|
Wolverhampton Temporary Railway Station
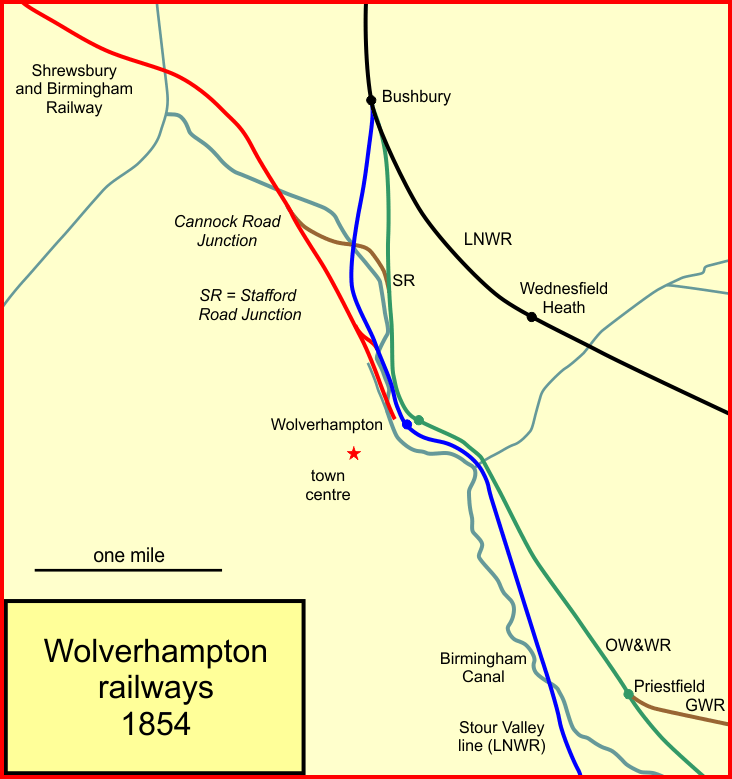
Wolverhampton Temporary railway station was a station was the eastern terminus of the Shrewsbury and Birmingham Railway The Shrewsbury and Birmingham Railway was authorised in 1846. It agreed to joint construction with others of the costly Wolverhampton to Birmingham section, the so-called Stour Valley Line. This work was dominated by the hostile London and North ... from 1849 to 1852. The station opened on 12 November 1849 as a temporary terminus for the S&B after they were given rights to run trains over the Birmingham, Wolverhampton and Stour Valley Railway (BW&SV). It closed on 24 June 1852, after Wolverhampton High Level opened just to the south. The station buildings were demolished in the 1970s. References {{West Midlands railway stations, disused Disused railway stations in Wolverhampton Railway stations in Great Britain opened in 1849 Railway stations in Great Britain closed in 1852 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wolverhampton
Wolverhampton () is a city, metropolitan borough and administrative centre in the West Midlands, England. The population size has increased by 5.7%, from around 249,500 in 2011 to 263,700 in 2021. People from the city are called "Wulfrunians". Historically part of Staffordshire, the city grew initially as a market town specialising in the wool trade. In the Industrial Revolution, it became a major centre for coal mining, steel production, lock making, and the manufacture of cars and motorcycles. The economy of the city is still based on engineering, including a large aerospace industry, as well as the service sector. Toponym The city is named after Wulfrun, who founded the town in 985, from the Anglo-Saxon ''Wulfrūnehēantūn'' ("Wulfrūn's high or principal enclosure or farm"). Before the Norman Conquest, the area's name appears only as variants of ''Heantune'' or ''Hamtun'', the prefix ''Wulfrun'' or similar appearing in 1070 and thereafter. Alternatively, the city ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ordnance Survey National Grid
The Ordnance Survey National Grid reference system (OSGB) (also known as British National Grid (BNG)) is a system of geographic grid references used in Great Britain, distinct from latitude and longitude. The Ordnance Survey (OS) devised the national grid reference system, and it is heavily used in their survey data, and in maps based on those surveys, whether published by the Ordnance Survey or by commercial map producers. Grid references are also commonly quoted in other publications and data sources, such as guide books and government planning documents. A number of different systems exist that can provide grid references for locations within the British Isles: this article describes the system created solely for Great Britain and its outlying islands (including the Isle of Man); the Irish grid reference system was a similar system created by the Ordnance Survey of Ireland and the Ordnance Survey of Northern Ireland for the island of Ireland. The Universal Transverse Merca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shrewsbury And Birmingham Railway
The Shrewsbury and Birmingham Railway was authorised in 1846. It agreed to joint construction with others of the costly Wolverhampton to Birmingham section, the so-called Stour Valley Line. This work was dominated by the hostile London and North Western Railway, which used underhand and coercive tactics. The section between Shrewsbury and Wellington was also built jointly, in this case with the Shropshire Union Railway. The S&BR opened from Shrewsbury to its own Wolverhampton terminus in 1849. The Stour Valley Line was still delayed by the LNWR, but the S&BR eventually got access to it in 1852. By this time it was obvious that the LNWR was an impossible partner, and the S&BR allied itself to the Great Western Railway, which reached Wolverhampton in 1854. The S&BR merged with the GWR in 1854. With the S&BR and other absorbed railways, the GWR obtained a through route between London and the River Mersey at Birkenhead, and to Manchester and Liverpool by the use of running powers. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birmingham, Wolverhampton And Stour Valley Railway
The Stour Valley Line is the present-day name given to the railway line between Birmingham and Wolverhampton, in England. It was authorised as the Birmingham, Wolverhampton and Stour Valley Railway in 1836; the title was often shortened to the Stour Valley Railway. The line opened in 1852, and the line is now the main line between those places. Associated with its construction was the building of the major passenger station that was later named New Street station, and also lines in tunnel each side of the station, connecting to the existing routes. The station was opened in 1854. Before completion, the Company became controlled by the London and North Western Railway, which used dubious methods to harm competitor railways that were to be dependent on its completion. The line was electrified in 1966 and now forms part of the Rugby–Birmingham–Stafford Line, an important and very heavily used part of the railway network. Origins Birmingham's first main railway passenger term ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wolverhampton Railway Station
Wolverhampton railway station in Wolverhampton, West Midlands, England is on the Birmingham Loop of the West Coast Main Line. It is served by Avanti West Coast, CrossCountry, Transport for Wales and West Midlands Trains services, and was historically known as Wolverhampton High Level. History The first station named ''Wolverhampton'' had opened on the edge of the town centre in 1837 on the Grand Junction Railway, this station was renamed Wednesfield Heath in 1855, shortly after the present station was opened, and then was closed in 1873. On 12 November 1849, the Shrewsbury and Birmingham Railway opened a temporary terminus to its line, at a location very close to the present station. The present station was opened on 1 July 1852 by the Birmingham, Wolverhampton and Stour Valley Railway, a subsidiary of the London and North Western Railway (LNWR); it was named ''Wolverhampton Queen Street''. The only visible remnant of the original station is the Queen's Building, the ga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stafford Road (closed 1852) Railway Station
Stafford Road railway station served the city of Wolverhampton, England from 1850 to 1852 on the Wolverhampton-Shrewsbury line. The station opened in October 1850 by the Shrewsbury and Birmingham Railway. The station was situated to the west of Stafford Road at the present site of Stafford Road Junction. The station was served by six trains on Mondays to Saturdays with two on Sundays in both directions between Wolverhampton Temporary and Shrewsbury Shrewsbury ( , also ) is a market town, civil parish, and the county town of Shropshire, England, on the River Severn, north-west of London; at the 2021 census, it had a population of 76,782. The town's name can be pronounced as either 'Sh .... It was a short distance from Wolverhampton station and so Stafford Road proved to be unprofitable and closed completely in June or July 1852. There is no evidence of the station's existence today. References External links Disused railway stations in Staffordshire Ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railway Stations In Great Britain Opened In 1849
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a prepared flat surface, rail vehicles (rolling stock) are directionally guided by the tracks on which they run. Tracks usually consist of steel rails, installed on sleepers (ties) set in ballast, on which the rolling stock, usually fitted with metal wheels, moves. Other variations are also possible, such as "slab track", in which the rails are fastened to a concrete foundation resting on a prepared subsurface. Rolling stock in a rail transport system generally encounters lower frictional resistance than rubber-tyred road vehicles, so passenger and freight cars (carriages and wagons) can be coupled into longer trains. The operation is carried out by a railway company, providing transport between train stations or freight customer facil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |