|
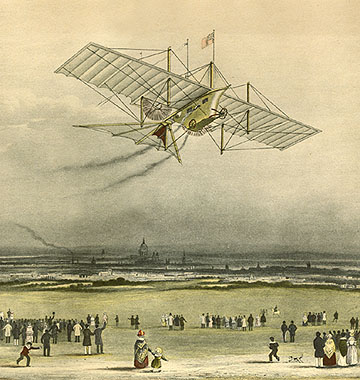
William Samuel Henson
William Samuel Henson (3 May 1812 – 22 March 1888) was a British-born pre- Wright brothers aviation pioneer, engineer and inventor. He is best known for his work on the aerial steam carriage alongside John Stringfellow. Biography Henson was born in Nottingham, England on 3 May 1812. Henson was involved in lace-making in Chard and he obtained a patent on improved lace-making machines in 1835. Henson is best known as an early pioneer in aviation, but patented many other inventions, some of which are in wide use today. In 1849 William Henson and his wife, Sarah, left England and moved to the United States, joining his father and settling in Newark, New Jersey. Henson never did any further aviation research while in the United States and worked as a machinist, civil engineer and inventor. He had 7 children, only 4 of whom lived to adulthood. Henson remained in the United States for the remainder of his life, except for a short period between 1864–1866 when he lived in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nottingham
Nottingham ( , East Midlands English, locally ) is a city status in the United Kingdom, city and Unitary authorities of England, unitary authority area in Nottinghamshire, East Midlands, England. It is located north-west of London, south-east of Sheffield and north-east of Birmingham. Nottingham has links to the legend of Robin Hood and to the lace-making, bicycle and Tobacco industry, tobacco industries. The city is also the county town of Nottinghamshire and the settlement was granted its city charter in 1897, as part of Queen Victoria's Diamond Jubilee celebrations. Nottingham is a tourist destination; in 2018, the city received the second-highest number of overnight visitors in the Midlands and the highest number in the East Midlands. In 2020, Nottingham had an estimated population of 330,000. The wider conurbation, which includes many of the city's suburbs, has a population of 768,638. It is the largest urban area in the East Midlands and the second-largest in the Midland ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Balloon-Hoax
"The Balloon-Hoax" is the title used in collections and anthologies of a newspaper article by American writer Edgar Allan Poe, first published in 1844 in ''The Sun'' newspaper in New York. Originally presented as a true story, it detailed European Monck Mason's trip across the Atlantic Ocean in only three days in a gas balloon. It was later revealed as a hoax and the story was retracted two days later. Overview The story now known as "The Balloon-Hoax" was first printed in '' The Sun'' newspaper in New York. The article provided a detailed and highly plausible account of a lighter-than-air balloon trip by European balloonist Monck Mason across the Atlantic Ocean taking 75 hours, along with a diagram and specifications of the craft. Poe may have been inspired, at least in part, by a prior journalistic hoax known as the " Great Moon Hoax", published in the same newspaper in 1835. One of the suspected writers of that hoax, Richard Adams Locke, was Poe's editor at the time "The B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Of Commons Of The United Kingdom
The House of Commons is the lower house of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Like the upper house, the House of Lords, it meets in the Palace of Westminster in London, England. The House of Commons is an elected body consisting of 650 members known as members of Parliament (MPs). MPs are elected to represent constituencies by the first-past-the-post system and hold their seats until Parliament is dissolved. The House of Commons of England started to evolve in the 13th and 14th centuries. In 1707 it became the House of Commons of Great Britain after the political union with Scotland, and from 1800 it also became the House of Commons for Ireland after the political union of Great Britain and Ireland. In 1922, the body became the House of Commons of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland after the independence of the Irish Free State. Under the Parliament Acts 1911 and 1949, the Lords' power to reject legislation was reduced to a delaying power. The g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Cayley
Sir George Cayley, 6th Baronet (27 December 1773 – 15 December 1857) was an English engineer, inventor, and aviator. He is one of the most important people in the history of aeronautics. Many consider him to be the first true scientific aerial investigator and the first person to understand the underlying principles and forces of flight and the first man to create the wire wheel. * * * In 1799, he set forth the concept of the modern aeroplane as a fixed-wing flying machine with separate systems for lift, propulsion, and control. He was a pioneer of aeronautical engineering and is sometimes referred to as "the father of aviation." He identified the four forces which act on a heavier-than-air flying vehicle: weight, lift, drag and thrust. Modern aeroplane design is based on those discoveries and on the importance of cambered wings, also proposed by Cayley. He constructed the first flying model aeroplane and also diagrammed the elements of vertical flight. He also designed the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glider (aircraft)
A glider is a fixed-wing aircraft that is supported in flight by the dynamic reaction of the air against its lifting surfaces, and whose free flight does not depend on an engine. Most gliders do not have an engine, although motor-gliders have small engines for extending their flight when necessary by sustaining the altitude (normally a sailplane relies on rising air to maintain altitude) with some being powerful enough to take off by self-launch. There are a wide variety of types differing in the construction of their wings, aerodynamic efficiency, location of the pilot, controls and intended purpose. Most exploit meteorological phenomena to maintain or gain height. Gliders are principally used for the air sports of gliding, hang gliding and paragliding. However some spacecraft have been designed to descend as gliders and in the past military gliders have been used in warfare. Some simple and familiar types of glider are toys such as paper planes and balsa wood gliders. Etym ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Propellers
A propeller (colloquially often called a screw if on a ship or an airscrew if on an aircraft) is a device with a rotating hub and radiating blades that are set at a pitch to form a helical spiral which, when rotated, exerts linear thrust upon a working fluid such as water or air. Propellers are used to pump fluid through a pipe or duct, or to create thrust to propel a boat through water or an aircraft through air. The blades are specially shaped so that their rotational motion through the fluid causes a pressure difference between the two surfaces of the blade by Bernoulli's principle which exerts force on the fluid. Most marine propellers are screw propellers with helical blades rotating on a propeller shaft with an approximately horizontal axis. History Early developments The principle employed in using a screw propeller is derived from sculling. In sculling, a single blade is moved through an arc, from side to side taking care to keep presenting the blade to the water at t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contra-rotating
Contra-rotating, also referred to as coaxial contra-rotating, is a technique whereby parts of a mechanism rotate in opposite directions about a common axis, usually to minimise the effect of torque. Examples include some aircraft propellers, resulting in the maximum power of a single piston or turboprop engine to drive two propellers in opposite rotation. Contra-rotating propellers are also common in some marine transmission systems, in particular for large speed boats with planing hulls. Two propellers are arranged one behind the other, and power is transferred from the engine via planetary gear transmission. The configuration can also be used in helicopter designs termed coaxial rotors, where similar issues and principles of torque apply. Contra-rotating propellers should not be confused with counter-rotating propellers, a term which describes non-coaxial propellers on separate shafts; one turning clockwise and the other counter-clockwise. Tandem-rotor helicopters such as th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Flight Of The Phoenix (1965 Film)
''The Flight of the Phoenix'' is a 1965 American survival drama film produced and directed by Robert Aldrich, based on the 1964 novel of the same name by English author Elleston Trevor. The story follows a small group of men struggling to survive their aircraft's emergency landing in the Sahara. It stars an ensemble cast, with James Stewart, Richard Attenborough, Peter Finch, Hardy Kruger, Ernest Borgnine, Ian Bannen, Ronald Fraser, Christian Marquand, Dan Duryea and George Kennedy. Though the film was not a financial success, it was well-received by critics, who praised Aldrich’s direction and the performances of its cast. It was nominated for two Academy Awards: Best Supporting Actor for Bannen and Best Editing for Michael Luciano. Hardy Krüger was nominated for a Golden Globe Award for Best Supporting Actor, and Aldrich was nominated for Best Motion Picture – Drama. ''The Flight of the Phoenix'' was remade in 2004, titled as ''Flight of the Phoenix''. Plot Frank ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WikiProject Missing Encyclopedic Articles/Antarctica/H3
A WikiProject, or Wikiproject, is a Wikimedia movement affinity group for contributors with shared goals. WikiProjects are prevalent within the largest wiki, Wikipedia, and exist to varying degrees within sister projects Wikipedia is a free, web-based, collaborative and multilingual encyclopedia website and project supported by the non-profit Wikimedia Foundation. It has more than 48 million articles ( in English) written collaboratively by volunteers around t ... such as Wiktionary, Wikiquote, Wikidata, and Wikisource. They also exist in different languages, and translation of articles is a form of their collaboration. During the COVID-19 pandemic, CBS News noted the role of Wikipedia's WikiProject Medicine in maintaining the accuracy of articles related to the disease. Another WikiProject that has drawn attention is WikiProject Women Scientists, which was profiled by ''Smithsonian Magazine, Smithsonian'' for its efforts to improve coverage of women scientists which the profi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest continent, being about 40% larger than Europe, and has an area of . Most of Antarctica is covered by the Antarctic ice sheet, with an average thickness of . Antarctica is, on average, the coldest, driest, and windiest of the continents, and it has the highest average elevation. It is mainly a polar desert, with annual precipitation of over along the coast and far less inland. About 70% of the world's freshwater reserves are frozen in Antarctica, which, if melted, would raise global sea levels by almost . Antarctica holds the record for the lowest measured temperature on Earth, . The coastal regions can reach temperatures over in summer. Native species of animals include mites, nematodes, penguins, seals and tardigrades. Where vegetation o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glacier
A glacier (; ) is a persistent body of dense ice that is constantly moving under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its Ablation#Glaciology, ablation over many years, often Century, centuries. It acquires distinguishing features, such as Crevasse, crevasses and Serac, seracs, as it slowly flows and deforms under stresses induced by its weight. As it moves, it abrades rock and debris from its substrate to create landforms such as cirques, moraines, or fjords. Although a glacier may flow into a body of water, it forms only on land and is distinct from the much thinner sea ice and lake ice that form on the surface of bodies of water. On Earth, 99% of glacial ice is contained within vast ice sheets (also known as "continental glaciers") in the polar regions, but glaciers may be found in mountain ranges on every continent other than the Australian mainland, including Oceania's high-latitude oceanic island countries such as New Zealand. Between lati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
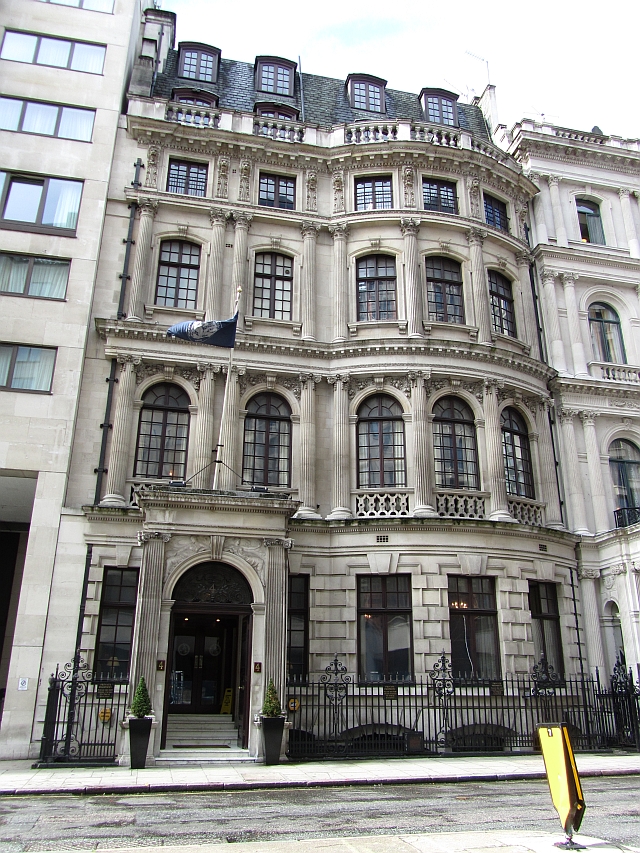
Royal Aeronautical Society
The Royal Aeronautical Society, also known as the RAeS, is a British multi-disciplinary professional institution dedicated to the global aerospace community. Founded in 1866, it is the oldest aeronautical society in the world. Members, Fellows, and Companions of the society can use the post-nominal letters MRAeS, FRAeS, or CRAeS, respectively. Function The objectives of The Royal Aeronautical Society include: to support and maintain high professional standards in aerospace disciplines; to provide a unique source of specialist information and a local forum for the exchange of ideas; and to exert influence in the interests of aerospace in the public and industrial arenas, including universities. The Royal Aeronautical Society is a worldwide society with an international network of 67 branches. Many practitioners of aerospace disciplines use the Society's designatory post-nominals such aFRAeS CRAeS, MRAeS, AMRAeS, and ARAeS (incorporating the former graduate grade, GradRAeS). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |