|
Wumengosaurus
''Wumengosaurus'' is an extinct aquatic reptile from the Middle Triassic (late Anisian stage) Guanling Formation of Guizhou, southwestern China. It was originally described as a basal eosauropterygian and usually is recovered as such by phylogenetic analyses, although one phylogeny has placed it as the sister taxon to Ichthyosauromorpha while refraining from a formal re-positioning. It was a relatively small reptile, measuring in total body length and weighing . In 2021, Qin ''et al''. described an additional specimen from Guizhou ( Panzhou District) as a new species of ''Wumengosaurus'', ''W. rotundicarpus''. Classification In the 2023 description of ''Luopingosaurus'', Xu ''et al''. recovered ''Wumengosaurus'' as a derived pachypleurosaurid, as the sister taxon to the clade formed by ''Luopingosaurus'' and ''Honghesaurus''. The results of their phylogenetic analyses are shown in the cladogram A cladogram (from Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
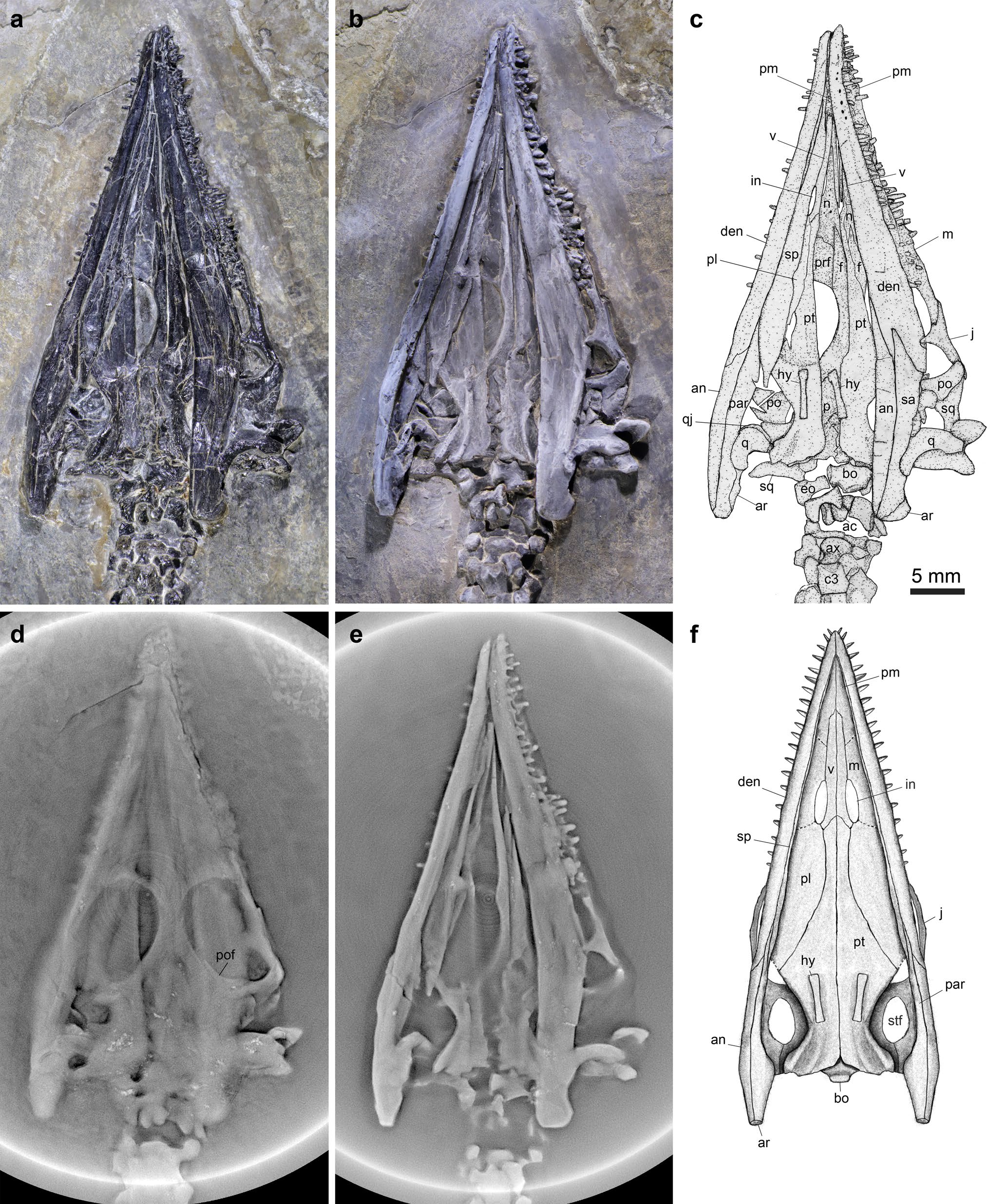
Luopingosaurus
''Luopingosaurus'' (meaning "Luoping lizard") is an extinct genus of pachypleurosaurid sauropterygian from the Middle Triassic Guanling Formation of Yunnan Province, China. The genus contains a single species, ''L. imparilis'', known from a well-preserved, nearly complete skeleton. Discovery and naming The ''Luopingosaurus'' holotype specimen, IVPP V19049, was discovered in sediments of the Guanling Formation, dated to the Anisian age (Pelsonian substage) of the middle Triassic period, in Luoping County, Yunnan Province, China. This specimen consists of a nearly complete, ventrally-exposed, articulated individual, lacking only the end of the tail. The preserved portion of the skeleton measures long. In 2023, Xu ''et al''. described ''Luopingosaurus imparilis'', a new genus and species of pachypleurosaurid, based on these fossil remains. The generic name, "''Luopingosaurus''", combines a reference to the type locality in Luoping County with the Greek word "saurus", meaning ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pachypleurosaurid
left, 220px, '' Pachypleurosaurus'' Pachypleurosauria is an extinct clade of primitive sauropterygian reptiles that vaguely resembled aquatic lizards, and were limited to the Triassic period. They were elongate animals, ranging in size from , with small heads, long necks, paddle-like limbs, and long, deep tails. The limb girdles are greatly reduced, so it is unlikely these animals could move about on land. The widely spaced peg-like teeth project at the front of the jaws, indicating that these animals fed on fish. In the species ''Prosantosaurus'', it was observed that they fed on small fishes and crustaceans which they devoured entirely and that its teeth regrew after they broke off. This was the first observation of tooth replacement in a European pachypleurosaur, the only other discovery of such an event was made in China. Classification Pachypleurosaurs were originally and are often still included within the Nothosauroidea (Carroll 1988, Benton 2004). In some more recen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keichousauridae
left, 220px, '' Pachypleurosaurus'' Pachypleurosauria is an extinct clade of primitive sauropterygian reptiles that vaguely resembled aquatic lizards, and were limited to the Triassic period. They were elongate animals, ranging in size from , with small heads, long necks, paddle-like limbs, and long, deep tails. The limb girdles are greatly reduced, so it is unlikely these animals could move about on land. The widely spaced peg-like teeth project at the front of the jaws, indicating that these animals fed on fish. In the species ''Prosantosaurus'', it was observed that they fed on small fishes and crustaceans which they devoured entirely and that its teeth regrew after they broke off. This was the first observation of tooth replacement in a European pachypleurosaur, the only other discovery of such an event was made in China. Classification Pachypleurosaurs were originally and are often still included within the Nothosauroidea (Carroll 1988, Benton 2004). In some more recent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pachypleurosauroidea
left, 220px, '' Pachypleurosaurus'' Pachypleurosauria is an extinct clade of primitive sauropterygian reptiles that vaguely resembled aquatic lizards, and were limited to the Triassic period. They were elongate animals, ranging in size from , with small heads, long necks, paddle-like limbs, and long, deep tails. The limb girdles are greatly reduced, so it is unlikely these animals could move about on land. The widely spaced peg-like teeth project at the front of the jaws, indicating that these animals fed on fish. In the species ''Prosantosaurus'', it was observed that they fed on small fishes and crustaceans which they devoured entirely and that its teeth regrew after they broke off. This was the first observation of tooth replacement in a European pachypleurosaur, the only other discovery of such an event was made in China. Classification Pachypleurosaurs were originally and are often still included within the Nothosauroidea (Carroll 1988, Benton 2004). In some more recen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pachypleurosauridae
left, 220px, '' Pachypleurosaurus'' Pachypleurosauria is an extinct clade of primitive sauropterygian reptiles that vaguely resembled aquatic lizards, and were limited to the Triassic period. They were elongate animals, ranging in size from , with small heads, long necks, paddle-like limbs, and long, deep tails. The limb girdles are greatly reduced, so it is unlikely these animals could move about on land. The widely spaced peg-like teeth project at the front of the jaws, indicating that these animals fed on fish. In the species ''Prosantosaurus'', it was observed that they fed on small fishes and crustaceans which they devoured entirely and that its teeth regrew after they broke off. This was the first observation of tooth replacement in a European pachypleurosaur, the only other discovery of such an event was made in China. Classification Pachypleurosaurs were originally and are often still included within the Nothosauroidea (Carroll 1988, Benton 2004). In some more recent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eosauropterygia
Sauropterygia (" lizard flippers") is an extinct taxon of diverse, aquatic reptiles that developed from terrestrial ancestors soon after the end-Permian extinction and flourished during the Triassic before all except for the Plesiosauria became extinct at the end of that period. The plesiosaurs would continue to diversify until the end of the Mesozoic. Sauropterygians are united by a radical adaptation of their pectoral girdle, adapted to support powerful flipper strokes. Some later sauropterygians, such as the pliosaurs, developed a similar mechanism in their pelvis. Uniquely among reptiles, sauropterygians moved their tail vertically like modern cetaceans and sirenians. Origins and evolution The earliest sauropterygians appeared about 247 million years ago (Ma), at the start of the Middle Triassic: the first definite sauropterygian with exact stratigraphic datum lies within the Spathian division of the Olenekian era in South China. Early examples were small (around 60&n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guanling Formation
The Guanling Formation is a Middle Triassic (Anisian or Pelsonian in the regional chronostratigraphy) geologic formation in southwestern China. Description The formation encompasses two members. The first member is primarily calcareous mudstone and dolomite, indicative of a coastal environment. The second member is a thicker marine sequence of dark micritic limestone with some dolomite. Two distinct fossil assemblages are found in the second member. The older Luoping biota preserves abundant arthropods along with fossils from other invertebrates and vertebrates, which are rare but well-preserved. The slightly younger Panxian fauna has a more diverse and common assortment of marine reptiles such as sauropterygians. Fossil content Among others, the following fossils were reported from the formation: * ''Atopodentatus'' * ''Barracudasauroides'' * ''Diandongosaurus'' * ''Dianopachysaurus'' * ''Honghesaurus'' * ''Kyphosichthys'' * ''Largocephalosaurus'' * ''Luopingosaurus'' * '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2008 In Paleontology
Protozoa New taxa Plants Angiosperms Monocots Arthropoda Arachnids Insects Xiphosurans Fishes Bony fish Placoderms General research *Hilton & Grande redescribe the fossil mooneyes of western North America synonymizing the genus ''Eohiodon'' with ''Hiodon''. *Cicimurri, Paris, & Everhart describe a partial dentition from a Holocephali chimaeroid fish found in the Niobrara Chalk. Amphibians Jenkins, F. A., jr, Shubin, N. H., Gatesy, S. M., and Warren, A., 2008, Gerrothorax pulcherrimus from the Upper Triassic Fleming Fjord Formation of East Greenland and a reassessment of head lifting in temnospondyl feeding: Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology, v. 28, n. 4, p. 935-950. Newly named amphibians Archosaurs Newly named pseudosuchians Newly named pterosaurs Dinosaurs * Oviraptorosaurian eggs with embryonic skeletons are discovered for the first time in China. * Mongolian Late Jurassic theropod fossils are found for the first time. * A new study on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eosauropterygia
Sauropterygia (" lizard flippers") is an extinct taxon of diverse, aquatic reptiles that developed from terrestrial ancestors soon after the end-Permian extinction and flourished during the Triassic before all except for the Plesiosauria became extinct at the end of that period. The plesiosaurs would continue to diversify until the end of the Mesozoic. Sauropterygians are united by a radical adaptation of their pectoral girdle, adapted to support powerful flipper strokes. Some later sauropterygians, such as the pliosaurs, developed a similar mechanism in their pelvis. Uniquely among reptiles, sauropterygians moved their tail vertically like modern cetaceans and sirenians. Origins and evolution The earliest sauropterygians appeared about 247 million years ago (Ma), at the start of the Middle Triassic: the first definite sauropterygian with exact stratigraphic datum lies within the Spathian division of the Olenekian era in South China. Early examples were small (around 60&n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Honghesaurus
''Honghesaurus'' is an extinct genus of pachypleurosaur from the Anisian-age Guanling Formation of China. The type specimen measures about in total body length. Classification The cladogram below follows Xu and colleagues (2022), when they used ''Youngina'' as a reference point for rooting the tree. Using a selection of placodont Placodonts (" Tablet teeth") are an extinct order of marine reptiles that lived during the Triassic period, becoming extinct at the end of the period. They were part of Sauropterygia, the group that includes plesiosaurs. Placodonts were genera ...s resulted in a less resolved topology. References Triassic sauropterygians Pachypleurosaurs Fossil taxa described in 2022 Anisian life {{triassic-reptile-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reptile
Reptiles, as most commonly defined are the animals in the class Reptilia ( ), a paraphyletic grouping comprising all sauropsids except birds. Living reptiles comprise turtles, crocodilians, squamates (lizards and snakes) and rhynchocephalians (tuatara). As of March 2022, the Reptile Database includes about 11,700 species. In the traditional Linnaean classification system, birds are considered a separate class to reptiles. However, crocodilians are more closely related to birds than they are to other living reptiles, and so modern cladistic classification systems include birds within Reptilia, redefining the term as a clade. Other cladistic definitions abandon the term reptile altogether in favor of the clade Sauropsida, which refers to all amniotes more closely related to modern reptiles than to mammals. The study of the traditional reptile orders, historically combined with that of modern amphibians, is called herpetology. The earliest known proto-reptiles originated around ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Placodontia
Placodonts (" Tablet teeth") are an extinct order of marine reptiles that lived during the Triassic period, becoming extinct at the end of the period. They were part of Sauropterygia, the group that includes plesiosaurs. Placodonts were generally between in length, with some of the largest measuring long. The first specimen was discovered in 1830. They have been found throughout central Europe, North Africa, the Middle East and China. Palaeobiology The earliest forms, like ''Placodus'', which lived in the early to middle Triassic, resembled barrel-bodied lizards superficially similar to the marine iguana of today, but larger. In contrast to the marine iguana, which feeds on algae, the placodonts ate molluscs and so their teeth were flat and tough to crush shells. In the earliest periods, their size was probably enough to keep away the top sea predators of the time: the sharks. However, as time passed, other kinds of carnivorous reptiles began to colonize the seas, such as ich ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |