Konrad I, Duke Of Głogów on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Konrad I of Głogów ( pl, Konrad I głogowski; – 6 August 1273/74), a member of the
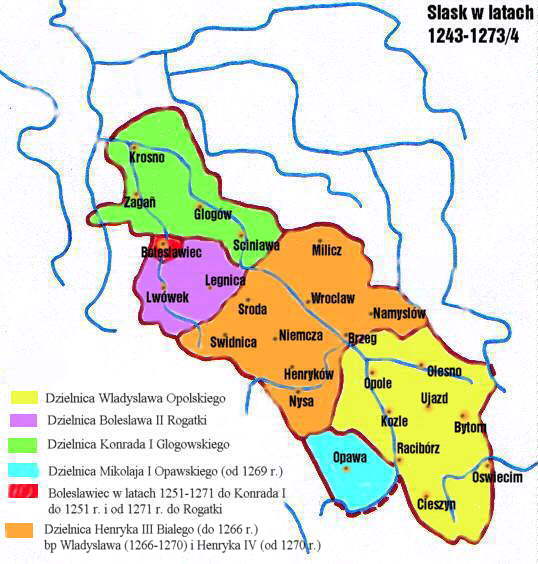 In June 1249 Konrad fled to
In June 1249 Konrad fled to
Chronological Dates in Stoyan
("object not found" 7 Jan 2020)
*''This article was translated from his original in Polish Wikipedia.'' {{DEFAULTSORT:Konrad 01 of Glogow Piast dynasty Dukes of Legnica 13th-century births 1270s deaths
Silesian Piasts
The Silesian Piasts were the elder of four lines of the Polish Piast dynasty beginning with Władysław II the Exile (1105–1159), eldest son of Duke Bolesław III of Poland. By Bolesław's testament, Władysław was granted Silesia as his h ...
, was Silesian duke of Głogów
Głogów (; german: Glogau, links=no, rarely , cs, Hlohov, szl, Głogōw) is a city in western Poland. It is the county seat of Głogów County, in Lower Silesian Voivodeship (since 1999), and was previously in Legnica Voivodeship (1975–1998) ...
from 1249/50 until his death.
Life
Konrad was the fourth son ofHenry II the Pious
Henry II the Pious ( pl, Henryk II Pobożny; 1196 – 9 April 1241) was Duke of Silesia and High Duke of Poland as well as Duke of South-Greater Poland from 1238 until his death. Between 1238 and 1239 he also served as regent of Sandomierz and ...
, Duke of Silesia
Silesia (, also , ) is a historical region of Central Europe that lies mostly within Poland, with small parts in the Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately , and the population is estimated at around 8,000,000. Silesia is split ...
and High Duke of Poland
Poland was ruled at various times either by dukes and princes (10th to 14th centuries) or by kings (11th to 18th centuries). During the latter period, a tradition of free election of monarchs made it a uniquely electable position in Europe (16t ...
from 1238, by his wife Anna
Anna may refer to:
People Surname and given name
* Anna (name)
Mononym
* Anna the Prophetess, in the Gospel of Luke
* Anna (wife of Artabasdos) (fl. 715–773)
* Anna (daughter of Boris I) (9th–10th century)
* Anna (Anisia) (fl. 1218 to 12 ...
, daughter of the Přemyslid king Ottokar I of Bohemia
Ottokar I ( cs, Přemysl Otakar I.; c. 1155 – 1230) was Duke of Bohemia periodically beginning in 1192, then acquired the title of King of Bohemia, first in 1198 from Philip of Swabia, later in 1203 from Otto IV of Brunswick and in 1212 (a ...
. At the time of his father's death in the 1241 Battle of Legnica
The Battle of Legnica ( pl, bitwa pod Legnicą), also known as the Battle of Liegnitz (german: Schlacht von Liegnitz) or Battle of Wahlstatt (german: Schlacht bei Wahlstatt), was a battle between the Mongol Empire and combined European forces t ...
against the Golden Horde
The Golden Horde, self-designated as Ulug Ulus, 'Great State' in Turkic, was originally a Mongols, Mongol and later Turkicized khanate established in the 13th century and originating as the northwestern sector of the Mongol Empire. With the fr ...
, he and his younger brother Władysław were placed under the guardianship of their eldest brother Duke Bolesław II Rogatka Boleslav or Bolesław may refer to:
In people:
* Boleslaw (given name)
In geography:
* Bolesław, Dąbrowa County, Lesser Poland Voivodeship, Poland
* Bolesław, Olkusz County, Lesser Poland Voivodeship, Poland
* Bolesław, Silesian Voivodeship, ...
. After Henry's sudden death, the Silesian Piasts were not able to maintain their dominant position: Bolesław II tried to succeed his father on the Polish throne at Kraków
Kraków (), or Cracow, is the second-largest and one of the oldest cities in Poland. Situated on the Vistula River in Lesser Poland Voivodeship, the city dates back to the seventh century. Kraków was the official capital of Poland until 1596 ...
, but eventually could not prevail against his Piast
The House of Piast was the first historical ruling dynasty of Poland. The first documented List of Polish monarchs, Polish monarch was Duke Mieszko I of Poland, Mieszko I (c. 930–992). The Poland during the Piast dynasty, Piasts' royal rule i ...
cousin Konrad I of Masovia
Konrad I of Masovia (ca. 1187/88 – 31 August 1247), from the Polish Piast dynasty, was the sixth Duke of Masovia and Kuyavia from 1194 until his death as well as High Duke of Poland from 1229 to 1232 and again from 1241 to 1243.
Life
Konrad was ...
.
In order to avoid further fragmentation of the paternal lands, the elder duke, with the approval of their mother, sent Konrad to study in Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. S ...
, where he was to be educated with the intention of becoming a priest in the future. However, in 1248, when the young man found out about the division of the family lands between his older brothers Bolesław II, ruling as a Duke of Legnica, and Henry III the White
Henry III the White ( pl, Henryk III Biały) ( – 3 December 1266), a member of the Silesian Piasts, was Duke of Silesia at Wrocław from 1248 until his death, as co-ruler with his brother Władysław.
Life
He was the third son of the Polish hi ...
, Duke at Wrocław
Wrocław (; german: Breslau, or . ; Silesian German: ''Brassel'') is a city in southwestern Poland and the largest city in the historical region of Silesia. It lies on the banks of the River Oder in the Silesian Lowlands of Central Europe, rou ...
, he returned to the country and claimed his part of the Silesian inheritance. Soon a preliminary agreement was reached under which Konrad remained under the protection and care of his older brother, who gave him the title of co-ruler in Legnica.
Bolesław II (who wanted to get rid of him) still proposed Konrad for spiritual posts: first, as Provost of Głogów Cathedral, and then Bishop of Passau
The Diocese of Passau is a Roman Catholic diocese in Germany that is a suffragan of the Archdiocese of Munich and Freising.Bavaria
Bavaria ( ; ), officially the Free State of Bavaria (german: Freistaat Bayern, link=no ), is a state in the south-east of Germany. With an area of , Bavaria is the largest German state by land area, comprising roughly a fifth of the total lan ...
. Though he had not reached the canonical age
In the canon law of the Catholic Church, a person is a subject of certain legal rights and obligations. Persons may be distinguished between physical and juridic persons. Juridic persons may be distinguished as collegial or non-collegial, and pub ...
, he was elected by the Passau cathedral
St. Stephen's Cathedral (german: Dom St. Stephan) is a baroque church from 1688 in Passau, Germany, dedicated to Saint Stephen. It is the seat of the Catholic Bishop of Passau and the main church of his diocese.
Since 730, there have been many c ...
chapter to succeed the deposed bishop Rüdiger of Bergheim Bistumswappen of Passau.Rüdiger von Bergheim (c.1175 – 14 April 1258) was Bishop of Chiemsee from 1216 to 1233 and Bishop of Passau from 1233 to 1250.
Biography
Rüdiger came from the Salzburg ministerial of the Bergheimer. Since 1198 he was ...
; however, without approval by the Roman Curia. Konrad, nevertheless, didn't have any intention of pursuing an ecclesiastical career. He never entered Passau and soon resumed his conflict with Bolesław II.
 In June 1249 Konrad fled to
In June 1249 Konrad fled to Greater Poland
Greater Poland, often known by its Polish name Wielkopolska (; german: Großpolen, sv, Storpolen, la, Polonia Maior), is a Polish historical regions, historical region of west-central Poland. Its chief and largest city is Poznań followed ...
, where he could count on the support of Duke Przemysł I. In 1251 he campaigned Bolesław's ducal lands and he managed to conquer Bytom Odrzański. Konrad's bonds with the Piast dukes of Greater Poland were reinforced after his marriage with Przemysł I's sister Salome. His other brother Henry III the White soon became another ally in the fight against Bolesław II. With the help of his new allies, and thanks to the revolt of the townspeople of Głogów, the campaign against Bolesław II ended in complete success. The Duke of Legnica was forced to accept his defeat and give the Lower Silesia
Lower Silesia ( pl, Dolny Śląsk; cz, Dolní Slezsko; german: Niederschlesien; szl, Dolny Ślōnsk; hsb, Delnja Šleska; dsb, Dolna Šlazyńska; Silesian German: ''Niederschläsing''; la, Silesia Inferior) is the northwestern part of the ...
n lands of Głogów up to Krosno Odrzańskie
Krosno Odrzańskie (german: Crossen an der Oder) is a city on the east bank of Oder River, at the confluence with the Bóbr. The town in Western Poland with 11,319 inhabitants (2019) is the capital of Krosno Odrzańskie County, Krosno County. I ...
and Żagań
Żagań ( French and german: Sagan, hsb, Zahań, la, Saganum) is a town in western Poland, on the Bóbr river, with 25,731 inhabitants (2019). The town is the capital of Żagań County in the historic region of Silesia. Previously in the Zielon ...
to Konrad as a duchy in his own right.
Until the end of his life Konrad's relations with his brother Bolesław II remain strained. In 1257 Konrad made a dangerous move and kidnapped Bolesław from his residence in Legnica
Legnica (Polish: ; german: Liegnitz, szl, Lignica, cz, Lehnice, la, Lignitium) is a city in southwestern Poland, in the central part of Lower Silesia, on the Kaczawa River (left tributary of the Oder) and the Czarna Woda (Kaczawa), Czarna Woda ...
. The duke regained his freedom after a few months, but it is unknown at what price. It can be said that after that the duke never left Bolesław II a moment of happiness, but in 1271 the Duke of Legnica managed to regain the town of Bolesławiec
Bolesławiec (pronounced , szl, Bolesławiec, german: Bunzlau) is a historic city situated on the Bóbr River in the Lower Silesian Voivodeship, in western Poland. It is the administrative seat of Bolesławiec County, and of Gmina Bolesławiec ...
near the Bóbr
Bóbr ( cs, Bobr, german: Bober, ) is a river which carries water through the north of the Czech Republic and the southwest of Poland, a left tributary of the Oder.
Course
The Bóbr has a length of (3 in Czech Republic, 276 in Poland, 10th ...
river.
From about 1260 Konrad established closer contacts with the Kingdom of Bohemia
The Kingdom of Bohemia ( cs, České království),; la, link=no, Regnum Bohemiae sometimes in English literature referred to as the Czech Kingdom, was a medieval and early modern monarchy in Central Europe, the predecessor of the modern Czec ...
and became involved in the expansionist politics of King Ottokar II. Also he promoted the colonization
Colonization, or colonisation, constitutes large-scale population movements wherein migrants maintain strong links with their, or their ancestors', former country – by such links, gain advantage over other inhabitants of the territory. When ...
in his lands, mostly by German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ger ...
settlers. This was a decisive contribution to the institution of the Magdeburg town law in his Głogów
Głogów (; german: Glogau, links=no, rarely , cs, Hlohov, szl, Głogōw) is a city in western Poland. It is the county seat of Głogów County, in Lower Silesian Voivodeship (since 1999), and was previously in Legnica Voivodeship (1975–1998) ...
residence in 1253. In contrast to his brother Bolesław II, Konrad vigorously supported Bishop Thomas I of Wrocław in his defence of church rights. However, when the bishop died in 1268 Konrad began to violate the privileges conferred by him, which led to conflicts with the new Bishop Thomas II Zaremba.
At the end of his life he founded a church in Zielona Góra
Zielona Góra is the largest city in Lubusz Voivodeship, located in western Poland, with 140,403 inhabitants (2021). Zielona Góra has a favourable geographical position, being close to the Polish-German border and on several international road ...
(now a Co-cathedral) dedicated to his grandmother, St. Hedwig of Silesia
Hedwig of Silesia ( pl, Święta Jadwiga Śląska), also Hedwig of Andechs (german: Heilige Hedwig von Andechs, la, Hedvigis; 1174 – 15 October 1243), a member of the Bavarian comital House of Andechs, was Duchess of Silesia from 1201 and o ...
. The church was completed only twenty years after his death by his son and heir Henry III.
Marriages and Children
In 1249 Konrad contracted his first marriage to Salome (b. ca. 1225 - d. April 1267/74), daughter of Duke Władysław ofGreater Poland
Greater Poland, often known by its Polish name Wielkopolska (; german: Großpolen, sv, Storpolen, la, Polonia Maior), is a Polish historical regions, historical region of west-central Poland. Its chief and largest city is Poznań followed ...
. They had six children:
#Anna
Anna may refer to:
People Surname and given name
* Anna (name)
Mononym
* Anna the Prophetess, in the Gospel of Luke
* Anna (wife of Artabasdos) (fl. 715–773)
* Anna (daughter of Boris I) (9th–10th century)
* Anna (Anisia) (fl. 1218 to 12 ...
(b. 1250/52 - d. 28 May 1271), married on 24 August 1260 to Duke Louis II of Upper Bavaria.
# Henry III (b. 1251/60 - d. 9 December 1310).
#Konrad II the Hunchback Konrad II the Hunchback ( pl, Konrad II Garbaty) (1252/65 – 11 October 1304) was Duke of Ścinawa from 1278 to 1284, patriarch of Aquileia in 1299, and Duke of Żagań from 1284 until his death.
Biography
He was the second son of Konrad I, Duke ...
(b. 1252/60 - d. 11 October 1304).
#Euphemia (b. 12 January 1251/52 - d. 1266-74), married by 13 May 1266 to Count Albert I of Gorizia
Albert I ( – 1 April 1304), a member of the House of Gorizia (''Meinhardiner'' dynasty), ruled the counties of Gorizia (''Görz'') and Tyrol from 1258, jointly with his elder brother Meinhard IV. In 1271, the brothers divided their heritage ...
.
# Przemko (b. 1255/65 - d. killed in battle, Siewierz, 26 February 1289).
#Jadwiga (b. 1265? - d. 9 June 1318), Abbess of St. Klara, Wroclaw (1283).
By 1271/74, Konrad married his second wife, Sophie (b. ca. 1259 - d. 24 August 1318), daughter of Dietrich the Wise, Margrave
Margrave was originally the medieval title for the military commander assigned to maintain the defence of one of the border provinces of the Holy Roman Empire or of a kingdom. That position became hereditary in certain feudal families in the Emp ...
of Landsberg (second son of Henry III, Margrave of Meissen
Henry III, called Henry the Illustrious (''Heinrich der Erlauchte'') (c. 1215 – 15 February 1288) from the House of Wettin was Margrave of Meissen and last Margrave of Lusatia (as Henry IV) from 1221 until his death; from 1242 also Landgrave ...
) and – according to some sources – widow of the last legitimate male member of the House of Hohenstaufen
The Hohenstaufen dynasty (, , ), also known as the Staufer, was a noble family of unclear origin that rose to rule the Duchy of Swabia from 1079, and to royal rule in the Holy Roman Empire during the Middle Ages from 1138 until 1254. The dynasty ...
, Conradin
Conrad III (25 March 1252 – 29 October 1268), called ''the Younger'' or ''the Boy'', but usually known by the diminutive Conradin (german: link=no, Konradin, it, Corradino), was the last direct heir of the House of Hohenstaufen. He was Duke ...
, King of Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
and Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. i ...
. They had no children.
See also
* Beatrix von Silesia-Glogau *Silesia
Silesia (, also , ) is a historical region of Central Europe that lies mostly within Poland, with small parts in the Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately , and the population is estimated at around 8,000,000. Silesia is split ...
*Duchy
A duchy, also called a dukedom, is a Middle Ages, medieval country, territory, fiefdom, fief, or domain ruled by a duke or duchess, a ruler hierarchically second to the king or Queen regnant, queen in Western European tradition.
There once exis ...
References
* *Chronological Dates in Stoyan
("object not found" 7 Jan 2020)
*''This article was translated from his original in Polish Wikipedia.'' {{DEFAULTSORT:Konrad 01 of Glogow Piast dynasty Dukes of Legnica 13th-century births 1270s deaths