|
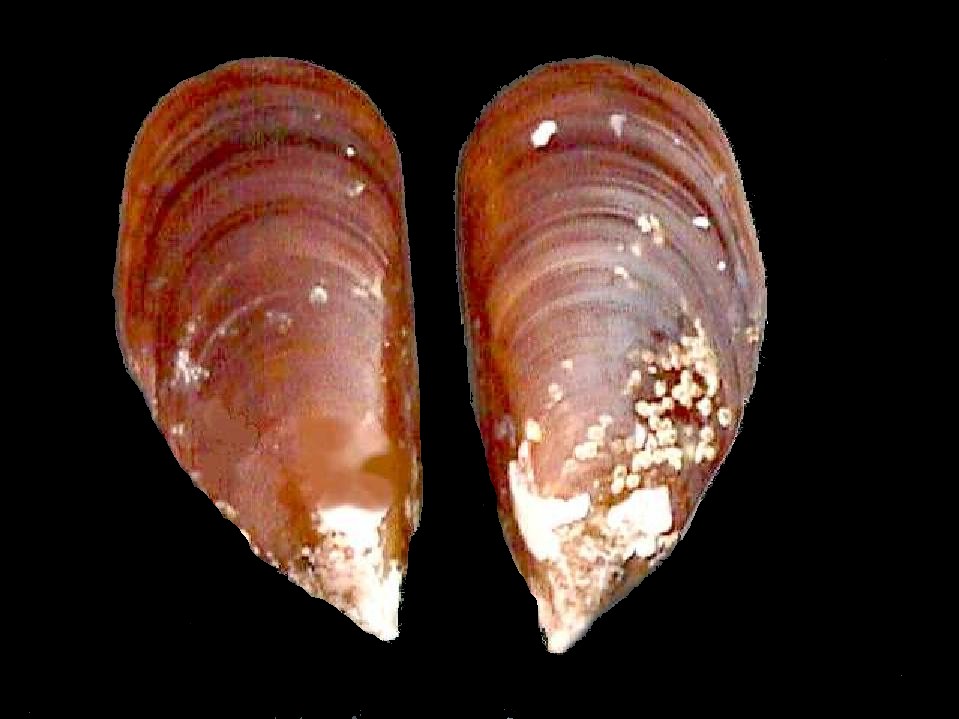
Warty Venus
''Venus verrucosa'', the warty venus, is a species of saltwater clam. It is a species of marine bivalve mollusc in the family Veneridae, sometimes collectively known as the venus clams. Distribution This species is found around the European coast and also the southern African coast, from the Namibian coast to Mozambique, subtidally to 155 m.Branch, G. M., Branch, M. L., Griffiths, C. L. and Beckley, L. E. (2005): ''Two Oceans: a guide to the marine life of southern Africa'' Description This animal grows up to 60 mm in diameter. It has a bulky, oval shell with well-defined concentric ridges. The shell edges are knobbly and crossed. Economic import and gastronomy Known as ''praire'' in France, it is an expensive delicacy there, and harvesting periods and size of catch (both minimum shell size and numbers taken) have had to be strictly regulated for its conservation. It is eaten either raw or baked in the oven with garlic butter Garlic butter, also known as ''beurre à la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (; 23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after his ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné Blunt (2004), p. 171. (), was a Swedish botanist, zoologist, taxonomist, and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, the modern system of naming organisms. He is known as the "father of modern taxonomy". Many of his writings were in Latin; his name is rendered in Latin as and, after his 1761 ennoblement, as . Linnaeus was born in Råshult, the countryside of Småland, in southern Sweden. He received most of his higher education at Uppsala University and began giving lectures in botany there in 1730. He lived abroad between 1735 and 1738, where he studied and also published the first edition of his ' in the Netherlands. He then returned to Sweden where he became professor of medicine and botany at Uppsala. In the 1740s, he was sent on several journeys through Sweden to find and classify plants and animals. In the 1750s and 1760s, he continued to collect an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. Other ways of defining species include their karyotype, DNA sequence, morphology, behaviour or ecological niche. In addition, paleontologists use the concept of the chronospecies since fossil reproduction cannot be examined. The most recent rigorous estimate for the total number of species of eukaryotes is between 8 and 8.7 million. However, only about 14% of these had been described by 2011. All species (except viruses) are given a two-part name, a "binomial". The first part of a binomial is the genus to which the species belongs. The second part is called the specific name or the specific epithet (in botanical nomenclature, also sometimes i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marine (ocean)
The ocean (also the sea or the world ocean) is the body of salt water that covers approximately 70.8% of the surface of Earth and contains 97% of Earth's water. An ocean can also refer to any of the large bodies of water into which the world ocean is conventionally divided."Ocean." ''Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary'', Merriam-Webster, |
Bivalve
Bivalvia (), in previous centuries referred to as the Lamellibranchiata and Pelecypoda, is a class of marine and freshwater molluscs that have laterally compressed bodies enclosed by a shell consisting of two hinged parts. As a group, bivalves have no head and they lack some usual molluscan organs, like the radula and the odontophore. They include the clams, oysters, cockles, mussels, scallops, and numerous other families that live in saltwater, as well as a number of families that live in freshwater. The majority are filter feeders. The gills have evolved into ctenidia, specialised organs for feeding and breathing. Most bivalves bury themselves in sediment, where they are relatively safe from predation. Others lie on the sea floor or attach themselves to rocks or other hard surfaces. Some bivalves, such as the scallops and file shells, can swim. The shipworms bore into wood, clay, or stone and live inside these substances. The shell of a bivalve is composed of calc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mollusc
Mollusca is the second-largest phylum of invertebrate animals after the Arthropoda, the members of which are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 85,000 extant species of molluscs are recognized. The number of fossil species is estimated between 60,000 and 100,000 additional species. The proportion of undescribed species is very high. Many taxa remain poorly studied. Molluscs are the largest marine phylum, comprising about 23% of all the named marine organisms. Numerous molluscs also live in freshwater and terrestrial habitats. They are highly diverse, not just in size and anatomical structure, but also in behaviour and habitat. The phylum is typically divided into 7 or 8 taxonomic classes, of which two are entirely extinct. Cephalopod molluscs, such as squid, cuttlefish, and octopuses, are among the most neurologically advanced of all invertebrates—and either the giant squid or the colossal squid is the largest known invertebrate species. The gastropods ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Family (biology)
Family ( la, familia, plural ') is one of the eight major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy. It is classified between order and genus. A family may be divided into subfamilies, which are intermediate ranks between the ranks of family and genus. The official family names are Latin in origin; however, popular names are often used: for example, walnut trees and hickory trees belong to the family Juglandaceae, but that family is commonly referred to as the "walnut family". What belongs to a family—or if a described family should be recognized at all—are proposed and determined by practicing taxonomists. There are no hard rules for describing or recognizing a family, but in plants, they can be characterized on the basis of both vegetative and reproductive features of plant species. Taxonomists often take different positions about descriptions, and there may be no broad consensus across the scientific community for some time. The publishing of new data and opini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Veneridae
The Veneridae or venerids, common name: Venus clams, are a very large family of minute to large, saltwater clams, marine bivalve molluscs. Over 500 living species of venerid bivalves are known, most of which are edible, and many of which are exploited as food sources. Many of the most important edible species are commonly known (in the USA) simply as "clams". Venerids make up a significant proportion of the world fishery of edible bivalves. The family includes some species that are important commercially, such as (in the USA) the hard clam or quahog, ''Mercenaria mercenaria''. Taxonomy The classification within the family Veneridae has been controversial at least since the 1930s. Molecular approaches show that much of this traditional classification is unnatural. Some common species have been moved between genera (including genera in different subfamilies) because of repeated attempts to bring a more valid organization to the classification or taxonomy of the family, therefor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Marine Molluscs Of South Africa
The list of marine molluscs of South Africa is a list of saltwater species that form a part of the molluscan fauna of South Africa. This list does not include the land or freshwater molluscs. Gastropoda See List of marine gastropods of South Africa Bivalvia Bivalves in South Africa include: Nuculidae *'' Nucula nucleus'' Linnaeus, 1758 Mytilidae – Mussels *Estuarine mussel '' Arcuatula capensis'' (Cape Agulhas to Mozambique)Branch, G.M. Griffiths, C.L. Branch, M.L. Beckley, L.E. ''Two Oceans: A guide to the marine life of southern Africa.'' 5th impression, David Philip, Cape Town, 2000. *Ribbed mussel '' Aulacomya ater'' (Namibia to Eastern Cape)Jones, Georgina. ''A field guide to the marine animals of the Cape Peninsula.'' SURG, Cape Town, 2008. *Brack-water mussel '' Brachidontes virgiliae'' (Eastern Cape to Mozambique) *Semistriated mussel '' Brachidontes semistriatus'' (Port Elizabeth to Mozambique) *Black mussel '' Choromytilus meridionalis'' (Namibia to Tsitsikamma) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Marine Molluscs Of Mozambique
The list of marine molluscs of Mozambique is a list of saltwater species that form a part of the molluscan fauna of Mozambique. This list does not include the land or freshwater molluscs. Gastropoda Gastropods in Mozambique include: Patellogastropoda Patellidae - True limpets *'' Cellana radiata capensis'' (Gmelin, 1791)(Port Alfred to Kenya)Branch, G.M. Griffiths, C.L. Branch, M.L. Beckley, L.E. ''Two Oceans: A guide to the marine life of southern Africa.'' 5th impression, David Philip, Cape Town, 2000. (syn. ''Cellana capensis'' Gmelin, ''Helcioniscus capensis'' (Gmelin, 1790), ''Patella capensis'' Gmelin, 1791) *Variable limpet ''Helcion concolor'' Krauss, 1848 (Eastern Cape to Mozambique) *'' Patella flexuosa'' (Quoy & Gaimard, 1834) (Northern KwaZulu-Natal to Mzambique) (syn. ''Scutellastra flexuosa'') *''Patella pica'' Reeve, 1854 (Zululand to Mozambique) (syn. ''Scutellastra pica'') Vetigastropoda Pleurotomariidae *'' Bayerotrochus africanus'' (Tomlin, 1948) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venus Verrucosa2
Venus is the second planet from the Sun. It is sometimes called Earth's "sister" or "twin" planet as it is almost as large and has a similar composition. As an interior planet to Earth, Venus (like Mercury) appears in Earth's sky never far from the Sun, either as morning star or evening star. Aside from the Sun and Moon, Venus is the brightest natural object in Earth's sky, capable of casting visible shadows on Earth at dark conditions and being visible to the naked eye in broad daylight. Venus is the second largest terrestrial object of the Solar System. It has a surface gravity slightly lower than on Earth and has a very weak induced magnetosphere. The atmosphere of Venus, mainly consists of carbon dioxide, and is the densest and hottest of the four terrestrial planets at the surface. With an atmospheric pressure at the planet's surface of about 92 times the sea level pressure of Earth and a mean temperature of , the carbon dioxide gas at Venus's surface is in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |