|
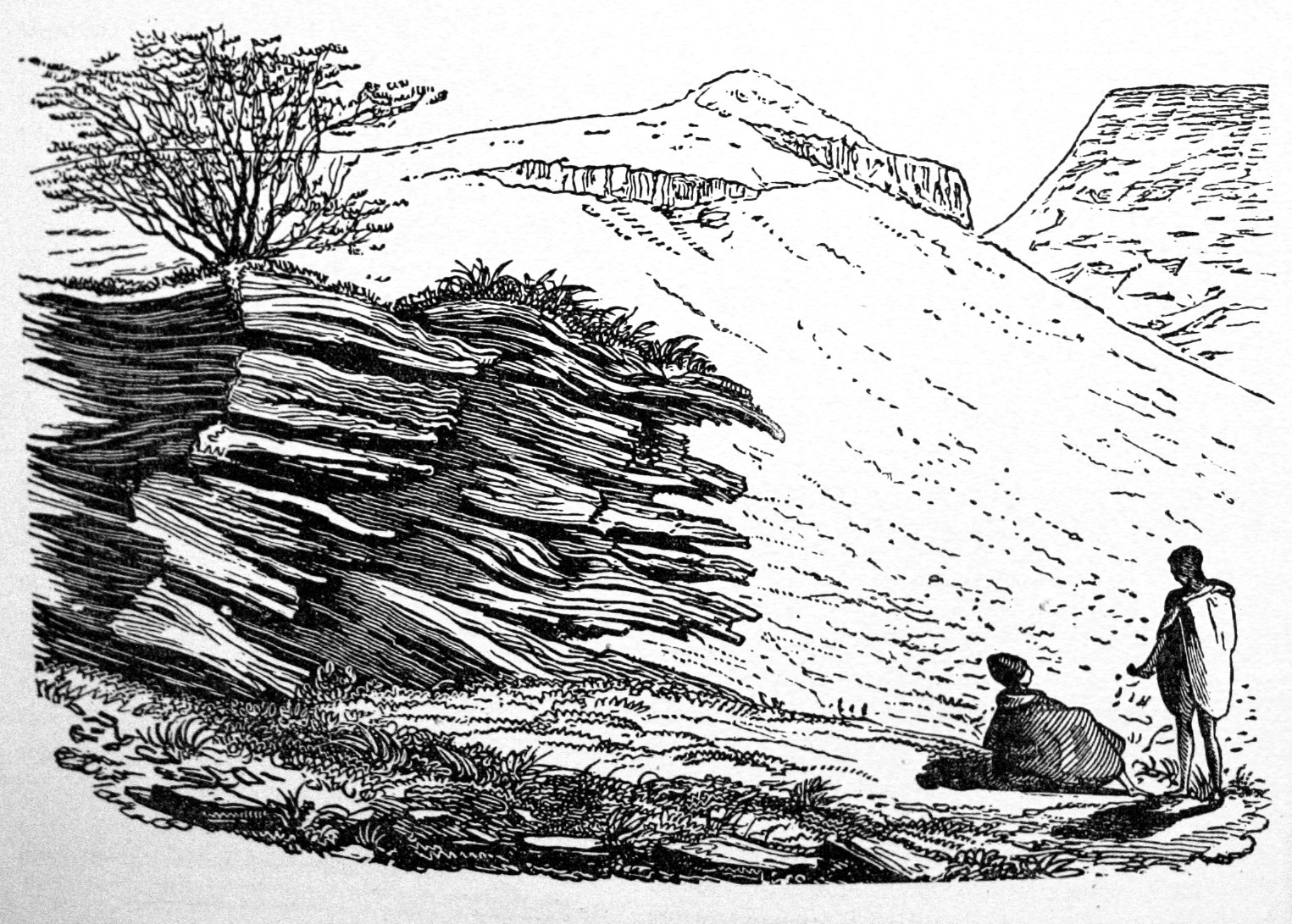
Wonderwerk Cave
Wonderwerk Cave is an archaeological site, formed originally as an ancient solution cavity in dolomite rocks of the Kuruman Hills, situated between Danielskuil and Kuruman in the Northern Cape Province, South Africa. It is a National Heritage Site, managed as a satellite of the McGregor Museum in Kimberley. Geologically, hillside erosion exposed the northern end of the cavity, which extends horizontally for about into the base of a hill. Accumulated deposits inside the cave, up to in-depth, reflect natural sedimentation processes such as water and wind deposition as well as the activities of animals, birds, and human ancestors over some 2 million years. The site has been studied and excavated by archaeologists since the 1940s and research here generates important insights into human history in the subcontinent of Southern Africa. Evidence within Wonderwerk cave has been called the oldest controlled fire. Wonderwerk means "miracle" in the Afrikaans language. Archaeological seq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asbestos Mountains
The Asbestos Mountains is a range of hills in the Northern Cape province of South Africa, stretching south-southwest from Kuruman, where the range is known as the ''Kuruman Hills'', to Prieska. It passes Boetsap, Danielskuil, Lime Acres, Douglas, Northern Cape , Douglas and Griekwastad. The range lies about 150 km west of Kimberley, Northern Cape, Kimberley and rises from the Ghaap Plateau. The mountains were named after the asbestos which was mined in the 20th century and is found as a variety of amphibole called crocidolite. Veins occur in slate, slaty rocks, and are associated with jasper and quartzite rich in magnetite and brown iron-ore. Geologically it belongs to the Griquatown series. The Griquas, for whom Griquatown was named, were a Khoikhoi people who in 1800 were led by a freed slave, Adam Kok, from Piketberg in the western Cape to the foothills of the Asbestos Mountains where they settled at a place called Klaarwater. John Campbell (missionary), John Campbell, (1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zamani Project
The Zamani Project is part of the African Cultural Heritage Sites and Landscapes Database. Zamani is a research group at the University of Cape Town, which acquires, models, presents and manages spatial and other data from cultural heritage sites. The present focus of the Zamani project is Africa, with the principal objective of developing “The African Cultural Heritage Sites and Landscapes Database”. Zamani comes from the Swahili phrase “Hapo zamani za kale” which means “Once upon a time”, and can be used to mean 'the past'. The word is derived from Arabic root for temporal vocabulary, ‘Zaman,’ and appears in several languages around the world. History The Zamani initiative was conceptualised in the Geomatics Division of the University of Cape Town by Professor Heinz Rüther in 2001 in collaboration with ITHAKA and Aluka ow an initiative of JSTORas the “African Cultural Heritage Sites and Landscapes Database” in 2004 with a number of sequential grants from t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
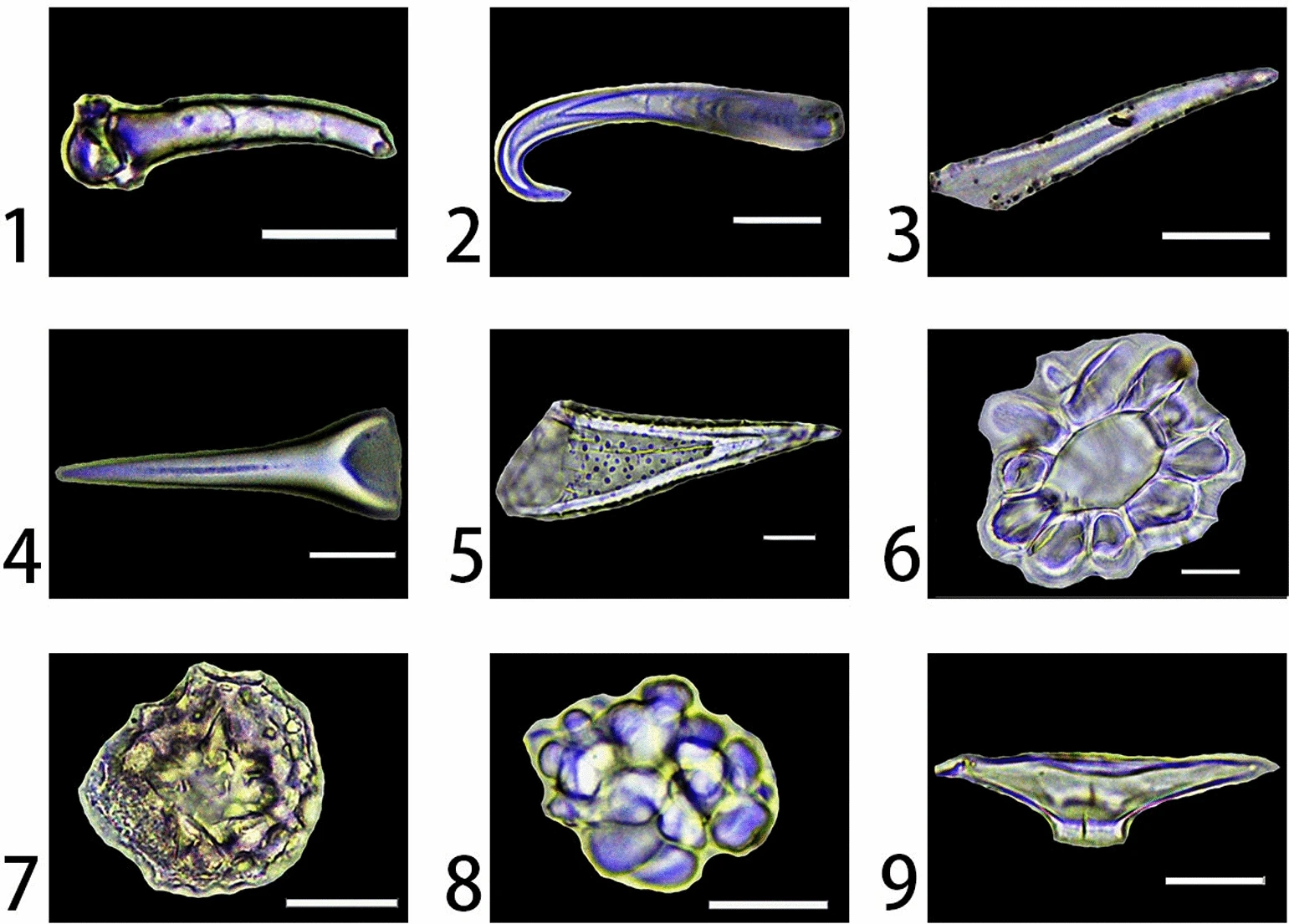
Marion Bamford
Marion Kathaleen Bamford is a Zimbabwean paleobotanist, and is a professor at University of the Witwatersrand in Johannesburg, South Africa. Early life And education Marion was born in Zimbabwe. She received her PhD, MSc, and BSc (Honors) at University of the Witwatersrand. Career At University Of The Witwatersrand, she gives lectures about paleobotany to undergraduate students, and researches fossil woods, as well as leaf fossils, seed pollen, phytolith, and stems from the Permian period to the Holocene period. She has published more than 100 journal papers, and is a Fellow of The Royal Society of South Africa. See also * University of the Witwatersrand * Paleobotany Paleobotany, which is also spelled as palaeobotany, is the branch of botany dealing with the recovery and identification of plant remains from geological contexts, and their use for the biological reconstruction of past environments (paleogeogr ... References External links * * Marion Bam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phytolith
Phytoliths (from Greek, "plant stone") are rigid, microscopic structures made of silica, found in some plant tissues and persisting after the decay of the plant. These plants take up silica from the soil, whereupon it is deposited within different intracellular and extracellular structures of the plant. Phytoliths come in varying shapes and sizes. Although some use "phytolith" to refer to all mineral secretions by plants, it more commonly refers to siliceous plant remains. In contrast, mineralized calcium secretions in cacti are composed of calcium oxalates.Piperno, Dolores R. (2006). Phytoliths: A Comprehensive Guide for Archaeologists and Paleoecologists. AltaMira Press . The silica is absorbed in the form of monosilicic acid (Si(OH)4), and is carried by the plant's vascular system to the cell walls, cell lumen, and intercellular spaces. Depending on the plant taxa and soil condition, absorbed silica can range from 0.1% to 10% of the plant's total dry weight. When deposited, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eduard Meine Van Zinderen-Bakker
Eduard Meine van Zinderen Bakker (15 April 1907 Opsterland, Friesland – 19 March 2002 Somerset West) was a Dutch-born South African palynologist who made significant contributions to the fields of plant ecology, palynology and palaeo-ecology of Africa. After obtaining a PhD in botany from the University of Amsterdam he taught biology in Apeldoorn. In 1947 he emigrated to South Africa with his wife and 2 sons. He served as the Netherlands' Honorary Consul for 20 years, an office for which he received the Order of Oranje-Nassau. Initially appointed as lecturer in botany at the University of the Orange Free State in 1947, he stayed until 1972 and ended as Professor of the Department. The University established the Institute of Environmental Sciences and on his retirement appointed him as Director, a position he held until 1976, working with a staff of local and foreign scientists. From 1977 to 1988 he acted as Research Officer at the Institute until his retirement at age 81. Durin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stone Age
The Stone Age was a broad prehistoric period during which stone was widely used to make tools with an edge, a point, or a percussion surface. The period lasted for roughly 3.4 million years, and ended between 4,000 BC and 2,000 BC, with the advent of metalworking. Though some simple metalworking of malleable metals, particularly the use of gold and copper for purposes of ornamentation, was known in the Stone Age, it is the melting and smelting of copper that marks the end of the Stone Age. In Western Asia, this occurred by about 3,000 BC, when bronze became widespread. The term Bronze Age is used to describe the period that followed the Stone Age, as well as to describe cultures that had developed techniques and technologies for working copper alloys (bronze: originally copper and arsenic, later copper and tin) into tools, supplanting stone in many uses. Stone Age artifacts that have been discovered include tools used by modern humans, by their predecessor species in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oldowan
The Oldowan (or Mode I) was a widespread stone tool archaeological industry (style) in prehistory. These early tools were simple, usually made with one or a few flakes chipped off with another stone. Oldowan tools were used during the Lower Paleolithic period, 2.6 million years ago up until at least 1.7 million years ago, by ancient Hominins (early humans) across much of Africa. This technological industry was followed by the more sophisticated Acheulean industry (two sites associated with ''Homo erectus'' at Gona in the Afar Region of Ethiopia dating from 1.5 and 1.26 million years ago have both Oldowan and Acheulean tools). The term ''Oldowan'' is taken from the site of Olduvai Gorge in Tanzania, where the first Oldowan stone tools were discovered by the archaeologist Louis Leakey in the 1930s. However, some contemporary archaeologists and palaeoanthropologists prefer to use the term ''Mode 1'' tools to designate pebble tool industries (including Oldowan), with ''Mode 2'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quaternary Science Reviews
''Quaternary Science Reviews'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal covering quaternary science. It was established in 1982 by Pergamon Press and is currently published by Elsevier. The editor-in-chief is C.V. Murray Wallace (University of Wollongong). According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2013 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published in the last two years in a given journal, as i ... of 4.571. References External links * Elsevier academic journals Biweekly journals English-language journals Publications established in 1982 Quaternary science journals Archaeology journals {{archaeology-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface Exposure Dating
Surface exposure dating is a collection of geochronological techniques for estimating the length of time that a rock has been exposed at or near Earth's surface. Surface exposure dating is used to date glacial advances and retreats, erosion history, lava flows, meteorite impacts, rock slides, fault scarps, cave development, and other geological events. It is most useful for rocks which have been exposed for between 103 and 106 years. Cosmogenic radionuclide dating The most common of these dating techniques is ''Cosmogenic radionuclide dating''. Earth is constantly bombarded with primary cosmic rays, high energy charged particles – mostly protons and alpha particles. These particles interact with atoms in atmospheric gases, producing a cascade of secondary particles that may in turn interact and reduce their energies in many reactions as they pass through the atmosphere. This cascade includes a small fraction of hadrons, including neutrons. When one of these particles strikes an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetostratigraphy
Magnetostratigraphy is a geophysical correlation technique used to date sedimentary and volcanic sequences. The method works by collecting oriented samples at measured intervals throughout the section. The samples are analyzed to determine their ''characteristic remanent magnetization'' (ChRM), that is, the polarity of Earth's magnetic field at the time a stratum was deposited. This is possible because volcanic flows acquire a thermoremanent magnetization and sediments acquire a depositional remanent magnetization, both of which reflect the direction of the Earth's field at the time of formation. This technique is typically used to date sequences that generally lack fossils or interbedded igneous rock. Technique When measurable magnetic properties of rocks vary stratigraphically they may be the basis for related but different kinds of stratigraphic units known collectively as ''magnetostratigraphic units (magnetozones)''. The magnetic property most useful in stratigraphic work is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hebrew University Of Jerusalem
The Hebrew University of Jerusalem (HUJI; he, הַאוּנִיבֶרְסִיטָה הַעִבְרִית בִּירוּשָׁלַיִם) is a public research university based in Jerusalem, Israel. Co-founded by Albert Einstein and Dr. Chaim Weizmann in July 1918, the public university officially opened in April 1925. It is the second-oldest Israeli university, having been founded 30 years before the establishment of the State of Israel but six years after the older Technion university. The HUJI has three campuses in Jerusalem and one in Rehovot. The world's largest library for Jewish studies—the National Library of Israel—is located on its Edmond J. Safra campus in the Givat Ram neighbourhood of Jerusalem. The university has five affiliated teaching hospitals (including the Hadassah Medical Center), seven faculties, more than 100 research centers, and 315 academic departments. , one-third of all the doctoral candidates in Israel were studying at the HUJI. Among its first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optically Stimulated Luminescence
In physics, optically stimulated luminescence (OSL) is a method for measuring doses from ionizing radiation. It is used in at least two applications: * Luminescence dating of ancient materials: mainly geological sediments and sometimes fired pottery, bricks etc., although in the latter case thermoluminescence dating is used more often * Radiation dosimetry, which is the measurement of accumulated radiation dose in the tissues of health care, nuclear, research and other workers, as well as in building materials in regions of nuclear disaster The method makes use of electrons trapped between the valence and conduction bands in the crystalline structure of certain minerals (most commonly quartz and feldspar). The trapping sites are imperfections of the lattice — impurities or defects. The ionizing radiation produces electron-hole pairs: Electrons are in the conduction band and holes in the valence band. The electrons that have been excited to the conduction band may become entrap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |