|
William Dubh MacLeod
William Dubh MacLeod (Scottish Gaelic: Uilleam Dubh MacLeòid) (–1480) is considered to be the 7th Chief of Clan MacLeod. He is thought to have been a younger son, yet because of the death of his elder brother, William Dubh succeeded his father, Iain Borb, in the year 1442. William Dubh was an old man when he was killed, leading his clan, at the Battle of Bloody Bay in 1480. He was the last MacLeod chief to be buried on the island of Iona. He was succeeded by his son, Alasdair Crotach. Life Succession According to early 20th-century clan historian R.C. MacLeod, William Dubh was born in about the year 1415. He was the son of the MacLeod chief Iain Borb. The ''Bannatyne manuscript'' records that Iain Borb married a granddaughter of the Earl of Douglas—several 20th-century clan historians gave her name as ''Margaret''. The couple had two sons, named ''William'' and ''Norman'' (''Tormod''), as well as two daughters. The manuscript maintains that Norman was the elder of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
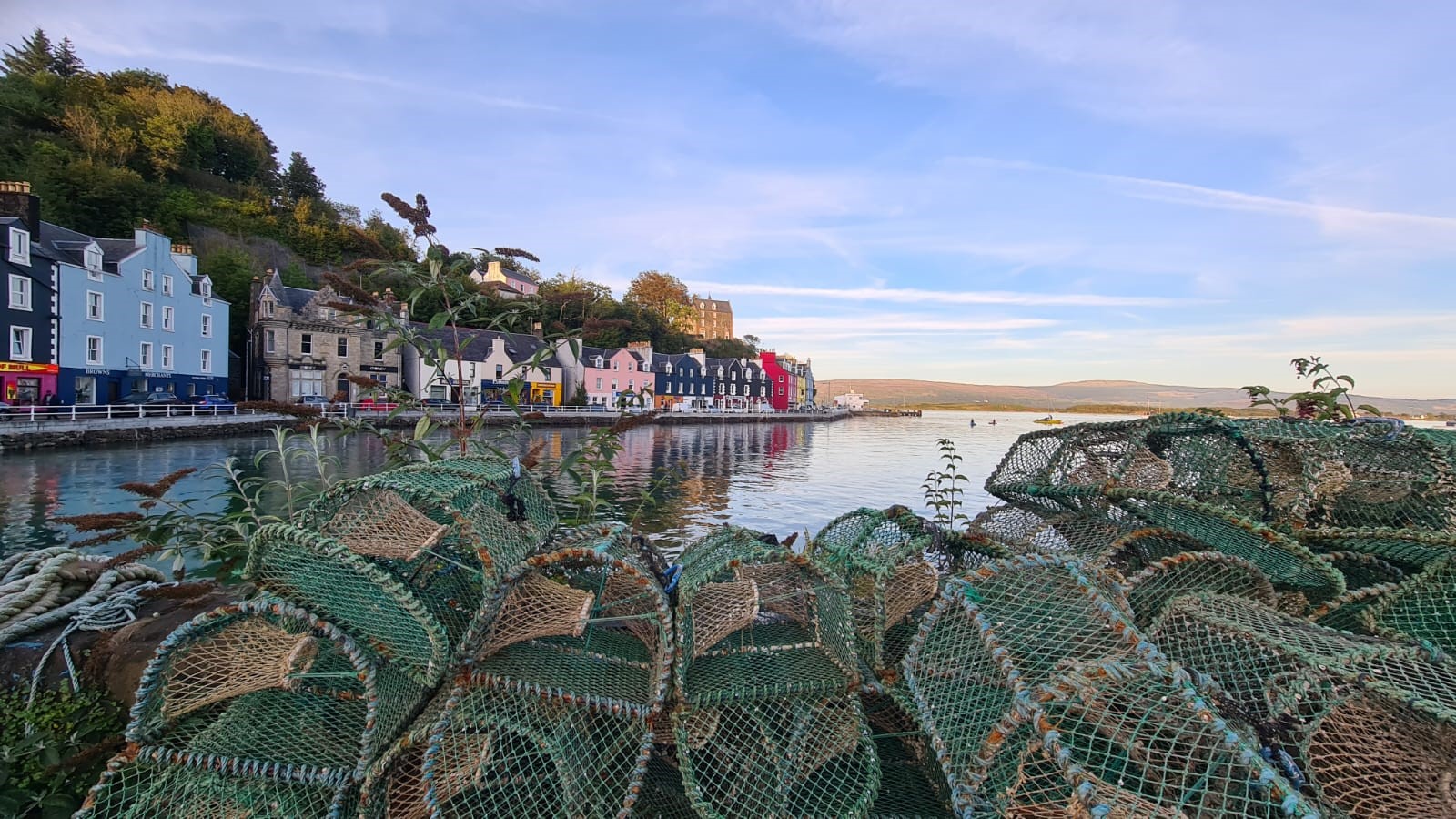
Tobermory, Mull
Tobermory (; gd, Tobar Mhoire) is the capital of, and until 1973 the only burgh on, the Isle of Mull in the Scottish Inner Hebrides. It is located on the east coast of Mishnish, the most northerly part of the island, near the northern entrance of the Sound of Mull. The village was founded as a fishing port in 1788; its layout was based on the designs of Dumfriesshire engineer Thomas Telford. It has a current population of about 1,000. Etymology The name ''Tobermory'' is derived from the Gaelic ', meaning "Mary's well". The name refers to a well located nearby which was dedicated in ancient times to the Virgin Mary. Prehistory and archaeology Archaeological Excavations have taken place at Baliscate just outside of the town. The site was first noted by Hylda Marsh and Beverley Langhorn as part of the Scotland's Rural Past. In 2009, it was partially excavated Time Team and a further longer excavation took place in 2012 as part of a community archaeology project through the Mul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
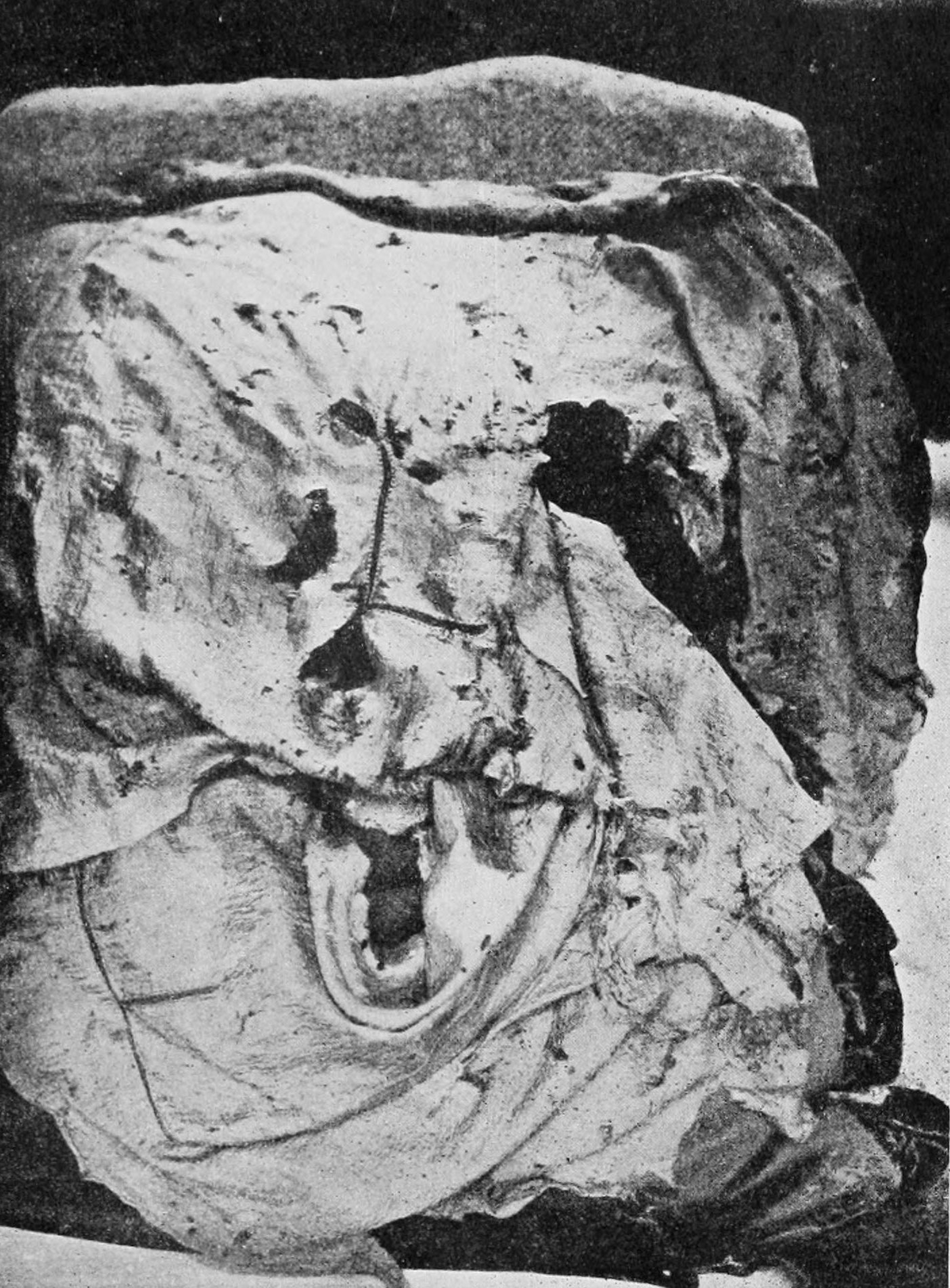
Fairy Flag
The Fairy Flag (Scottish Gaelic: ''Am Bratach Sìth'') is an heirloom of the chiefs of Clan MacLeod. It is held in Dunvegan Castle along with other notable heirlooms, such as the Dunvegan Cup and Sir Rory Mor's Horn. The Fairy Flag is known for the numerous traditions of celtic fairies, and magical properties associated with it. The flag is made of silk, is yellow or brown in colour, and is a square of side about . It has been examined numerous times in the last two centuries, and its condition has somewhat deteriorated. It is ripped and tattered, and is considered to be extremely fragile. The flag is covered in small red "elf dots". In the early part of the 19th century, the flag was also marked with small crosses, but these have since disappeared. The silk of the flag has been stated to have originated in the Far East, and was therefore extremely precious, which led some to believe that the flag may have been an important relic of some sort. Others have attempted to associate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dirk
A dirk is a long bladed thrusting dagger.Chisholm, Hugh (ed.), ''Dagger'', The Encyclopædia Britannica, 11th ed., Vol. VII, New York, NY: Cambridge University Press (1910), p. 729 Historically, it gained its name from the Highland Dirk (Scots Gaelic "Dearg") where it was a personal weapon of officers engaged in naval hand-to-hand combat during the Age of SailO'Brian, Patrick, ''Men-of-War: Life In Nelson's Navy'', New York: W.W. Norton & Co., (1974), p. 35 as well as the personal sidearm of Highlanders. It was also the traditional sidearm of the Highland Clansman and later used by the officers, pipers, and drummers of Scottish Highland regiments around 1725 to 1800 and by Japanese naval officers. Etymology The term is associated with Scotland in the Early Modern Era, being attested from about 1600. The term was spelled ''dork'' or ''dirk'' during the 17th century,Head, T.F. ''The Concise Oxford Dictionary of English Etymology'' Oxford University Press (1996) presumed relate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Axe
A battle axe (also battle-axe, battle ax, or battle-ax) is an axe specifically designed for combat. Battle axes were specialized versions of utility axes. Many were suitable for use in one hand, while others were larger and were deployed two-handed. Axes designed for warfare ranged in weight from just over , and in length from just over to upwards of , as in the case of the Danish axe or the sparth axe. Cleaving weapons longer than 150 cm would arguably fall into the category of polearms. Overview Through the course of human history, commonplace objects have been pressed into service as weapons. Axes, by virtue of their ubiquity, are no exception. Besides axes designed for combat, there were many battle axes that doubled as tools. Axes could be modified into deadly projectiles as well (see the francisca for an example). Axes were often cheaper than swords and considerably more available. Battle axes generally weigh far less than modern splitting axes, especially mauls ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birlinn
The birlinn ( gd, bìrlinn) or West Highland galley was a wooden vessel propelled by sail and oar, used extensively in the Hebrides and West Highlands of Scotland from the Middle Ages on. Variants of the name in English and Lowland Scots include "berlin" and "birling". The Gaelic term may derive from the Norse ''byrðingr'' (ship of boards), a type of cargo vessel. It has been suggested that a local design lineage might also be traceable to vessels similar to the Broighter-type boat (first century BC), equipped with oars and a square sail, without the need to assume a specific Viking design influence. It is uncertain, however, whether the Broighter model represents a wooden vessel or a skin-covered boat of the currach type. The majority of scholars emphasise the Viking influence on the birlinn. The birlinn was clinker-built and could be sailed or rowed. It had a single mast with a square sail. Smaller vessels of this type might have had as few as twelve oars, with the larger W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clan MacNeil
Clan MacNeil, also known in Scotland as Clan Niall, is a highland Scottish clan of Irish origin. According to their early genealogies and some sources they're descended from Eógan mac Néill and Niall of the Nine Hostages. The clan is particularly associated with the Outer Hebridean island of Barra. The early history of Clan MacNeil is obscure, however despite this the clan claims to descend from the legendary Irish King Niall of the Nine Hostages, who is counted as the 1st Clan Chief, the current Clan Chief being the 47th. The clan itself takes its name from a ''Niall'' who lived in the 13th or early 14th century, and who belonged to the same dynastic family of Cowal and Knapdale as the ancestors of the Lamonts, MacEwens of Otter, Maclachlans, and the MacSweens. While the clan is centred in Barra in the Outer Hebrides, there is a branch of the clan in Argyll (McNeill/MacNeill) that some historians have speculated was more senior in line, or possibly even unrelated. However, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clan MacLeod Of Lewis
Clan MacLeod of The Lewes, commonly known as Clan MacLeod of Lewis ( gd, Clann Mhic Leòid Leòdhais), is a Scottish Highlands, Highland Scottish clan, which at its height held extensive lands in the Western Isles and west coast of Scotland. From the 14th century up until the beginning of the 17th century there were two branches of Macleods: the MacLeods of Dunvegan and Harris, Outer Hebrides, Harris (Clan MacLeod); and the Macleods of the Isle of Lewis. In Scottish Gaelic, Gaelic the Macleods of Lewis were known as Sìol Thorcaill ("Seed of Torquil"), and the MacLeods of Dunvegan and Harris were known as Sìol Thormoid ("Seed of Tormod"). The traditional progenitor of the MacLeods was Leod, made a son of Olaf the Black, King of Mann and the Isles, by a now-discredited tradition. An older, more accepted tradition names his father Olvir and describes the clan as Sliochd Olbhur. Tradition gave Leod two sons, Tormod, son of Leod, Tormod - progenitor of the Macleods of Harris and Dunve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clan Donald
Clan Donald, also known as Clan MacDonald ( gd, Clann Dòmhnaill; Mac Dòmhnaill ), is a Highland Scottish clan and one of the largest Scottish clans. The Lord Lyon King of Arms, the Scottish official with responsibility for regulating heraldry in that country, issuing new grants of coats of arms, and serving as the judge of the Court of the Lord Lyon, recognises under Scottish law the ''High Chief of Clan Donald''. Historically the chiefs of the Clan Donald held the title of Lord of the Isles until 1493 and two of those chiefs also held the title of Earl of Ross until 1476. There are also numerous branches to the Clan Donald and several of these have chiefs recognised by the Lord Lyon King of Arms; these are: Clan Macdonald of Sleat, Clan Macdonald of Clanranald, Clan MacDonell of Glengarry, Clan MacDonald of Keppoch, and Clan MacAlister. There are also notable historic branches of Clan Donald without chiefs so-recognised, these are: the Clan MacDonald of Dunnyveg, Clan MacDona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aonghas Óg
Aonghas Óg (died 1490) was a Scottish nobleman who was the last independent Lord of the Isles. Aonghas became a rebel against both his father and the Scottish crown, in a civil clan war which would see the end of the independent Lordship of the Isles. Biography Aonghas was born the bastard son of John MacDonald, Earl of Ross a.k.a. (John of Islay, Lord of the Isles). In time, Aonghas would become a rebel against both his father and against the Scottish crown. In 1476, a secret treaty that was made by Aonghas's father, John MacDonald, with King Edward IV of England was discovered by King James III of Scotland, who then stripped MacDonald of his earldom, as well as the sheriffdoms of Nairn and Inverness, and the lordships of Kintyre and Knapdale; the King however confirmed MacDonald with the remainder of his lands and the title Lord of the Isles. It appears that Aonghas, as MacDonald's heir, was not prepared to accept this settlement. Aonghas campaigned to regain Ross and the ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.png)
