|
William Thomas Clifford Beckett
Brigadier-General William Thomas Clifford Beckett CBE DSO VD (1862 – 4 March 1956) was a British railway engineer in India and a British Army officer. Beckett was the eldest son of William Henry Beckett, a colonel in the Indian Army and his wife Sarah Philadelphia Beckett (née Walton). He was educated at Tonbridge School (1877–1880, as a day-boy) and Crystal Palace School of Engineering. His uncle, Frederick Thomas Granville Walton, was an acclaimed bridge engineer in India, who was in charge of the construction of the Dufferin Bridge over the Ganges at Benares between 1881 and 1887, and who served from 1900 as the engineer-in-chief for the construction of the iconic Havelock Bridge, a 2700-metre crossing of the Godavari River in Andhra Pradesh. In 1887, Beckett was appointed a district engineer with the Bengal-Nagpur Railway in India. He became an associate member of the Institution of Civil Engineers in 1889 and a member in 1895. He was promoted to superintendi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Thomas Clifford Beckett
Brigadier-General William Thomas Clifford Beckett CBE DSO VD (1862 – 4 March 1956) was a British railway engineer in India and a British Army officer. Beckett was the eldest son of William Henry Beckett, a colonel in the Indian Army and his wife Sarah Philadelphia Beckett (née Walton). He was educated at Tonbridge School (1877–1880, as a day-boy) and Crystal Palace School of Engineering. His uncle, Frederick Thomas Granville Walton, was an acclaimed bridge engineer in India, who was in charge of the construction of the Dufferin Bridge over the Ganges at Benares between 1881 and 1887, and who served from 1900 as the engineer-in-chief for the construction of the iconic Havelock Bridge, a 2700-metre crossing of the Godavari River in Andhra Pradesh. In 1887, Beckett was appointed a district engineer with the Bengal-Nagpur Railway in India. He became an associate member of the Institution of Civil Engineers in 1889 and a member in 1895. He was promoted to superintendi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andhra Pradesh
Andhra Pradesh (, abbr. AP) is a state in the south-eastern coastal region of India. It is the seventh-largest state by area covering an area of and tenth-most populous state with 49,386,799 inhabitants. It is bordered by Telangana to the north-west, Chhattisgarh to the north, Odisha to the north-east, Tamil Nadu to the south, Karnataka to the west and the Bay of Bengal to the east. It has the second longest coastline in India after Gujarat, of about . Andhra State was the first state to be formed on a linguistic basis in India on 1 October 1953. On 1 November 1956, Andhra State was merged with the Telugu-speaking areas (ten districts) of the Hyderabad State to form United Andhra Pradesh. ln 2014 these merged areas of Hyderabad State are bifurcated from United Andhra Pradesh to form new state Telangana . Present form of Andhra similar to Andhra state.but some mandalas like Bhadrachalam still with Telangana. Visakhapatnam, Guntur, Kurnool is People Capital of And ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pioneer (military)
A pioneer () is a soldier employed to perform engineering and construction tasks. The term is in principle similar to sapper or combat engineer. Pioneers were originally part of the artillery branch of European armies. Subsequently, they formed part of the engineering branch, the logistic branch, part of the infantry, or even comprised a branch in their own right. Historically, the primary role of pioneer units was to assist other arms in tasks such as the construction of field fortifications, military camps, bridges and roads. Prior to and during the First World War, pioneers were often engaged in the construction and repair of military railways. During World War II, pioneer units were used extensively by all major forces, both on the front line and in supporting roles. During the 20th century, British Commonwealth military forces came to distinguish between small units of "assault pioneers" belonging to infantry regiments and separate pioneer units (as in the former Royal P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loyal North Lancashire Regiment
The Loyal Regiment (North Lancashire) (until 1921 known as the Loyal North Lancashire Regiment) was a line infantry regiment of the British Army that was in existence from 1881 to 1970. In 1970, the regiment was amalgamated with the Lancashire Regiment to form the Queen's Lancashire Regiment which was, in 2006, amalgamated with the King's Own Royal Border Regiment and the King's Regiment (Liverpool and Manchester) to form the Duke of Lancaster Regiment (King's, Lancashire and Border). History Formation The Loyal North Lancashire Regiment was formed as part of the Childers Reforms of 1881 by the amalgamation of the 47th (Lancashire) Regiment of Foot, 81st Regiment of Foot (Loyal Lincoln Volunteers), 3rd Royal Lancashire Militia (The Duke of Lancaster's Own) and the 11th and 14th Lancashire Rifle Volunteer Corps. The Loyals were one of seven county regiments recruiting in Lancashire. The depot was at Preston, and the regimental district also included the towns of Bolton, Chorl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fighting occurring throughout Europe, the Middle East, Africa, the Pacific, and parts of Asia. An estimated 9 million soldiers were killed in combat, plus another 23 million wounded, while 5 million civilians died as a result of military action, hunger, and disease. Millions more died in genocides within the Ottoman Empire and in the 1918 influenza pandemic, which was exacerbated by the movement of combatants during the war. Prior to 1914, the European great powers were divided between the Triple Entente (comprising France, Russia, and Britain) and the Triple Alliance (containing Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Italy). Tensions in the Balkans came to a head on 28 June 1914, following the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lieutenant-colonel
Lieutenant colonel ( , ) is a rank of commissioned officers in the armies, most marine forces and some air forces of the world, above a major and below a colonel. Several police forces in the United States use the rank of lieutenant colonel. The rank of lieutenant colonel is often shortened to simply "colonel" in conversation and in unofficial correspondence. Sometimes, the term 'half-colonel' is used in casual conversation in the British Army. In the United States Air Force, the term 'light bird' or 'light bird colonel' (as opposed to a 'full bird colonel') is an acceptable casual reference to the rank but is never used directly towards the rank holder. A lieutenant colonel is typically in charge of a battalion or regiment in the army. The following articles deal with the rank of lieutenant colonel: * Lieutenant-colonel (Canada) * Lieutenant colonel (Eastern Europe) * Lieutenant colonel (Turkey) * Lieutenant colonel (Sri Lanka) * Lieutenant colonel (United Kingdom) * Lie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
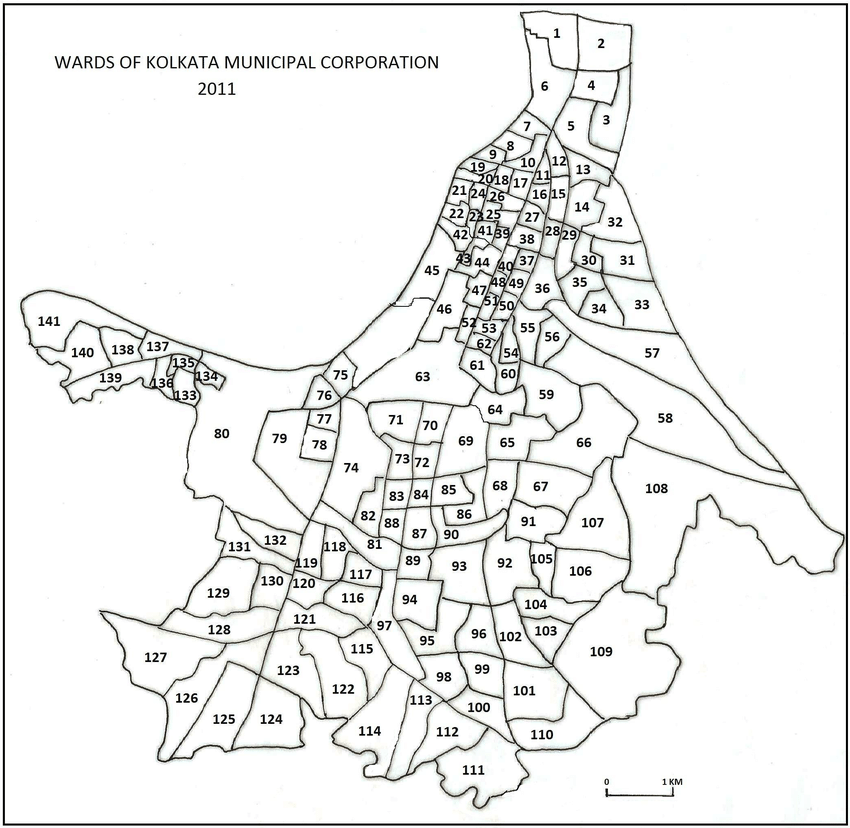
Calcutta Corporation
Kolkata Municipal Corporation (abbreviated KMC; also Calcutta Municipal Corporation) is the local government of the Indian city of Kolkata, the state capital of West Bengal. This civic administrative body administers an area of . Its motto, ''Purosri Bibardhan'', is inscribed on its emblem in Bengali script. Geography The Kolkata Municipal Corporation is located at in Kolkata, West Bengal. Department Structure Kolkata Municipal Corporation was established in 1876. Under the guidance of the first Minister of Local Self-Government in Bengal, Sir Surendranath Banerjee, the Calcutta Municipal Act of 1923 made provision for the enfranchisement of women and the election of a Mayor of Kolkata annually. Deshbandhu Chittaranjan Das was the first Mayor of Kolkata Municipal Corporation with Subhas Chandra Bose as his Chief Executive Officer. Later mayors include Deshapriya Jatindra Mohan Sengupta, Subhas Chandra Bose, Bidhan Chandra Roy, Nalini Ranjan Sarkar, Abul Kasem Fazlul Haqu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kolkata Port Trust
Port of Kolkata or Kolkata Port, officially known as Syama Prasad Mookerjee Port Trust (formerly Kolkata Port Trust), is the only riverine major port of India, located in the city of Kolkata, West Bengal, around from the sea. It is the oldest operating port in India and was constructed by the British East India Company. Kolkata is a freshwater port with no variation in salinity. The port has two distinct dock systems — Kolkata Dock at Kolkata and a deep water dock at Haldia Dock Complex, Haldia. In the 19th century, the Kolkata Port was the premier port in British India. After slavery was abolished in 1833, there was a high demand for labourers on sugar cane plantations in the British Empire. From 1838 to 1917, the British used this port to ship off over half a million Indians from all over India — mostly from the Hindi Belt (especially Bhojpur and Awadh) — and take them to places across the world, such as Mauritius, Fiji, South Africa, Trinidad and Tobago, Guyana, S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cuttack
Cuttack (, or officially Kataka ) in Odia is the former capital and the second largest city in the Indian state of Odisha. It is the headquarters of the Cuttack district. The name of the city is an anglicised form of ''Kataka'' which literally means ''The Fort'', a reference to the ancient Barabati Fort around which the city initially developed. Cuttack is known as the ''Millennium City'' as well as the ''Silver City'' due to its history of 1000 years and famous silver filigree works. The Orissa High Court is located there. It is the commercial capital of Odisha which hosts many trading and business houses in and around the city. Cuttack is famous for its Durga puja which is one of the most important festivals of Odisha. Cuttack is also the birthplace of Netaji Subhas Chandra Bose. The city is categorised as a Tier-II city as per the ranking system used by Government of India. The old and the most important part of the city is centred on a strip of land between the Kathajod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mahanadi
The Mahanadi is a major river in East Central India. It drains an area of around and has a total length of . Mahanadi is also known for the Hirakud Dam. The river flows through the states of Chhattisgarh and Odisha and finally merged with Bay of Bengal. Etymology The word Mahanadi is a compound of the Sanskrit words ''maha'' ("great") and ''nadi'' ("river"). In different era, this river was known by several names, such as: *Ancient era – Kanaknandini * Dvapara Yuga – Chitrotpala (Similar name in Matsya Purana) *Treta Yuga – Nilotpala (Similar name in vayu Purana) *Mahabharata era – Mahanad * Kali Yuga – Mahanadi or Mahashweta Course Source and Upper Course Like many other seasonal Indian rivers, the Mahanadi too is a combination of many mountain streams and thus its precise source is impossible to pinpoint. However its farthest headwaters lie from Pharsiya village in Nagri Sihawa above sea level about 11 km, in a dense patch of forest, south of Sihawa town in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telford Medal
The Telford Medal is a prize awarded by the British Institution of Civil Engineers (ICE) for a paper or series of papers. It was introduced in 1835 following a bequest made by Thomas Telford, the ICE's first president. It can be awarded in gold, silver or bronze; the Telford Gold Medal is the highest award the institution can bestow. History In 1834 Scottish civil engineer and the Institution of Civil Engineers' first president (1820-1834), Thomas Telford died, leaving in his will his library of technical works to the Institution of Civil Engineers, as well as a bequest of £2000; the interest from which was to be used to for the purpose of "Annual Premiums". The council of the institute decided to expend the premiums on both honorary and monetary rewards, the honorary awards being named Telford Medals, which would be awarded in gold, silver and bronze forms. Suitable candidates for the awards were submitters of drawings, models, diagrams or essays relating to civil engineering ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |