|
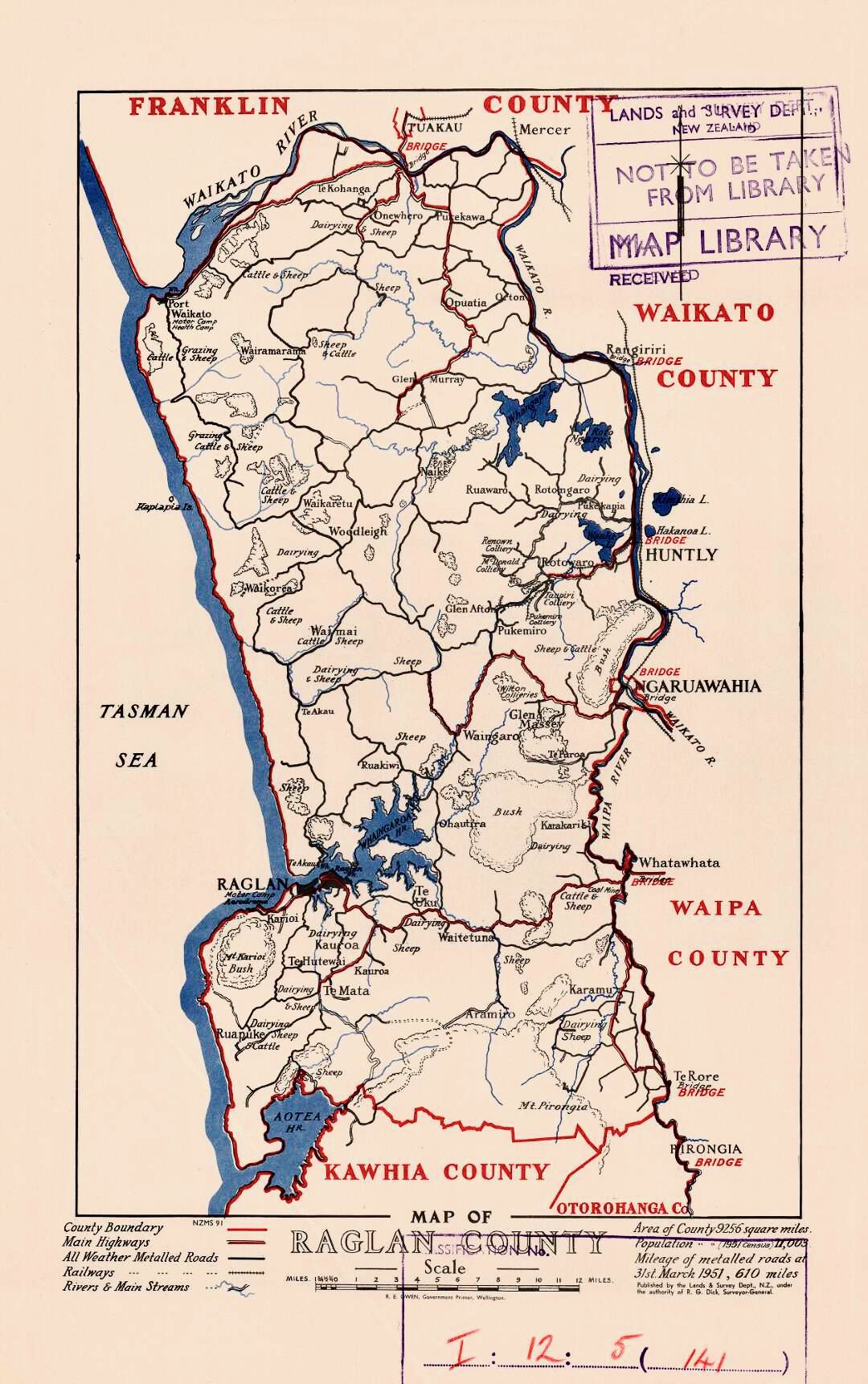
Waingaro
Waingaro is a rural community in the Waikato District and Waikato region of New Zealand's North Island, on the banks of the Waingaro River, where it is fed by a hot spring. Demographics Waingaro is in an SA1 statistical area which covers . The SA1 area is part of the larger Te Ākau statistical area. Waingaro had a population of 180 at the 2018 New Zealand census, an increase of 33 people (22.4%) since the 2013 census, and an increase of 6 people (3.4%) since the 2006 census. There were 63 households, comprising 99 males and 81 females, giving a sex ratio of 1.22 males per female. The median age was 47.3 years (compared with 37.4 years nationally), with 21 people (11.7%) aged under 15 years, 30 (16.7%) aged 15 to 29, 99 (55.0%) aged 30 to 64, and 33 (18.3%) aged 65 or older. Ethnicities were 71.7% European/Pākehā, and 45.0% Māori. People may identify with more than one ethnicity. Although some people chose not to answer the census's question about religious affiliati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waingaro River (Waikato)
The Waingaro River is a river of the Waikato region of New Zealand's North Island. It flows generally southwest from its origins near Glen Afton and Glen Massey, west of Ngāruawāhia, to reach a northern arm of Raglan Harbour (se1:50,000 map. Its main tributary is Kahuhuru Stream, which Highway 22 follows for several kilometres. Tributaries total about . At Waingaro it is fed by a hot spring. Geology The lower river flows over Puaroan age (about 150 million years ago), blue-grey Puti siltstone.Geology of the Raglan-Kawhia Area: Institute of Geological & Nuclear Sciences (N.Z.), Barry Clayton Waterhouse, P. J. White 1994 Pollution The Waingaro River is one of the largest sources of sediment in Whaingaroa Harbour, partly because it is 99 percent unfenced. Pollution has been worsening for phosphorus, though nitrogen has improved, as shown in this table of important (i.e. slope direction probability over 95% and RSKSE over ±1% pa) improvements, or deteriorations (-) i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Te Ākau
Te Ākau is a small farming settlement in the North Island of New Zealand, located north west of Hamilton, New Zealand, Hamilton, south west of Huntly, New Zealand, Huntly, south of Port Waikato and , or by ferry and road, north of Raglan, New Zealand, Raglan. It has a hall and a school. (Te Ākau (officially, Te Ākau / Black Beach) is also the name of a beach in the Marlborough Region of the South Island.) Boundaries Te Ākau's only defined boundaries are as a New Zealand census 'statistical area' and a former station. Te Ākau hamlet is near the centre of both, but has no defined boundary. This article covers the southwestern part of the statistical area. Historically the name was applied to a sheep and cattle Station (New Zealand agriculture), station extending from Port Waikato to Raglan, as shown on maps of 1905 (south) and 1906 (north). Politically it is part of the Onewhero-Te Akau ward of Waikato District, Waikato District Council (Onewhero is the statistical a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waikato Tainui
Waikato Tainui, Waikato or Tainui is a group of Māori ''iwi'' based in Waikato Region, in the western central region of New Zealand's North Island. It is part of the larger Tainui confederation of Polynesian settlers who arrived to New Zealand on the Tainui ''waka'' (migration canoe). The tribe is named after the Waikato River, which plays a large part in its history and culture. Pōtatau Te Wherowhero, the first Māori king, was a member of the Waikato hapu (sub-tribe) of Ngāti Mahuta, and his descendants have succeeded him. The king movement is based at Tūrangawaewae ''marae'' (meeting place) in Ngāruawāhia. The Waikato-Tainui iwi comprises 33 hapū (sub-tribes) and 65 marae (family groupings). There are over 52,000 tribal members who affiliate to Waikato-Tainui. Hamilton City is now the tribe's largest population centre, but Ngāruawāhia remains the tribe's historical centre and modern capital. In the 2006 census, 33,429 people in New Zealand indicated they were affilia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waikato District
Waikato District is a territorial authority of New Zealand, in the northern part of Waikato region, North Island. Waikato District is administered by the Waikato District Council, with headquarters in Ngāruawāhia. The district is centred to the north and west of the city of Hamilton, and takes in much of the northern Waikato Plains and also the Hakarimata Range. The north of the district contains swampy floodplain of the Waikato River and several small lakes, of which the largest is Lake Waikare. Other than Ngāruawāhia, the main population centres are Huntly, Raglan, and Te Kauwhata. The main industries in the district are dairy farming, forestry, and coal mining. There is a major coal-fired power station at Huntly. Te Kauwhata is at the centre of a major wine region. Demographics At the 2006 census the district had a population of 43,959. Of these, 6834 lived in Huntly, 5106 in Ngāruawāhia, 2637 in Raglan, and 1294 in Te Kauwhata. In 2010, the district acquired part o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Whangape
Lake Whangape (also written as Wangape, Whangapu, or Whangapae) is shallow, supertrophic, lateral and the second largest lake (after Lake Waikare) in the lower Waikato River basin in New Zealand. One source said the name translated to 'a large sheet of water', another that it was a chief's name. From the 1860s the catchment has lost most of its forest cover and the lake has changed from clear and rich in aquatic vegetation to a murky, algal lake. Geology The lake is a lateral lake, dammed by a levee of the Waikato, probably built up as a result of sea-level rise and sediment from the Taupo Volcanic Zone about 2,000 years ago. To the west of the lake the rocks are made up of the 30m year old (Tertiary) Whaingaroa and Glen Massey Formations, the Whaingaroan rocks of the Te Kuiti Group. The Karapiro Formation (part of the Walton subgroup) outcrops towards the east of the lake. Hot springs Two springs (ranging from to and many seepages occur along Te Maire Stream, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Provincial Growth Fund
Shane Geoffrey Jones (born 3 September 1959) is a New Zealand politician. He served as a New Zealand First list MP from 2017 to 2020 and was previously a Labour list MP from 2005 to 2014. Jones was a cabinet minister in the Fifth Labour Government of New Zealand, becoming Minister of Building and Construction in his first term. He was a senior opposition MP from 2008 to 2014 and contested the leadership of the Labour Party in a 2013 leadership election, but lost to David Cunliffe. He left parliament at the end of May 2014 before returning as a New Zealand First MP at the 2017 general election. Jones was Minister for Regional Economic Development in the New Zealand First–Labour coalition government. Early life and career Jones is Māori, of Te Aupōuri and Ngāi Takoto descent, as well as having English, Welsh and Croatian ancestry. He was born in Awanui, near Kaitaia, one of six children to parents Peter, a farmer, and Ruth, a teacher. Jones' secondary education was ta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ministry Of Education (New Zealand)
The Ministry of Education (Māori: ''Te Tāhuhu o te Mātauranga'') is the public service department of New Zealand charged with overseeing the New Zealand education system. The Ministry was formed in 1989 when the former, all-encompassing Department of Education was broken up into six separate agencies. History The Ministry was established as a result of the Picot task force set up by the Labour government in July 1987 to review the New Zealand education system. The members were Brian Picot, a businessman, Peter Ramsay, an associate professor of education at the University of Waikato, Margaret Rosemergy, a senior lecturer at the Wellington College of Education, Whetumarama Wereta, a social researcher at the Department of Maori Affairs and Colin Wise, another businessman. The task force was assisted by staff from the Treasury and the State Services Commission (SSC), who may have applied pressure on the task force to move towards eventually privatizing education, as had ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Education Review Office
The Education Review Office (ERO) (Māori: ''Te Tari Arotake Mātauranga'') is the public service department of New Zealand charged with reviewing and publicly reporting on the quality of education and care of students in all New Zealand schools and early childhood services. Led by a Chief Review Officer - the department's chief executive, the Office has approximately 150 designated review officers located in five regions. These regions are: Northern, Waikato/Bay of Plenty, Central, Southern, and Te Uepū ā-Motu (ERO's Māori review services unit). The Education Review Office, and the Ministry of Education are two separate public service departments. The functions and powers of the office are set out in Part 28 (sections 323–328) of the Education Act 1989. Reviews ERO reviews the education provided for school students in all state schools, private schools and kura kaupapa Māori Kura Kaupapa Māori are Māori-language immersion schools () in New Zealand where the ph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a Geological period, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately Mya. The Jurassic constitutes the middle period of the Mesozoic, Mesozoic Era and is named after the Jura Mountains, where limestone strata from the period were first identified. The start of the Jurassic was marked by the major Triassic–Jurassic extinction event, associated with the eruption of the Central Atlantic magmatic province, Central Atlantic Magmatic Province. The beginning of the Toarcian Stage started around 183 million years ago and is marked by an extinction event associated with widespread Anoxic event, oceanic anoxia, ocean acidification, and elevated temperatures likely caused by the eruption of the Karoo-Ferrar, Karoo-Ferrar large igneous provinces. The end of the Jurassic, however, has no clear boundary with the Cretaceous and i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium
Sodium is a chemical element with the symbol Na (from Latin ''natrium'') and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 of the periodic table. Its only stable isotope is 23Na. The free metal does not occur in nature, and must be prepared from compounds. Sodium is the sixth most abundant element in the Earth's crust and exists in numerous minerals such as feldspars, sodalite, and halite (NaCl). Many salts of sodium are highly water-soluble: sodium ions have been leached by the action of water from the Earth's minerals over eons, and thus sodium and chlorine are the most common dissolved elements by weight in the oceans. Sodium was first isolated by Humphry Davy in 1807 by the electrolysis of sodium hydroxide. Among many other useful sodium compounds, sodium hydroxide (lye) is used in soap manufacture, and sodium chloride (edible salt) is a de-icing agent and a nutrient for animals including h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithium
Lithium (from el, λίθος, lithos, lit=stone) is a chemical element with the symbol Li and atomic number 3. It is a soft, silvery-white alkali metal. Under standard conditions, it is the least dense metal and the least dense solid element. Like all alkali metals, lithium is highly reactive and flammable, and must be stored in vacuum, inert atmosphere, or inert liquid such as purified kerosene or mineral oil. When cut, it exhibits a metallic luster, but moist air corrodes it quickly to a dull silvery gray, then black tarnish. It never occurs freely in nature, but only in (usually ionic) compounds, such as pegmatitic minerals, which were once the main source of lithium. Due to its solubility as an ion, it is present in ocean water and is commonly obtained from brines. Lithium metal is isolated electrolytically from a mixture of lithium chloride and potassium chloride. The nucleus of the lithium atom verges on instability, since the two stable lithium isotopes foun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |