (grilled inside their own shells and then eaten after dipping them in garlic mayonnaise
Mayonnaise (; ), colloquially referred to as "mayo" , is a thick, cold, and creamy sauce or dressing commonly used on sandwiches, hamburgers, composed salads, and French fries. It also forms the base for various other sauces, such as tartar ...
) and ''a la gormanda'' (boiled in tomato and onion sauce).
In Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders wit ...
, snails are especially popular in the island of Crete
Crete ( el, Κρήτη, translit=, Modern: , Ancient: ) is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the 88th largest island in the world and the fifth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, after Sicily, Sardinia, Cypru ...
, but are also eaten in many parts of the country and can even be found in supermarket
A supermarket is a self-service Retail#Types of outlets, shop offering a wide variety of food, Drink, beverages and Household goods, household products, organized into sections. This kind of store is larger and has a wider selection than earli ...
s, sometimes placed alive near partly refrigerated vegetables. In this regard, snails are one of the few live organisms sold at supermarkets as food. They are eaten either boiled with vinegar
Vinegar is an aqueous solution of acetic acid and trace compounds that may include flavorings. Vinegar typically contains 5–8% acetic acid by volume. Usually, the acetic acid is produced by a double fermentation, converting simple sugars to ...
added, or sometimes cooked alive in a casserole with tomato, potatoes and squashes
Squash may refer to:
Sports
* Squash (sport), the high-speed racquet sport also known as squash racquets
* Squash (professional wrestling), an extremely one-sided match in professional wrestling
* Squash tennis, a game similar to squash but pla ...
. Limpets and sea snail
Sea snail is a common name for slow-moving marine gastropod molluscs, usually with visible external shells, such as whelk or abalone. They share the taxonomic class Gastropoda with slugs, which are distinguished from snails primarily by the ...
s also find their way to the Greek table around the country. Another snail cooking method is the ''Kohli Bourbouristi'' (''κοχλιοί μπου(ρ)μπουριστοί''), a traditional Cretan dish, which consists of fried snails in olive oil
Olive oil is a liquid fat obtained from olives (the fruit of ''Olea europaea''; family Oleaceae), a traditional tree crop of the Mediterranean Basin, produced by pressing whole olives and extracting the oil. It is commonly used in cooking: f ...
with salt, vinegar and rosemary.
They often feature on Cyprus
Cyprus ; tr, Kıbrıs (), officially the Republic of Cyprus,, , lit: Republic of Cyprus is an island country located south of the Anatolian Peninsula in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Its continental position is disputed; while it is ...
taverna menus, in the meze section, under the name ''karaoloi'' (''καράολοι'').
In Sicily, snails (or ''babbaluci'' as they are commonly called in Sicilian) are a very popular dish. They are usually boiled with salt first, then served with tomato sauce or bare with oil, garlic and parsley. Snails are similarly appreciated in other Italian regions, such as Piedmont
it, Piemontese
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1_info1 =
, demographics1_title2 ...
where in Cherasco there is the Italian National Institute of Heliculture.
Snails (or ''bebbux'' as they are called in Maltese
Maltese may refer to:
* Someone or something of, from, or related to Malta
* Maltese alphabet
* Maltese cuisine
* Maltese culture
* Maltese language, the Semitic language spoken by Maltese people
* Maltese people, people from Malta or of Malte ...
) are a dish on the Mediterranean island of Malta, generally prepared and served in the Sicilian manner.
In southwestern Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG),, is a country in Central Europe. It is the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany lies between the Baltic and North Sea to the north and the Alps to the sou ...
there is a regional specialty of soup with snails and herbs, called "Black Forest Snail Chowder" (''Badener Schneckensuepple'').
Heliciculture is the farming of snails. Some species such as the Roman snail
''Helix pomatia'', common names the Roman snail, Burgundy snail, or escargot, is a species of large, edible, air-breathing land snail, a pulmonate gastropod terrestrial mollusc in the family Helicidae.MolluscaBase eds. (2021). MolluscaBase. ...
are protected in the wild in several European countries and must not be collected, but the Roman Snail and the Garden Snail (''Cornu aspersum'') are cultivated on snail farms.
Although there is not usually considered to be a tradition of snail eating in Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It is ...
, common garden snails '' Cornu aspersum'' were eaten in the Southwick area of Sunderland
Sunderland () is a port city in Tyne and Wear, England. It is the City of Sunderland's administrative centre and in the Historic counties of England, historic county of County of Durham, Durham. The city is from Newcastle-upon-Tyne and is on t ...
in North East England
North East England is one of nine official regions of England at the first level of ITL for statistical purposes. The region has three current administrative levels below the region level in the region; combined authority, unitary authorit ...
. They were collected from quarries and along the stone walls of railway embankments during the winter when the snails were hibernating and had voided the contents of their guts. Gibson writes that this tradition was introduced in the 19th century by French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
immigrant glass workers. "Snail suppers" were a feature of local pubs and Southwick working men were collecting and eating snails as late as the 1970s, though the tradition may now have died out.
Oceania
 In
In New Caledonia
)
, anthem = ""
, image_map = New Caledonia on the globe (small islands magnified) (Polynesia centered).svg
, map_alt = Location of New Caledonia
, map_caption = Location of New Caledonia
, mapsize = 290px
, subdivision_type = Sovereign st ...
, ''Placostylus fibratus
''Placostylus fibratus'' is a species of large air-breathing land snail, a pulmonate gastropod mollusk in the family Bothriembryontidae. This species is endemic to New Caledonia.
;Subspecies:
* ''Placostylus fibratus alexander'' (Crosse, 1855)
* ...
'' (French: ''bulime'') is considered a highly prized delicacy and is locally farmed to ensure supplies. It is often served by restaurants prepared in the French style with garlic butter.
See also
*Terrestrial mollusc
Terrestrial molluscs or land molluscs (mollusks) are an ecological group that includes all molluscs that live on land in contrast to freshwater and marine molluscs. They probably first occurred in the Carboniferous, arising from freshwater on ...
* Snail slime
* Slug
Slug, or land slug, is a common name for any apparently shell-less terrestrial gastropod mollusc. The word ''slug'' is also often used as part of the common name of any gastropod mollusc that has no shell, a very reduced shell, or only a sm ...
* Freshwater snail
* Sea snail
Sea snail is a common name for slow-moving marine gastropod molluscs, usually with visible external shells, such as whelk or abalone. They share the taxonomic class Gastropoda with slugs, which are distinguished from snails primarily by the ...
* Sea slug
* Cretan cuisine
References
{{Reflist, 30emExternal links
Recipes for snails
on the UF /
IFAS IFAS may refer:
* Institute of Food and Agricultural Sciences
* Integrated Fixed-Film Activated Sludge, a sewage treatment process
* International French adjectival system
In rock climbing, mountaineering, and other climbing disciplines, clim ...
Featured Creatures Web site.Site with many photographs
Mollusc common names