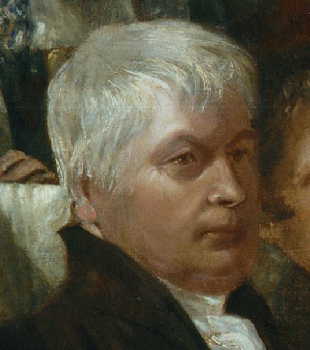|
William Forster (philanthropist)
William Forster (23 March 1784 – 27 January 1854) was a preacher, Quaker elder and a fervent abolitionist. He was an early member of the British and Foreign Anti-Slavery Society in 1839. It was William and Stephen Grellet who introduced Elizabeth Fry to her life's work with prisons, but it was William's brother, Josiah, who accompanied Fry on her tour and inspection of prisons in France. Biography Forster was born in 1784. He initially trained as a land agent with his mother's brother in Sheffield, but he then started to tour England and Scotland as a minister. He visited the Hebrides in 1812 and Ireland in 1813–14. When visiting Newgate prison with Stephen Grellet, Forster was amazed at its state. He contacted Elizabeth Fry and she gathered together a group of women to help with improving prison conditions. Forster thereby alerted Elizabeth Fry to what was to be her life's work. In 1816, Forster married Anna Buxton and they moved to Dorset. When his brother-in-law, Sir Thom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Stacey (abolitionist)
George Stacey (1787–1857) was a leading English Quaker and abolitionist. He was active in trying to prevent a schism within the Quakers. Biography Stacey was born in Kendal.The Quaker Lloyds in the Industrial Revolution Humphrey Lloyd, 1975, , accessed April 2009 Stacey married a fellow Quaker and cousin, Deborah Lloyd, of the Lloyds banking family. Stacey was then living in Tottenham. He was a business partner in a Chemists business called ''Corbyn, Beaumont, Stacey and Messer''. The Stacey's involvement in this partnership dated from 1772 when Thomas Corbyn took in another George Stacey; who were both Quakers. That George Stacey died in 1816. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sir Thomas Buxton, 1st Baronet
Sir Thomas Fowell Buxton, 1st Baronet (1 April 1786Olwyn Mary Blouet, "Buxton, Sir Thomas Fowell, first baronet (1786–1845)", ''Oxford Dictionary of National Biography'', Oxford University Press, 2004; online ed., May 201accessed 25 April 2013 – 19 February 1845) was an English Member of Parliament, brewer, abolitionist and social reformer. He had connections with the Gurney family. Early life Buxton was born at Castle Hedingham, Essex. His father, also named Thomas Fowell Buxton, died young, leaving three sons and two daughters. His Quaker mother's maiden name was Anna Hanbury. He completed his education at Trinity College Dublin, graduating in 1807. Through his mother's influence Buxton became associated with the Gurney family of Earlham Hall, Norwich, especially with Joseph John Gurney and Gurney's sister, the prison reformer Elizabeth Fry. He married their sister Hannah in May 1807. He lived at Belfield House, Weymouth, Dorset in the constituency he represented as an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iowa
Iowa () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States, bordered by the Mississippi River to the east and the Missouri River and Big Sioux River to the west. It is bordered by six states: Wisconsin to the northeast, Illinois to the east and southeast, Missouri to the south, Nebraska to the west, South Dakota to the northwest, and Minnesota to the north. During the 18th and early 19th centuries, Iowa was a part of French Louisiana and Spanish Louisiana; its state flag is patterned after the flag of France. After the Louisiana Purchase, people laid the foundation for an agriculture-based economy in the heart of the Corn Belt. In the latter half of the 20th century, Iowa's agricultural economy transitioned to a diversified economy of advanced manufacturing, processing, financial services, information technology, biotechnology, and green energy production. Iowa is the 26th most extensive in total area and the 31st most populous of the 50 U.S. states, with a populat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salem, Iowa
Salem is a city in Henry County, Iowa, United States. The population was 394 at the time of the 2020 census. History Salem was settled originally by Quakers with the intent that it be a community of Friends. In 1835 Aaron Street, while wending his way westward, came upon an uninhabited spot and declared "Now have mine eyes beheld a country teeming with every good thing…Hither will I come with my flocks and my herds, with my children and my children's children, and our city shall be called Salem, for thus was the city of our fathers, even near unto the seacoast." Independently another Quaker, Isaac Pigeon, who may have visited the spot before Street, brought his family to the area. They became the first citizens of Salem, and with Peter Boyer, began to recruit other Quakers to migrate westward to join them. As early as 1837, Friends meetings were held in private homes, and after the village was laid out in 1839 by Aaron Street Jr., and Peter Boyer, a meeting house was built. F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Forster
Robert Wallace Forster Jr. (July 13, 1941 – October 11, 2019) was an American actor, known for his roles as John Cassellis in ''Medium Cool'' (1969), Captain Dan Holland in ''The Black Hole'' (1979), Abdul Rafai in ''The Delta Force'' (1986), and Max Cherry in ''Jackie Brown'' (1997), for which he was nominated for the Academy Award for Best Supporting Actor. Forster's varied filmography includes: '' Reflections in a Golden Eye'' (1967), ''Alligator'' (1980), ''Me, Myself & Irene'' (2000), ''Mulholland Drive'' (2001), ''The Descendants'' (2011), '' Olympus Has Fallen'' (2013), ''London Has Fallen'' (2016), ''What They Had'' (2018), and ''The Wolf of Snow Hollow'' (2020). He also had prominent roles in television series such as ''Banyon'' (1971–1973), ''Heroes'' (2007–2008), ''Twin Peaks'' (2017) and the ''Breaking Bad'' episode " Granite State" as Ed Galbraith, for which he won the Saturn Award for Best Guest Starring Role on Television. He reprised the role in the film '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Allen (English Quaker)
William Allen (29 August 1770 – 30 September 1843) was an English scientist and philanthropist who opposed slavery and engaged in schemes of social and penal improvement in early 19th-century England. Early life Allen was born in 1770, the eldest son in the Quaker family of Job Allen (1734–1800), a silk manufacturer, and his wife Margaret Stafford (died 1830). He was educated at a Quaker school in Rochester, Kent, and then went into his father's business. As a young man in the 1790s, he became interested in science. He attended meetings of scientific societies, including lectures at St. Thomas's Hospital and Guy's Hospital, becoming a member of the Chemical Society of the latter establishment. On Job Allen's death, the family silk firm was taken over by his father's assistant. Allen had concentrated on his own career in the field of pharmacy, taking over the Plough Court chemical business of Joseph Gurney Bevan who retired in 1795. In 1802, he was elected a Fellow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samuel Gurney (1786–1856)
Samuel Gurney (18 October 1786 – 5 June 1856) was an English banker and philanthropist from the Gurney family of Norwich. He should not be confused with his second son, Samuel (1816–1882), also described as banker and philanthropist, and a Member of Parliament. Early years and marriage Gurney was born at Earlham Hall near Norwich, England, 18 October 1786, the second son of John Gurney (1749–1809), a Quaker banker of Norwich, and Catherine, the daughter of Daniel Bell (1728–1750), a London merchant from Stamford Hill. The family's Gurney's Bank was founded in 1770. Gurney was educated at Wandsworth, Surrey, and at Hingham, Norfolk. Among his siblings were Joseph John Gurney, Daniel Gurney (1791–1880), Elizabeth Fry, Louisa Hoare (1784–1836), the wife of Samuel Hoare, and Hannah Buxton, the wife of Sir Thomas Buxton. At the age of 14, Gurney was placed in the counting-house of his brother-in-law, Joseph Fry (1777–1861), a tea merchant and banker, at St Mildred's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ODNB
The ''Dictionary of National Biography'' (''DNB'') is a standard work of reference on notable figures from British history, published since 1885. The updated ''Oxford Dictionary of National Biography'' (''ODNB'') was published on 23 September 2004 in 60 volumes and online, with 50,113 biographical articles covering 54,922 lives. First series Hoping to emulate national biographical collections published elsewhere in Europe, such as the '' Allgemeine Deutsche Biographie'' (1875), in 1882 the publisher George Smith (1824–1901), of Smith, Elder & Co., planned a universal dictionary that would include biographical entries on individuals from world history. He approached Leslie Stephen, then editor of the ''Cornhill Magazine'', owned by Smith, to become the editor. Stephen persuaded Smith that the work should focus only on subjects from the United Kingdom and its present and former colonies. An early working title was the ''Biographia Britannica'', the name of an earlier eightee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts established by England between the late 16th and early 18th centuries. At its height it was the largest empire in history and, for over a century, was the foremost global power. By 1913, the British Empire held sway over 412 million people, of the world population at the time, and by 1920, it covered , of the Earth's total land area. As a result, its constitutional, legal, linguistic, and cultural legacy is widespread. At the peak of its power, it was described as "the empire on which the sun never sets", as the Sun was always shining on at least one of its territories. During the Age of Discovery in the 15th and 16th centuries, Portugal and Spain pioneered European exploration of the globe, and in the process established large overse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Wilberforce
William Wilberforce (24 August 175929 July 1833) was a British politician, philanthropist and leader of the movement to abolish the slave trade. A native of Kingston upon Hull, Yorkshire, he began his political career in 1780, eventually becoming an independent Member of Parliament (MP) for Yorkshire (1784–1812). In 1785, he became an evangelical Christian, which resulted in major changes to his lifestyle and a lifelong concern for reform. In 1787, Wilberforce came into contact with Thomas Clarkson and a group of activists against the slave trade, including Granville Sharp, Hannah More and Charles Middleton. They persuaded Wilberforce to take on the cause of abolition, and he soon became the leading English abolitionist. He headed the parliamentary campaign against the British Slave Trade for 20 years until the passage of the Slave Trade Act of 1807. Wilberforce was convinced of the importance of religion, morality and education. He championed causes and campaigns such as t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reform Act
In the United Kingdom, Reform Act is most commonly used for legislation passed in the 19th century and early 20th century to enfranchise new groups of voters and to redistribute seats in the House of Commons of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Reform Acts The parliamentary franchise in the United Kingdom was expanded and made more uniform through a series of Reform Acts beginning with the Great Reform Act in 1832. Sources refer to up to six "Reform Acts", although the earlier three in 1832, 1867/8 and 1884 are better known by this name. Some other acts related to electoral matters also became known as Reform Acts. There are many other electoral reform acts in the United Kingdom that are not known by the name "Reform Act". Such legislation typically used the short title of Representation of the People Act, by which name the 1918, 1928 and other acts in the 20th century are better known and a term that was adopted in other countries around the world. * Reform Act 1832 (often ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |