|
Witige
Witege, Witige or Wittich ( ang, Wudga, Widia; Gothic language, Gotho- lat, Vidigoia) or Vidrik "Vidga" Verlandsson ( + ''Viðga'' or ''Videke'' + ''Verlandsson'', ''Vallandsson'', or ''Villandsson'') is a character in several Germanic heroic legends, poems about Dietrich von Bern, and later Scandinavian ballads.The article Vidrik Verlandsson' in ''Nordisk familjebok'' (1921). In German legends, he was one of the warriors of Dietrich von Bern, but betrayed him and took instead the side of his wicked Uncle Ermanaric, Ermenrich. In one of the Scandinavian ballads (The Types of the Scandinavian Medieval Ballad, TSB E 119), he won particular fame in his duel with Langben Rese/Risker (the giant Etgeir in the ''Þiðrekssaga''). During the Middle Ages, he became the son of Wayland the Smith and Böðvildr, and this entitled him to carry a hammer and tongs in his coat of arms. Later the origin of his name "Wayland's son" was forgotten, but the fame of the character prevailed. Durin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laurin (poem)
''Laurin'' or ''Der kleine Rosengarten'' (''The Small Rose Garden'') is an anonymous Middle High German poem about the legendary hero Dietrich von Bern, the counterpart of the historical Ostrogothic king Theodoric the Great in Germanic heroic legend. It is one of the so-called fantastical (''aventiurehaft'') Dietrich poems, so called because it more closely resembles a courtly romance than a heroic epic. It likely originates from the region of South Tyrol, possibly as early as 1230, though all manuscripts are later. The poem has five extant versions. In each, it concerns Dietrich's fight against the dwarf King Laurin, which takes place when Dietrich and Witege destroy Laurin's magical rose garden. The heroes are subsequently invited into Laurin's kingdom inside a mountain when it is discovered that Laurin has kidnapped and married the sister of Dietleib, one of Dietrich's heroes. Laurin betrays the heroes and imprisons them, but they are able to defeat him and save Dietleib' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rabenschlacht
''Die Rabenschlacht'' (The Battle of Ravenna) is an anonymous 13th-century Middle High German poem about the hero Dietrich von Bern, the counterpart of the historical Ostrogothic king Theodoric the Great in Germanic heroic legend. It is part of the so-called "historical" Dietrich material and is closely related to, and always transmitted together with, a second Dietrich poem, ''Dietrichs Flucht''. At one time, both poems were thought to have the same author, possibly a certain Heinrich der Vogler, but stylistic differences have led more recent scholarship to abandon this idea. ''Die Rabenschlacht'' concerns a failed attempt by the exiled Dietrich to reclaim his kingdom in Northern Italy from his treacherous uncle Ermenrich, with the help of an army provided by Etzel, king of the Huns. In the course of this attempt, Dietrich's younger brother and Etzel's young sons by his wife Helche are killed by Dietrich's former vassal Witege outside of Ravenna. Witege then flees into the sea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dietrich Von Bern
Dietrich von Bern is the name of a character in Germanic heroic legend who originated as a legendary version of the Ostrogothic king Theodoric the Great. The name "Dietrich", meaning "Ruler of the People", is a form of the Germanic name "Theodoric". In the legends, Dietrich is a king ruling from Verona (Bern) who was forced into exile with the Huns under Etzel by his evil uncle Ermenrich. The differences between the known life of Theodoric and the picture of Dietrich in the surviving legends are usually attributed to a long-standing oral tradition that continued into the sixteenth century. Most notably, Theodoric was an invader rather than the rightful king of Italy and was born shortly after the death of Attila and a hundred years after the death of the historical Gothic king Ermanaric. Differences between Dietrich and Theodoric were already noted in the Early Middle Ages and led to a long-standing criticism of the oral tradition as false. Legends about Theodoric may have exi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dietrichs Flucht
''Dietrichs Flucht'' (Dietrich's Flight) or ''Das Buch von Bern'' (The Book of Verona) is an anonymous 13th-century Middle High German poem about the legendary hero Dietrich von Bern, the legendary counterpart of the historical Ostrogothic king Theodoric the Great in Germanic heroic legend. It is part of the so-called "historical" Dietrich material and is closely related to, and always transmitted together with, a second Dietrich poem, the '' Rabenschlacht''. A Heinrich der Vogler is named as author in an excursus of the poem. Earlier scholarship considered him to be the author of ''Dietrichs Flucht'' and possibly also of the ''Rabenschlacht'', however more recent scholarship believes he is only author of this excursus. ''Dietrichs Flucht'' describes the rule of Dietrich's ancestors in his kingdom in northern Italy; his betrayal and exile by his wicked uncle Ermenrich, and his flight to the Huns, where he is warmly received by Etzel and his wife Helche. With Etzel's help, Dietr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
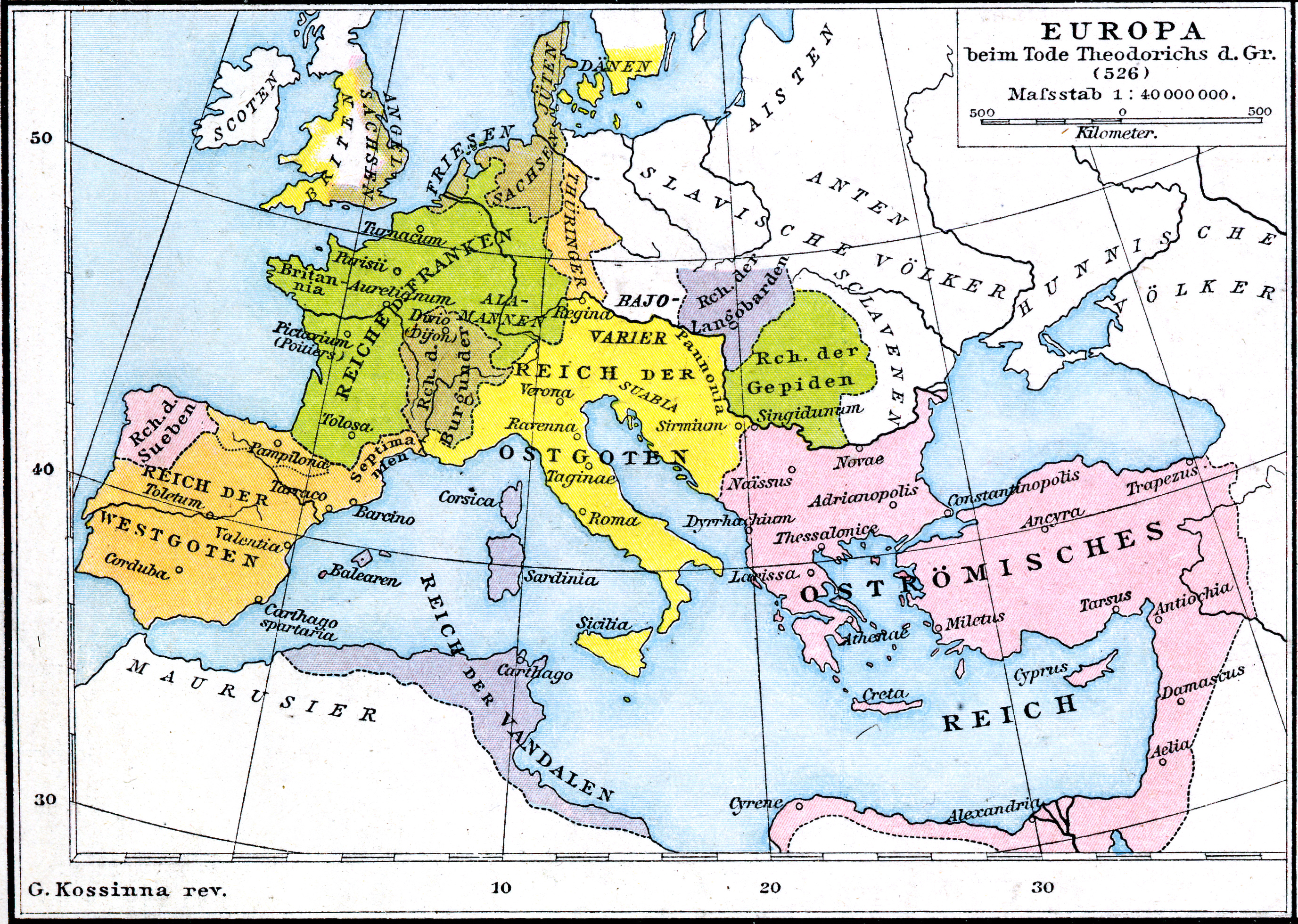
Theoderic The Great
Theodoric (or Theoderic) the Great (454 – 30 August 526), also called Theodoric the Amal ( got, , *Þiudareiks; Greek: , romanized: ; Latin: ), was king of the Ostrogoths (471–526), and ruler of the independent Ostrogothic Kingdom of Italy between 493 and 526, regent of the Visigoths (511–526), and a patrician of the Eastern Roman Empire. As ruler of the combined Gothic realms, Theodoric controlled an empire stretching from the Atlantic Ocean to the Adriatic Sea. Though Theodoric himself only used the title 'king' (''rex''), some scholars characterize him as a Western Roman Emperor in all but name, since he ruled large parts of the former Western Roman Empire, had received the former Western imperial regalia from Constantinople in 497, and was referred to by the title ''augustus'' by some of his subjects. As a young child of an Ostrogothic nobleman, Theodoric was taken as a hostage to Constantinople, where he spent his formative years and received an East Roman education ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Háma
Heime (German), Háma ( ang, Hāma), or Heimir (Old Norse) was a Germanic figure in Germanic heroic legend who often appears together with his friend Witige.The article Heimer' in '' Nordisk familjebok'' (1909). He appears in the Anglo-Saxon poems '' Beowulf'' and ''Widsith'', in the Scandinavian '' Þiðrekssaga'' and in German epics such as ''Alpharts Tod''.The entry ''Heime/Heimir'' in ''The Nibelungen Tradition: An Encyclopedia'' (2002) by Francis G. Gentry. p. 84 Origins Since Wudga is based on a Gothic hero named Vidigoia, it is possible that Hama has a similar origin, and the Anglo-Saxon poem ''Widsith'' talks of Hama and Wudga as Gothic warriors fighting against the Huns in the Vistula forests, where the Goths had an early settlement. Later, during the evolution of the legends, the two heroes were connected with both the Gothic kings Ermanaric and Theodoric the Great, and they were increasingly presented as traitors; it is as traitors that they appear in the '' Þiðrek ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wayland The Smith
In Germanic mythology, Wayland the Smith ( ang, Wēland; , ; Old Frisian: Wela(n)du; german: Wieland der Schmied; goh, Wiolant; ''Galans'' (''Galant'') in Old French; gem-x-proto, Wēlandaz, italic=no from ', lit. "crafting one") is a master blacksmith originating in Germanic heroic legend, described by Jessie Weston as "the weird and malicious craftsman, Weyland".Weston, J. (1929). 'Legendary Cycles of the Middle Age', in Tanner, J.R. (ed.), ''The Cambridge Medieval History'' Vol. VI, Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press, p. 841f. Wayland's story is most clearly told in the Old Norse sources '' Völundarkviða'' (a poem in the ''Poetic Edda'') and '' Þiðreks saga''. In them, Wayland is a smith who is enslaved by a king. Wayland takes revenge by killing the king's sons and then escapes by crafting a winged cloak and flying away. A number of other visual and textual sources clearly allude to similar stories, most prominently the Old English poem '' Deor'' and the Fran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walter Of Aquitaine
Walter or Walther of Aquitaine is a king of the Visigoths in Germanic heroic legend. Epic poetry Walter figures in several epic poems and narratives dealing with Germanic heroic legend in medieval languages: * ''Waldere'', a fragment of an Old English epic of which just over sixty lines survive. * ''Waltharius'', a 10th-century Latin epic written by the monk Ekkehard I of St Gall. * '' Chronicon Novaliciense'' ("Chronicle of Novalesa"), a Latin prose chronicle composed ''c.''1060, at Novalesa Abbey: Abbazia de Novalesa website Waltarius figures in chapters 7-13. * '''', a |
Nibelungenlied
The ( gmh, Der Nibelunge liet or ), translated as ''The Song of the Nibelungs'', is an epic poem written around 1200 in Middle High German. Its anonymous poet was likely from the region of Passau. The is based on an oral tradition of Germanic heroic legend that has some of its origin in historic events and individuals of the 5th and 6th centuries and that spread throughout almost all of Germanic-speaking Europe. Scandinavian parallels to the German poem are found especially in the heroic lays of the ''Poetic Edda'' and in the ''Völsunga saga''. The poem is split into two parts. In the first part, the prince Siegfried comes to Worms to acquire the hand of the Burgundian princess Kriemhild from her brother King Gunther. Gunther agrees to let Siegfried marry Kriemhild if Siegfried helps Gunther acquire the warrior-queen Brünhild as his wife. Siegfried does this and marries Kriemhild; however, Brünhild and Kriemhild become rivals, leading eventually to Siegfried's murder ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpharts Tod
''Alpharts Tod'' (The Death of Alphart) is an anonymous late medieval Middle High German poem in the poetic cycle of the hero Dietrich von Bern, the counterpart of the historical Ostrogothic king Theodoric the Great in Germanic heroic legend. It is part of the so-called "historical" Dietrich material. It may have written as early as between 1245 and 1300, but it is only transmitted in a single manuscript from around 1470 or 1480. The place of composition is unknown. ''Alpharts Tod'' concerns the young hero Alphart, one of Dietrich's heroes and the nephew of Hildebrand, at the start of a war between Dietrich and his uncle Ermenrich. Alphart insists on riding out alone, and while he is brave and a powerful warrior, he eventually encounters Witege and Heime, two traitors who have switched sides to Ermenrich. They kill him in a dishonorable fashion; Ermenrich, meanwhile, fails to defeat Dietrich. Summary The beginning of the epic is missing. Emperor Emenrich tells Heime to bring E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attila The Hun
Attila (, ; ), frequently called Attila the Hun, was the ruler of the Huns from 434 until his death in March 453. He was also the leader of a tribal empire consisting of Huns, Ostrogoths, Alans, and Bulgars, among others, in Central and Eastern Europe. During his reign, he was one of the most feared enemies of the Western and Eastern Roman Empires. He crossed the Danube twice and plundered the Balkans, but was unable to take Constantinople. His unsuccessful campaign in Persia was followed in 441 by an invasion of the Eastern Roman (Byzantine) Empire, the success of which emboldened Attila to invade the West. He also attempted to conquer Roman Gaul (modern France), crossing the Rhine in 451 and marching as far as Aurelianum (Orléans), before being stopped in the Battle of the Catalaunian Plains. He subsequently invaded Italy, devastating the northern provinces, but was unable to take Rome. He planned for further campaigns against the Romans, but died in 453. After At ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ravenna
Ravenna ( , , also ; rgn, Ravèna) is the capital city of the Province of Ravenna, in the Emilia-Romagna region of Northern Italy. It was the capital city of the Western Roman Empire from 408 until its collapse in 476. It then served as the capital of the Ostrogothic Kingdom until it was re-conquered in 540 by the Byzantine Empire. Afterwards, the city formed the centre of the Byzantine Exarchate of Ravenna until the last exarch was executed by the Lombards in 751. Although it is an inland city, Ravenna is connected to the Adriatic Sea by the Candiano Canal. It is known for its well-preserved late Roman and Byzantine architecture, with eight buildings comprising the UNESCO World Heritage Site "Early Christian Monuments of Ravenna". History The origin of the name ''Ravenna'' is unclear. Some have speculated that "Ravenna" is related to "Rasenna" (or "Rasna"), the term that the Etruscans used for themselves, but there is no agreement on this point. Ancient era The origins of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |









.png)