|
Władysław Of Salzburg
Władysław of Salzburg, also known as Władysław of Wrocław/Breslau ( pl, Władysław Wrocławski) or Władysław of Silesia (german: Wladislaus von Schlesien, cs, Vladislav Slezský; – 27 April 1270), a member of the Silesian Piasts, was co-ruler in the Duchy of Wroclaw since 1248. He served as chancellor of King Ottokar II of Bohemia from 1255 and was elected Bishop of Bamberg in 1257 and Bishop of Passau in 1265. Władysław became Prince-Archbishop of Salzburg in the same year, and from 1268 also served as administrator of the Wrocław diocese. Family Władysław was the fifth and youngest son of the Silesian duke Henry II the Pious, by his wife Anna, daughter of the Přemyslid king Ottokar I of Bohemia. The Silesian Piasts, elder line of the Polish ruling Piast dynasty, had been restored into their Silesian heritage by the aid of Emperor Frederick Barbarossa in 1163. Władysław's grandfather, Duke Henry the Bearded, also regained the Seniorate Province and the Pol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silesian Piasts
The Silesian Piasts were the elder of four lines of the Polish Piast dynasty beginning with Władysław II the Exile (1105–1159), eldest son of Duke Bolesław III of Poland. By Bolesław's testament, Władysław was granted Silesia as his hereditary province and also the Lesser Polish Seniorate Province at Kraków according to the principle of agnatic seniority. Early history The history of the Silesian Piasts began with the feudal fragmentation of Poland in 1138 following the death of the Polish duke Bolesław III Wrymouth. While the Silesian province and the Kraków seniorate were assigned to Władysław II the Exile, his three younger half–brothers Bolesław IV the Curly, Mieszko III the Old, and Henry of Sandomierz received Masovia, Greater Poland and Sandomierz, respectively, according to the Testament of Boleslaw III. Władysław soon entered into fierce conflicts with his brothers and the Polish nobility. When in 1146 he attempted to take control of the whole ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seniorate Province
Seniorate Province, also known as the Senioral Province, , was a district principality in the Duchy of Poland that was formed in 1138, following the fragmentation of the state. Its ruler held the title of the High Duke, ruling all duchies within Poland. In 1227, following the abolition of the High Duke title, the province was transformed into the Duchy of Kraków. Senioral principle The senioral principle established in the testament stated that at all times the eldest member of the dynasty was to have supreme power over the rest (''Dux'', the Dukes) and was also to control an indivisible "Seniorate Province". In 1138 Bolesław's III eldest son Władysław II, took up the rule over a vast strip of land running north–south down the middle of Poland, composed of: *Lesser Poland, except for the eastern Duchy of Sandomierz allocated to Bolesław's III minor son Henry; *eastern parts of Greater Poland around Gniezno, the Polish ecclesiastical center, and Kalisz; *western Kuy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wrocław
Wrocław (; german: Breslau, or . ; Silesian German: ''Brassel'') is a city in southwestern Poland and the largest city in the historical region of Silesia. It lies on the banks of the River Oder in the Silesian Lowlands of Central Europe, roughly from the Baltic Sea to the north and from the Sudeten Mountains to the south. , the official population of Wrocław is 672,929, with a total of 1.25 million residing in the metropolitan area, making it the third largest city in Poland. Wrocław is the historical capital of Silesia and Lower Silesia. Today, it is the capital of the Lower Silesian Voivodeship. The history of the city dates back over a thousand years; at various times, it has been part of the Kingdom of Poland, the Kingdom of Bohemia, the Kingdom of Hungary, the Habsburg monarchy of Austria, the Kingdom of Prussia and Germany. Wrocław became part of Poland again in 1945 as part of the Recovered Territories, the result of extensive border changes and expulsions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Padua
The University of Padua ( it, Università degli Studi di Padova, UNIPD) is an Italian university located in the city of Padua, region of Veneto, northern Italy. The University of Padua was founded in 1222 by a group of students and teachers from Bologna. Padua is the second-oldest university in Italy and the world's fifth-oldest surviving university. In 2010, the university had approximately 65,000 students. In 2021, it was ranked second "best university" among Italian institutions of higher education with more than 40,000 students according to Censis institute, and among the best 200 universities in the world according to ARWU. History The university is conventionally said to have been founded in 1222 when a large group of students and professors left the University of Bologna in search of more academic freedom ('Libertas scholastica'). The first subjects to be taught were law and theology. The curriculum expanded rapidly, and by 1399 the institution had divided in two: a ''Univ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Italy (Holy Roman Empire)
The Kingdom of Italy ( la, Regnum Italiae or ''Regnum Italicum''; it, Regno d'Italia; german: Königreich Italien), also called Imperial Italy ( it, Italia Imperiale, german: Reichsitalien, links=no), was one of the constituent kingdoms of the Holy Roman Empire, along with the kingdoms of Germany, Bohemia, and Burgundy. It originally comprised large parts of northern and central Italy. Its original capital was Pavia until the 11th century. In 773, Charlemagne, the king of the Franks, crossed the Alps to invade the Kingdom of the Lombards, which encompassed all of Italy except the Duchy of Rome, the Venetian Republic and the Byzantine possessions in the south. In June 774, the kingdom collapsed and the Franks became masters of northern Italy. The southern areas remained under Lombard control, as the Duchy of Benevento was changed into the rather independent Principality of Benevento. Charlemagne called himself king of the Lombards and in 800 was crowned emperor in Rome. Members ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Konrad I, Duke Of Głogów
Konrad I of Głogów ( pl, Konrad I głogowski; – 6 August 1273/74), a member of the Silesian Piasts, was Silesian duke of Głogów from 1249/50 until his death. Life Konrad was the fourth son of Henry II the Pious, Duke of Silesia and High Duke of Poland from 1238, by his wife Anna, daughter of the Přemyslid king Ottokar I of Bohemia. At the time of his father's death in the 1241 Battle of Legnica against the Golden Horde, he and his younger brother Władysław were placed under the guardianship of their eldest brother Duke Bolesław II Rogatka. After Henry's sudden death, the Silesian Piasts were not able to maintain their dominant position: Bolesław II tried to succeed his father on the Polish throne at Kraków, but eventually could not prevail against his Piast cousin Konrad I of Masovia. In order to avoid further fragmentation of the paternal lands, the elder duke, with the approval of their mother, sent Konrad to study in Paris, where he was to be educated with t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
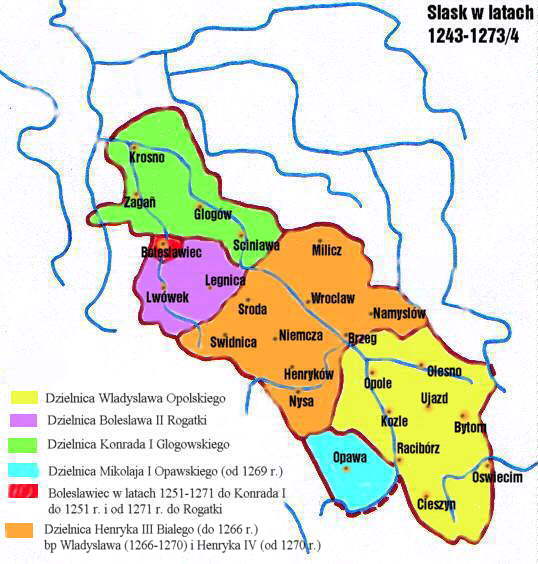
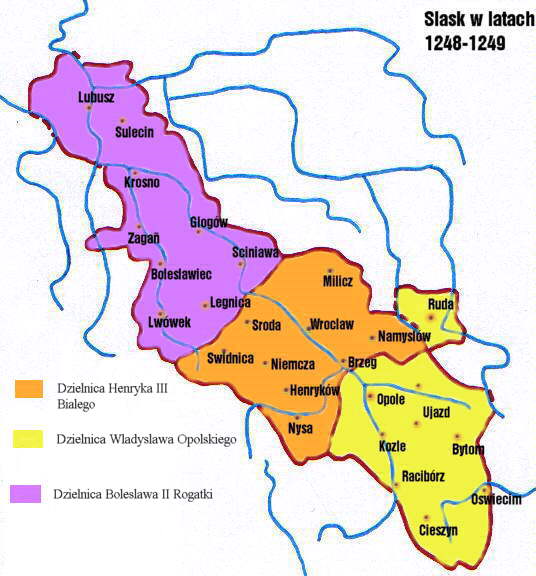
Silesia 1249-1273
Silesia (, also , ) is a historical region of Central Europe that lies mostly within Poland, with small parts in the Czech Silesia, Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately , and the population is estimated at around 8,000,000. Silesia is split into two main subregions, Lower Silesia in the west and Upper Silesia in the east. Silesia has a diverse culture, including Silesian architecture, architecture, National costumes of Poland, costumes, Silesian cuisine, cuisine, traditions, and the Silesian language (minority in Upper Silesia). Silesia is along the Oder River, with the Sudeten Mountains extending across the southern border. The region contains many historical landmarks and UNESCO World Heritage Sites. It is also rich in mineral and natural resources, and includes several important industrial areas. The largest city and Lower Silesia's capital is Wrocław; the historic capital of Upper Silesia is Opole. The biggest metropolitan area is the Upper Silesian metro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Konrad I Of Masovia
Konrad I of Masovia (ca. 1187/88 – 31 August 1247), from the Polish Piast dynasty, was the sixth Duke of Masovia and Kuyavia from 1194 until his death as well as High Duke of Poland from 1229 to 1232 and again from 1241 to 1243. Life Konrad was the youngest son of High Duke Casimir II the Just of Poland and Helen of Znojmo, daughter of the Přemyslid duke Conrad II of Znojmo (ruler of the Znojmo Appanage in southern Moravia, part of Duchy of Bohemia). His maternal grandmother was Maria of Serbia, apparently a daughter of the pre- Nemanjić ''župan'' Uroš I of Rascia. After his father's death in 1194, Konrad was brought up by his mother, who acted as regent of Masovia. In 1199, he received Masovia and in 1205 the adjacent lands of Kuyavia as well. In 1205, he and his brother, Duke Leszek I the White of Sandomierz, had their greatest military victory at Battle of Zawichost against Prince Roman the Great of Galicia–Volhynia. The Ruthenian army was crushed and Roman was killed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mieszko, Duke Of Lubusz
Mieszko of Lubusz ( pl, Mieszko lubuski; – 1242), a member of the Silesian Piasts, was Duke of Lubusz from 1241 until his death. Life Mieszko was the second son of the Silesian duke Henry II the Pious (1196–1241), by his consort Anne (d. 1265), a daughter of the Přemyslid king Ottokar I of Bohemia. His father succeeded as Polish high duke in 1238, ruling over Silesia and the Seniorate Province, as well as over large parts of Greater Poland. He had to ward off several attacks by the Ascanian margraves of Brandenburg and the Magdeburg archbishops on the westernmost Greater Polish lands, stretching around the former Veleti castle of Lubusz on the banks of the Oder river. When on 9 April 1241 High Duke Henry II was defeated and killed in the Mongol invasion of Poland at the Battle of Legnica, Mieszko and his older brother Bolesław II the Bald Boleslav or Bolesław may refer to: In people: * Boleslaw (given name) In geography: * Bolesław, Dąbrowa County, Lesser P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry III The White
Henry III the White ( pl, Henryk III Biały) ( – 3 December 1266), a member of the Silesian Piasts, was Duke of Silesia at Wrocław from 1248 until his death, as co-ruler with his brother Władysław. Life He was the third son of the Polish high duke Henry II the Pious, by his wife Princess Anna, daughter of the Přemyslid king Ottokar I of Bohemia. After the heroic death of his father at the Battle of Legnica on 9 April 1241, Henry III was still a minor and found himself under the care of the mother together with his youngest brothers Konrad and Władysław. In 1242, the unexpected death of his brother Mieszko, placed him in the second place immediately after his oldest brother Bolesław II the Bald. Since then, he became in the head of the political opposition in the Lower Silesia against the government of Bolesław II. Duke of Wrocław The first appearance of Henry III as adult was found only in 1247; however, Bolesław II didn't have any intentions to share the power w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Silesia
Lower Silesia ( pl, Dolny Śląsk; cz, Dolní Slezsko; german: Niederschlesien; szl, Dolny Ślōnsk; hsb, Delnja Šleska; dsb, Dolna Šlazyńska; Silesian German: ''Niederschläsing''; la, Silesia Inferior) is the northwestern part of the historical and geographical region of Silesia; Upper Silesia is to the southeast. In the Middle Ages Lower Silesia was part of Piast-ruled Poland. It was one of the leading regions of Poland, and its capital Wrocław was one of the main cities of the Polish Kingdom. Lower Silesia emerged as a distinctive region during the fragmentation of Poland, in 1172, when the Duchies of Opole and Racibórz, considered Upper Silesia since, were formed of the eastern part of the Duchy of Silesia, and the remaining, western part was since considered Lower Silesia. During the Ostsiedlung, German settlers were invited to settle in the sparsely populated region, which until then had a Polish majority. As a result, the region became largely Germanised in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bolesław II Rogatka
Boleslav or Bolesław may refer to: In people: * Boleslaw (given name) In geography: * Bolesław, Dąbrowa County, Lesser Poland Voivodeship, Poland * Bolesław, Olkusz County, Lesser Poland Voivodeship, Poland * Bolesław, Silesian Voivodeship, Poland *Brandýs nad Labem-Stará Boleslav, Czech Republic *Mladá Boleslav, Czech Republic See also * Pulß * Václav (other) * Wenceslaus (other) Wenceslaus, Wenceslas, Wenzeslaus and Wenzslaus (and other similar names) are Latinized forms of the Czech name Václav. The other language versions of the name are german: Wenzel, pl, Wacław, Więcesław, Wieńczysław, es, Wenceslao, russian: ... {{disambig, geo de:Bolesław ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |