|
William II De Warenne
William de Warenne, 2nd Earl of Surrey (died 11 May 1138) was the son of William de Warenne, 1st Earl of Surrey and his first wife Gundred. He was more often referred to as ''Earl Warenne'' or ''Earl of Warenne'' than as Earl of Surrey.G. E. Cokayne, ''The Complete Peerage'', Vol. XII/1 (The St. Catherine Press, London, 1953) p. 495 Life His father, the 1st Earl, was one of the Conqueror's most trusted and most rewarded barons who, at his death in 1088, was the 3rd or 4th richest magnate in England.C. Warren Hollister, 'The Taming of a Turbulent Earl: Henry I and William of Warenne', ''Historical Reflections'', Vol. 3 (1976), p. 87 In 1088 William II inherited his father's lands in England and his Norman estates including the castles of Mortemer and Bellencombre in Haute-Normandy. But William II was not as disposed to serve the king as his father was. In January 1091, William assisted Hugh de Grandmesnil (died 1094) in his defence of Courcy against the forces of Robert de Be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
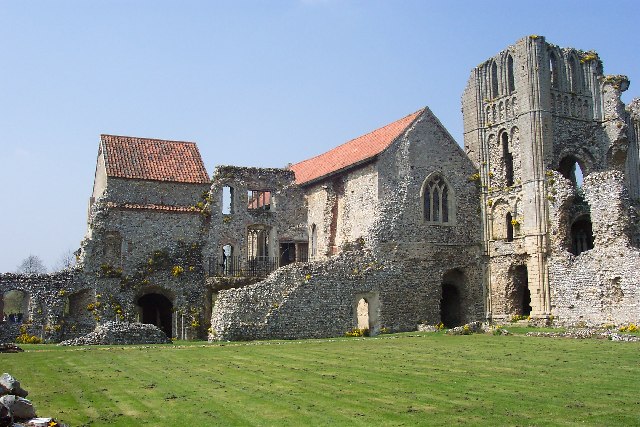
Lewes Priory
Lewes Priory is a part-demolished medieval Cluniac priory in Lewes, East Sussex in the United Kingdom. The ruins have been designated a Grade I listed building. History The Priory of St Pancras was the first Cluniac house in England and had one of the largest monastic churches in the country. It was set within an extensive walled and gated precinct laid out in a commanding location fronting the tidal shore-line at the head of the Ouse valley to the south of Lewes in the County of Sussex. The Priory had daughter houses, including Castle Acre Priory in Norfolk, and was endowed with churches and extensive holdings throughout England. In Lewes it had hospitiums dedicated to St James and to St Nicholas. In 1264, during the Battle of Lewes, King Henry III retreated with his forces to the Priory precinct which then came under attack from those of Simon de Montfort after his victory over Henry's army in battle. Henry was forced, in the Mise of Lewes, to accept the Council that was t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edith Of Scotland
Matilda of Scotland (originally christened Edith, 1080 – 1 May 1118), also known as Good Queen Maud, or Matilda of Blessed Memory, was Queen of England and Duchess of Normandy as the first wife of King Henry I. She acted as regent of England on several occasions during Henry's absences: in 1104, 1107, 1108, and 1111. Daughter of King Malcolm III of Scotland and the Anglo-Saxon princess Margaret of Wessex, Matilda was educated at a convent in southern England, where her aunt Christina was abbess, and forced her to wear a veil. In 1093, Matilda was engaged to an English nobleman until her father and her brother Edward were killed in the Battle of Alnwick in 1093. Her uncle Donald III seized the throne of Scotland, triggering a messy succession conflict. England opposed King Donald and supported first her half-brother Duncan II as king of Scotland, and after his death, her brother Edgar, who assumed the throne in 1097. Henry I succeeded his brother William Rufus as king of En ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
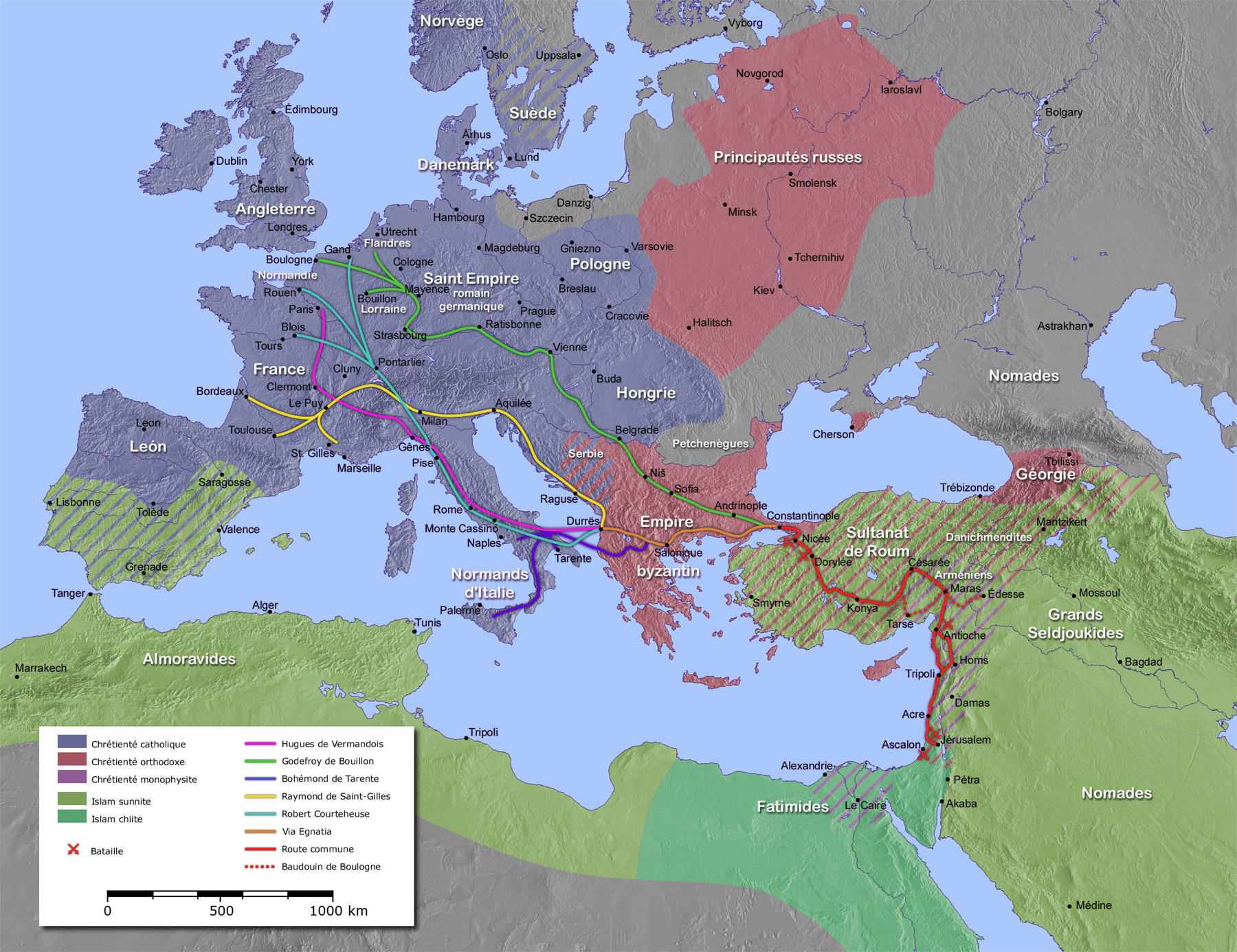
Hugh I, Count Of Vermandois
Hugh, Count of Vermandois (1057 – October 18, 1101), called the Great (french: Hugues le Grand, la, Hugo Magnus) was the first count of Vermandois from the House of Capet. He is known primarily for being one of the leaders of First Crusade. His nickname ''Magnus'' (greater or elder) is probably a bad translation into medieval Latin of an Old French nickname, ''le Maisné'', meaning "the younger", referring to Hugh as younger brother of King Philip I of France. Early years Hugh was a younger son of King Henry I of France and Anne of Kiev and younger brother of Philip I. He became the first Capetian count of Vermandois after his mentally deficient brother-in-law, Odo, was disinherited. In 1085, Hugh helped William the Conqueror repel a Danish invasion of England. First Crusade In early 1096, Hugh and Philip began discussing the First Crusade after news of the Council of Clermont reached them in Paris. Although Philip could not participate, as he had been excommunicated, Hugh was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chapter House
A chapter house or chapterhouse is a building or room that is part of a cathedral, monastery or collegiate church in which meetings are held. When attached to a cathedral, the cathedral chapter meets there. In monasteries, the whole community often met there daily for readings and to hear the abbot or senior monks talk. When attached to a collegiate church, the dean, prebendaries and canons of the college meet there. The rooms may also be used for other meetings of various sorts; in medieval times monarchs on tour in their territory would often take them over for their meetings and audiences. Synods, ecclesiastical courts and similar meetings often took place in chapter houses. Design When part of a monastery, the chapter house is generally located on the eastern wing of the cloister, which is next to the church. Since many cathedrals in England were originally monastic foundations, this is a common arrangement there also. Elsewhere it may be a separate building. The chap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Longueville Priory
Longueville may refer to: Places France *Longueville, Calvados, in the Calvados department *Longueville, Lot-et-Garonne, in the Lot-et-Garonne department *Longueville, Manche, in the Manche department *Longueville, Pas-de-Calais, in the Pas-de-Calais department *Longueville, Seine-et-Marne, in the Seine-et-Marne department *Longueville-sur-Aube, in the Aube department *Longueville-sur-Scie, in the Seine-Maritime department Elsewhere * Longueville, Jersey *Longueville, New South Wales, suburb of Sydney, Australia Other *County of Longueville *Duke of Longueville *Pichon Longueville, archaic Bordeaux wine estate, presently: **Château Pichon Longueville Baron, or Pichon Baron **Château Pichon Longueville Comtesse de Lalande, or Pichon Comtesse, or Pichon Lalande * Longueville baronets, an extinct baronetcy, originally of Nova Scotia and then of Great Britain *Longueville or Rongubiru, fictional secretary in ''The Familiar of Zero is a Japanese fantasy light nove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Bremule
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force commitment. An engagement with only limited commitment between the forces and without decisive results is sometimes called a skirmish. The word "battle" can also be used infrequently to refer to an entire operational campaign, although this usage greatly diverges from its conventional or customary meaning. Generally, the word "battle" is used for such campaigns if referring to a protracted combat encounter in which either one or both of the combatants had the same methods, resources, and strategic objectives throughout the encounter. Some prominent examples of this would be the Battle of the Atlantic, Battle of Britain, and Battle of Stalingrad, all in World War II. Wars and military campaigns are guided by military strategy, wherea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helias Of Saint-Saens
Helias of Saint Saens (?–1128),Stephanie L. Mooers, "Backers and Stabbers": Problems of Loyalty in Robert Curthose's Entourage, ''Journal of British Studies'', Vol. 21, No. 1, (Autumn, 1981). p. 17 Count of Arques was a Norman magnate of the eleventh and twelfth century, a loyal supporter of Robert Curthose and protector of his son William Clito. His support of the latter eventually brought him into conflict with Henry I of England, ending in his willing exile from Normandy.Stephanie L. Mooers, "Backers and Stabbers": Problems of Loyalty in Robert Curthose's Entourage, ''Journal of British Studies'', Vol. 21, No. 1, (Autumn, 1981). p. 4 His Life Helias was an important baron in Upper Normandy who held the fortress-stronghold of Saint-Saens.Frank Barlow, ''William Rufus'', (Methuen, London, 1983), p. 275 In 1090 he supported William Rufus against his brother Duke Robert of Normandy and led the attack on Rouen.William Farrer, Charles Travis Clay, ''Early Yorkshire Charters'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Clito
William Clito (25 October 110228 July 1128) was a member of the House of Normandy who ruled the County of Flanders from 1127 until his death and unsuccessfully claimed the Duchy of Normandy. As the son of Robert Curthose, the eldest son of William the Conqueror, William Clito was seen as a candidate to succeed his uncle King Henry I of England. Henry viewed him as a rival, however, and William allied himself with King Louis VI of France. Louis installed him as the new count of Flanders upon the assassination of Charles the Good, but the Flemings soon revolted and William died in the struggle against another claimant to Flanders, Thierry of Alsace. Youth William was the son of Duke Robert Curthose of Normandy and Sibylla of Conversano. His father was the first son of King William the Conqueror of England. His nickname ''Clito'' was a Medieval Latin term equivalent to the Anglo-Saxon ''" Aetheling"'' and its Latinized form ''"Adelinus"'' (used to refer to his first cousin, William ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Tinchebray
The Battle of Tinchebray (alternative spellings: Tinchebrai or Tenchebrai) took place on 28 September 1106, in Tinchebray (today in the Orne ''département'' of France), Normandy, between an invading force led by King Henry I of England, and the Norman army of his elder brother Robert Curthose, the Duke of Normandy.C. Warren Hollister, ''Henry I'', ed. Amanda Clark Frost (New Haven; London, Yale University Press, 2003), p. 199 Henry's knights won a decisive victory: they captured Robert, and Henry imprisoned him in England (in Devizes Castle) and then in Wales until Robert's death (in Cardiff Castle) in 1134. Prelude Henry invaded Normandy in 1105 in the course of an ongoing dynastic dispute with his brother. He took Bayeux and Caen, but broke off his campaign because of political problems arising from an investiture controversy.David Crouch, ''The Normans; The History of a Dynasty'' (London. New York: Hambledon Continuum, 2007), pp. 176-77 With these settled, he returned to Nor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Journal
''The Archaeological Journal'' is a peer-reviewed academic journal for archaeological and architectural reports and articles. It was established in 1844 by the British Archaeological Association as a quarterly journal, but was taken over by the British Archaeological Institute (now known as the Royal Archaeological Institute) in 1845, and the institute has remained its publisher ever since. The journal has been published annually since 1927. History The ''Archaeological Journal'' was established as a quarterly journal of the British Archaeological Association in 1844. When conflicts within that association led to the foundation of the rival British Archaeological Institute (now the Royal Archaeological Institute) in 1845, the Institute retained the journal, the Association instead publishing the ''Journal of the British Archaeological Association''. Publication was quarterly (sometimes falling to twice or three times a year) until 1926. In 1927 the journal became an annual publ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anselm Of Canterbury
Anselm of Canterbury, OSB (; 1033/4–1109), also called ( it, Anselmo d'Aosta, link=no) after his birthplace and (french: Anselme du Bec, link=no) after his monastery, was an Italian Benedictine monk, abbot, philosopher and theologian of the Catholic Church, who held the office of Archbishop of Canterbury from 1093 to 1109. After his death, he was canonized as a saint; his feast day is 21 April. As archbishop, he defended the church's interests in England amid the Investiture Controversy. For his resistance to the English kings William II and Henry I, he was exiled twice: once from 1097 to 1100 and then from 1105 to 1107. While in exile, he helped guide the Greek bishops of southern Italy to adopt Roman rites at the Council of Bari. He worked for the primacy of Canterbury over the bishops of York and Wales but, though at his death he appeared to have been successful, Pope Paschal II later reversed himself and restored York's independence. Beginning at Be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Normandy
Normandy (; french: link=no, Normandie ; nrf, Normaundie, Nouormandie ; from Old French , plural of ''Normant'', originally from the word for "northman" in several Scandinavian languages) is a geographical and cultural region in Northwestern Europe, roughly coextensive with the historical Duchy of Normandy. Normandy comprises mainland Normandy (a part of France) and the Channel Islands (mostly the British Crown Dependencies). It covers . Its population is 3,499,280. The inhabitants of Normandy are known as Normans, and the region is the historic homeland of the Norman language. Large settlements include Rouen, Caen, Le Havre and Cherbourg. The cultural region of Normandy is roughly similar to the historical Duchy of Normandy, which includes small areas now part of the departments of Mayenne and Sarthe. The Channel Islands (French: ''Îles Anglo-Normandes'') are also historically part of Normandy; they cover and comprise two bailiwicks: Guernsey and Jersey, which are B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |