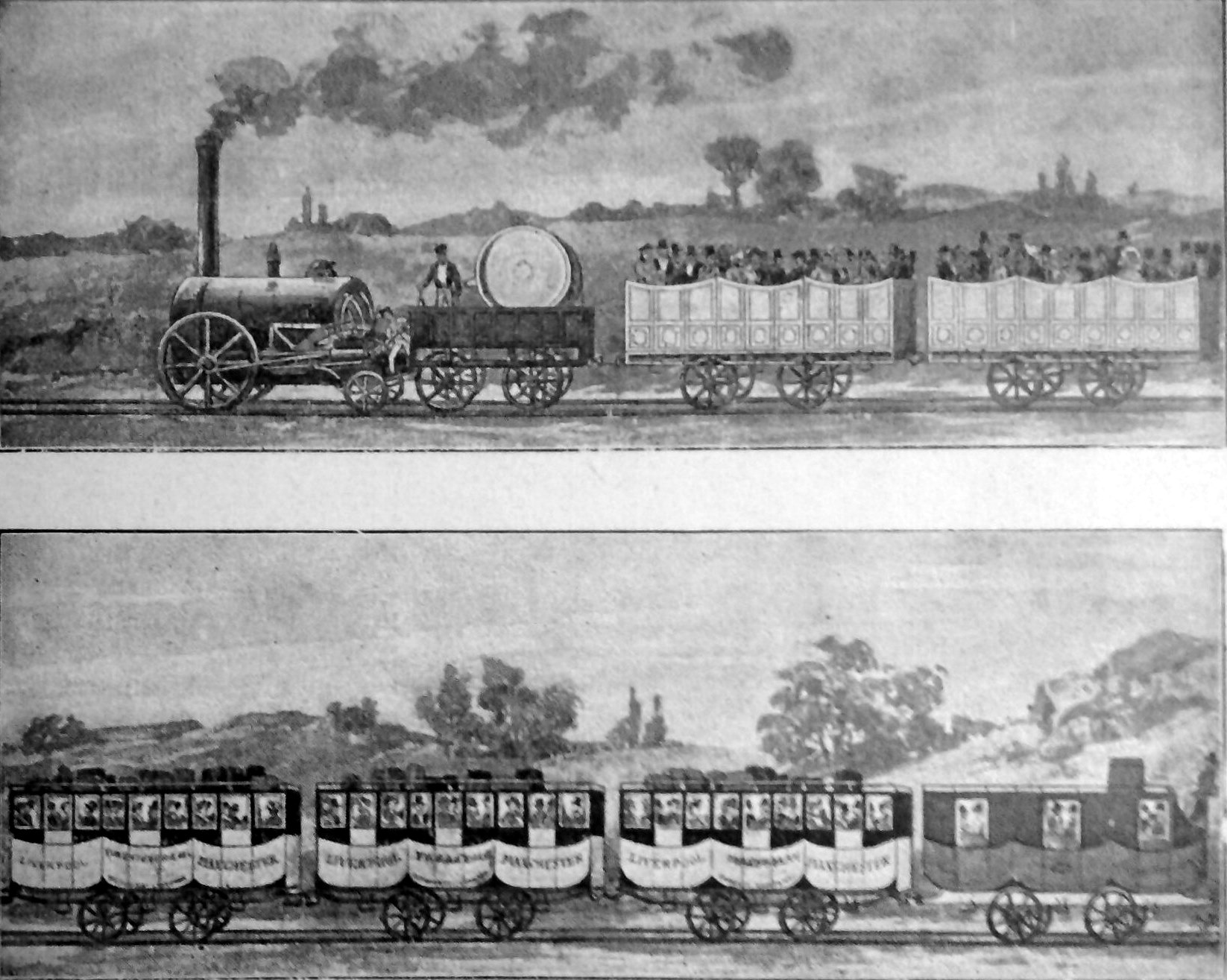|
William Mackenzie (contractor)
William Mackenzie (20 March 1794 – 29 October 1851) was an Anglo-Scottish civil engineer and civil engineering contractor who was one of the leading European contractors in the 1840s.Chrimes, Mike 'Mackenzie, William (1794-1851)', ''Oxford Dictionary of National Biography'', Oxford University Press, 2004; online edn, October 200 accessed 24 November 2007. Early life Mackenzie was born near Nelson, Lancashire, England, the eldest of the 11 children of Alexander Mackenzie, a Scottish contractor, and Mary née Roberts. He started his career as an apprentice weaver but changed to civil engineering, becoming a pupil of a lock carpenter on the Leeds and Liverpool Canal in 1811. He continued his training on a dry dock at Troon harbour, on Craigellachie Bridge and as an agent on the Edinburgh and Glasgow Union Canal. Career In 1822 he became an agent for the completion of the Gloucester and Berkeley Canal. Soon after this he was appointed resident engineer for Thomas Telford's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Henry Illidge
Thomas Henry Illidge (26 September 1799 – 13 May 1851) was an English portrait painter. Life and work Illidge was born in Birmingham on 26 September 1799, belonging to a family resident near Nantwich, Cheshire. Illidge's father moved to Manchester, and, dying young, left a young family ill-provided for. Illidge was educated in Manchester, and taught drawing. He was subsequently the pupil in succession of Mather Brown and William Bradley. He initially tried landscape painting, but married early, and, as a result, took up portrait-painting as a more profitable endeavour. Illidge was successful as a portrait-painter in the great manufacturing towns of Lancashire, painting many of the civic or financial celebrities of the locality. He was a frequent exhibitor at the Liverpool Academy from 1827. In 1842 he came to London, and was from that time was a constant exhibitor at the Royal Academy. In 1844, on the death of Henry Perronet Briggs, R.A., Illidge purchased the lease of the d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Telford
Thomas Telford FRS, FRSE, (9 August 1757 – 2 September 1834) was a Scottish civil engineer. After establishing himself as an engineer of road and canal projects in Shropshire, he designed numerous infrastructure projects in his native Scotland, as well as harbours and tunnels. Such was his reputation as a prolific designer of highways and related bridges, he was dubbed ''The Colossus of Roads'' (a pun on the Colossus of Rhodes), and, reflecting his command of all types of civil engineering in the early 19th century, he was elected as the first President of the Institution of Civil Engineers, a post he held for 14 years until his death. The town of Telford in Shropshire was named after him. Early career Telford was born on 9 August 1757, at Glendinning, a hill farm east of Eskdalemuir Kirk, in the rural parish of Westerkirk, in Eskdale, Dumfriesshire. His father John Telford, a shepherd, died soon after Thomas was born. Thomas was raised in poverty by his mother Janet Jac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rouen
Rouen (, ; or ) is a city on the River Seine in northern France. It is the prefecture of the Regions of France, region of Normandy (administrative region), Normandy and the Departments of France, department of Seine-Maritime. Formerly one of the largest and most prosperous cities of Middle Ages, medieval Europe, the population of the metropolitan area (french: functional area (France), aire d'attraction) is 702,945 (2018). People from Rouen are known as ''Rouennais''. Rouen was the seat of the Exchequer of Normandy during the Middle Ages. It was one of the capitals of the Anglo-Normans, Anglo-Norman dynasties, which ruled both England and large parts of modern France from the 11th to the 15th centuries. From the 13th century onwards, the city experienced a remarkable economic boom, thanks in particular to the development of textile factories and river trade. Claimed by both the French and the English during the Hundred Years' War, it was on its soil that Joan of Arc was tried ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. Since the 17th century, Paris has been one of the world's major centres of finance, diplomacy, commerce, fashion, gastronomy, and science. For its leading role in the arts and sciences, as well as its very early system of street lighting, in the 19th century it became known as "the City of Light". Like London, prior to the Second World War, it was also sometimes called the capital of the world. The City of Paris is the centre of the Île-de-France region, or Paris Region, with an estimated population of 12,262,544 in 2019, or about 19% of the population of France, making the region France's primate city. The Paris Region had a GDP of €739 billion ($743 billion) in 2019, which is the highest in Europe. According to the Economist Intelli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Locke
Joseph Locke FRSA (9 August 1805 – 18 September 1860) was a notable English civil engineer of the nineteenth century, particularly associated with railway projects. Locke ranked alongside Robert Stephenson and Isambard Kingdom Brunel as one of the major pioneers of railway development. Early life and career Locke was born in Attercliffe, Sheffield in Yorkshire, moving to nearby Barnsley when he was five. By the age of 17, Joseph had already served an apprenticeship under William Stobart at Pelaw, on the south bank of the Tyne, and under his own father, William. He was an experienced mining engineer, able to survey, sink shafts, to construct railways, tunnels and stationary engines. Joseph's father had been a manager at Wallbottle colliery on Tyneside when George Stephenson was a fireman there. In 1823, when Joseph was 17, Stephenson was involved with planning the Stockton and Darlington Railway. He and his son Robert Stephenson visited William Locke and his son at Barnsley ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Shannon
The River Shannon ( ga, Abhainn na Sionainne, ', '), at in length, is the longest river in the British Isles. It drains the Shannon River Basin, which has an area of , – approximately one fifth of the area of the island of Ireland. The Shannon divides the west of Ireland (principally the province of Connacht) from the east and south (Leinster and most of Munster). (County Clare, being west of the Shannon but part of the province of Munster, is the major exception.) The river represents a major physical barrier between east and west, with fewer than thirty-five crossing points between Limerick city in the south and the village of Dowra in the north. The river takes its name after ''Sionna'', a Celtic goddess. Known as an important waterway since antiquity, the Shannon first appeared in maps by the Graeco-Egyptian geographer Ptolemy ( 100 – 170 AD). The river flows generally southwards from the Shannon Pot in County Cavan before turning west and emptying into the A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glasgow, Paisley And Greenock Railway
The Glasgow, Paisley and Greenock Railway (GP&GR) was an early Scottish railway, opened in 1841, providing train services between Greenock and Glasgow. At the time the River Clyde was not accessible to sea-going ships, and the intention was to compete with river boats that brought goods to and from the city. In fact passenger traffic proved surprisingly buoyant, and connecting steamer services to island resorts in the Firth of Clyde provided a very great source of business. The GP&GR merged with the larger Caledonian Railway in 1851. The Greenock station was not alongside the steamer berths and as the trade developed, this became a significant disadvantage. The independent Greenock and Wemyss Bay Railway built a branch line to a pier at Wemyss Bay, giving much closer access to Rothesay, and in 1889 the Greenock line itself was extended to Gourock. The work involved the building of Newton Street Tunnel, the longest railway tunnel in Scotland. The line between Glasgow and Greenoc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Midland Counties Railway
The Midland Counties' Railway (MCR) was a railway company in the United Kingdom which existed between 1839 and 1844, connecting Nottingham, Leicester and Derby with Rugby and thence, via the London and Birmingham Railway, to London. The MCR system connected with the North Midland Railway and the Birmingham and Derby Junction Railway in Derby at what become known as the Tri Junct Station. The three later merged to become the Midland Railway. Origin The East Midlands had for some years been at centre of plans to link the major cities throughout the country. However, the MCR came about as a result of competition to supply coal to Leicester, a town which was rapidly industrialising and was a valuable market for coal. The competition was between the Coalville area of Leicestershire, and the Erewash Valley area of Nottinghamshire. For many years, the Nottinghamshire coal miners had enjoyed a competitive advantage over their counterparts in Leicestershire, but in 1832 the latt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Union Railway
The North Union Railway was an early British railway company, operating in Lancashire. It was created in 1834, continuing independently until 1889. Formation The North Union Railway (NUR) was created by an Act of Parliament on 22 May 1834 which authorised its founding as the first-ever railway amalgamation. The two companies amalgamated were the Wigan Branch Railway and the Preston and Wigan Railway. The Preston and Wigan Railway had the Act authorising it to construct the railway in place but was underfunded and sought the amalgamation to help gets its railway under way. The first chairman of the company was Sir Thomas Dalrymple Hesketh, Bart. He had previously held the same position at the Preston and Wigan Railway. Construction When it was created, the North Union Railway consisted of the line constructed by the Wigan Branch Railway (WBR) but little else. All its locomotives and rolling stock were supplied by the Liverpool and Manchester Railway. Within a month the railway ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liverpool Lime Street Railway Station
Liverpool Lime Street is a terminus railway station and the main station serving the city centre of Liverpool. Opened in August 1836, it is the oldest still-operating grand terminus mainline station in the world. A branch of the West Coast Main Line from London Euston terminates at the station, as does the original Liverpool and Manchester Railway. Journeys from Lime Street cover a wide range of destinations across England, Scotland and Wales. Having realised that their existing Crown Street railway station was too far away from the city centre, the Liverpool and Manchester Railway commenced construction of the more central Lime Street station in October 1833. Designed by John Cunningham, Arthur Holme and John Foster Jr, it was officially opened in August 1836. Proving to be very popular with train commuters, expansion of the station had become necessary within six years of its opening. The first expansion, which was collaboratively produced by Joseph Locke, Richard Turn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edge Hill Railway Station
Edge Hill railway station is a railway station that serves the district of Edge Hill, Liverpool, England and is one of the oldest railway stations in the world There have been two stations of that name. The first stood a short distance south-west of the present station and its remains are still visible, although the site is not open to the public. Edge Hill is the first station after departure from . The station, and all trains serving it, are operated by Northern Trains. Avanti West Coast, East Midlands Railway, TransPennine Express and West Midlands Trains services pass through the station, although, they are non stop. Early history The first station opened on 15 September 1830 as part of the Liverpool and Manchester Railway. It was located in a wide by long, deep sandstone cutting, with three tunnels at the west end. The largest bore, in the centre, was the Wapping Tunnel, a long downwards incline leading to Wapping Dock and the world's first tunnel to be bored un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liverpool And Manchester Railway
The Liverpool and Manchester Railway (L&MR) was the first inter-city railway in the world. It opened on 15 September 1830 between the Lancashire towns of Liverpool and Manchester in England. It was also the first railway to rely exclusively on locomotives driven by steam power, with no horse-drawn traffic permitted at any time; the first to be entirely double track throughout its length; the first to have a true signalling system; the first to be fully timetabled; and the first to carry mail. Trains were hauled by company steam locomotives between the two towns, though private wagons and carriages were allowed. Cable haulage of freight trains was down the steeply-graded Wapping Tunnel to Liverpool Docks from Edge Hill junction. The railway was primarily built to provide faster transport of raw materials, finished goods and passengers between the Port of Liverpool and the cotton mills and factories of Manchester and surrounding towns. Designed and built by George Stephen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)


.jpg)