|
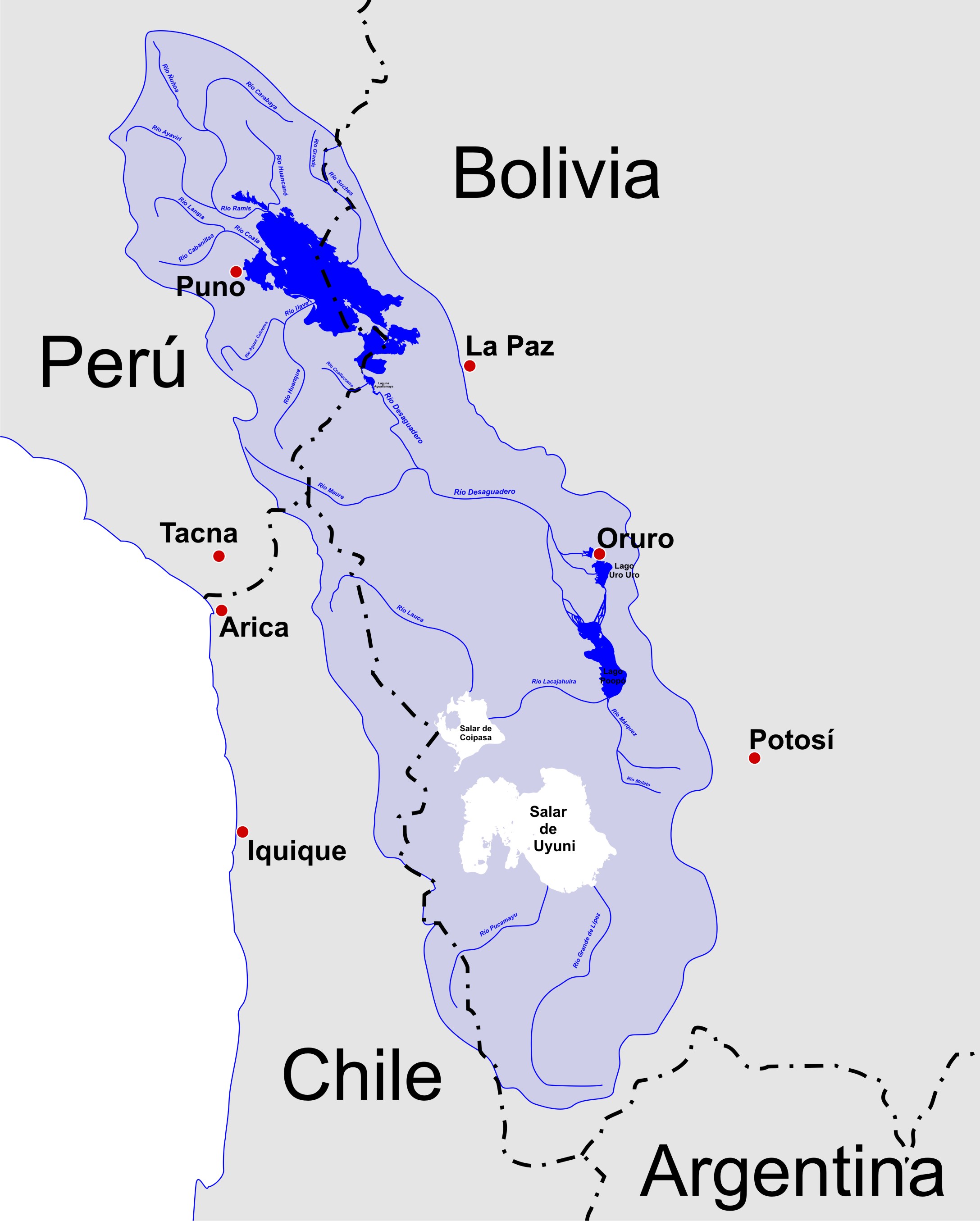
Wila Pukarani
Wila Pukarani (Aymara ''wila'' red or blood, ''pukara'' pucará (fortress) or mountain of protection, ''-ni'' Aymara suffix to indicate ownership, "the one with a red ''pukara''", Hispanicized spellings ''Vila Pucarani'' / ''Villa Pucarani'') is a volcano located in the Coipasa salt pan in the Bolivian Altiplano. It is approximately 4,920 m high reaching a prominence of at least 1,200 m. It is situated in the Oruro Department, Sabaya Province, Coipasa Municipality. The town of Coipasa lies on its northeastern side. An age of 3.7 million years has been inferred from the erosion status of the mountain, which shows evidence of Pleistocene glaciation. See also *Lauca River The Lauca River is a binational river. It originates in the Chilean Altiplano of the Arica and Parinacota Region, crosses the Andes and empties into Coipasa Lake in Bolivia. The upper reach of the river lies within the boundaries of Lauca Nation ... References Volcanoes of Oruro Department Fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bolivia
, image_flag = Bandera de Bolivia (Estado).svg , flag_alt = Horizontal tricolor (red, yellow, and green from top to bottom) with the coat of arms of Bolivia in the center , flag_alt2 = 7 × 7 square patchwork with the (top left to bottom right) diagonals forming colored stripes (green, blue, purple, red, orange, yellow, white, green, blue, purple, red, orange, yellow, from top right to bottom left) , other_symbol = , other_symbol_type = Dual flag: , image_coat = Escudo de Bolivia.svg , national_anthem = " National Anthem of Bolivia" , image_map = BOL orthographic.svg , map_width = 220px , alt_map = , image_map2 = , alt_map2 = , map_caption = , capital = La Paz Sucre , largest_city = , official_languages = Spanish , languages_type = Co-official languages , languages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oruro Department
Oruro (; Quechua: ''Uru Uru''; Aymara: ''Ururu'') is a department of Bolivia, with an area of . Its capital is the city of Oruro. According to the 2012 census, the Oruro department had a population of 494,178. Provinces of Oruro The department is divided into 16 provinces which are further subdivided into municipalities and cantons. Note: Eduardo Abaroa Province (#5) is both north of and south of Sebastián Pagador Province (#6). Government The chief executive officer of Bolivian departments (since May 2010) is the governor; until then, the office was called the prefect, and until 2006 the prefect was appointed by the president of Bolivia. The current governor, Santos Tito of the Movement for Socialism – Political Instrument for the Sovereignty of the Peoples, was elected on 4 April 2010. The chief legislative body of the department is the Departmental Legislative Assembly, a body also first elected on 4 April 2010. It consists of 33 members: 16 elected by each of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
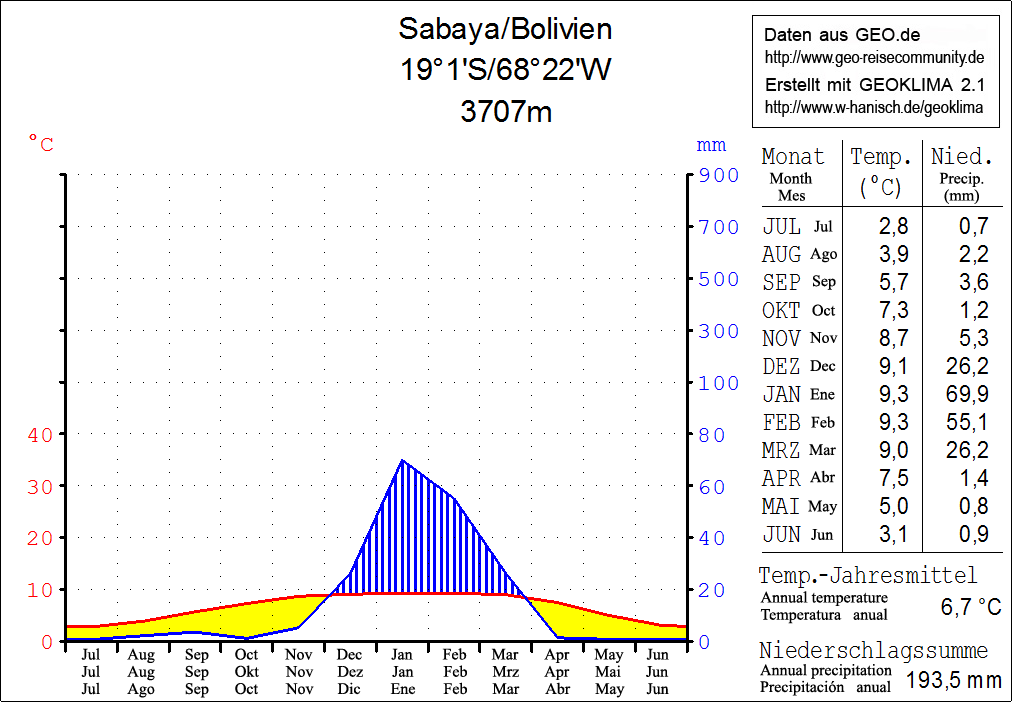
Sabaya Province
Sabaya (formerly: Atahuallpa) is a province in the central parts of the Bolivian Oruro Department. Its seat is Sabaya. Location Sabaya Province is one of sixteen provinces in the Oruro Department. It is located between 18° 35' and 19° 39' South and between 67° 31' and 68° 39' West. It borders Sajama Province in the north, the Republic of Chile and Puerto de Mejillones Province in the west, the Potosí Department in the southwest, the Ladislao Cabrera Province in the southeast, and the Litoral Province in the northeast. The province extends over 160 km from northwest to southeast, and 50 km from northeast to southwest. Geography One of the highest peaks of the province is Pukintika on the border to Chile. Other mountains are listed below:BIGM map 1:50,000 Cerro Capitan Hoja 5837-III Climate Population The main language in the province is Spanish, spoken by 92%, 67% of the population speak Aymara and 9% speak Quechua. The population increased from 3,567 i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andes
The Andes, Andes Mountains or Andean Mountains (; ) are the longest continental mountain range in the world, forming a continuous highland along the western edge of South America. The range is long, wide (widest between 18°S – 20°S latitude), and has an average height of about . The Andes extend from north to south through seven South American countries: Venezuela, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, Bolivia, Chile, and Argentina. Along their length, the Andes are split into several ranges, separated by intermediate depressions. The Andes are the location of several high plateaus—some of which host major cities such as Quito, Bogotá, Cali, Arequipa, Medellín, Bucaramanga, Sucre, Mérida, El Alto and La Paz. The Altiplano plateau is the world's second-highest after the Tibetan plateau. These ranges are in turn grouped into three major divisions based on climate: the Tropical Andes, the Dry Andes, and the Wet Andes. The Andes Mountains are the highest m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aymara Language
Aymara (; also ) is an Aymaran language spoken by the Aymara people of the Bolivian Andes. It is one of only a handful of Native American languages with over one million speakers.The other native American languages with more than one million speakers are Nahuatl, Quechua languages, and Guaraní. Aymara, along with Spanish and Quechua, is an official language in Bolivia and Peru. It is also spoken, to a much lesser extent, by some communities in northern Chile, where it is a recognized minority language. Some linguists have claimed that Aymara is related to its more widely spoken neighbor, Quechua. That claim, however, is disputed. Although there are indeed similarities, like the nearly identical phonologies, the majority position among linguists today is that the similarities are better explained as areal features rising from prolonged cohabitation, rather than natural genealogical changes that would stem from a common protolanguage. Aymara is an agglutinating and, to a cert ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pucará
The Pucará culture was an archaeological culture which developed in Qullaw, along the north-western shore of Lake Titicaca. It was characterized by a hierarchy of sites made up several smaller centers and villages scattered throughout the northern basin of the Titicaca, ruled from its nucleus - the town of Pukara (from which the given name derives) with an approximate extension of 6 square kilometers, constituted the first properly urban settlement in the Titicaca basin. Its sphere of influence reached as far north as the Cuzco Valley and as far south as Tiahuanaco. The culture had two phases of development within the Formative Period: the Middle Formative (1400 to 550 BC), and Late Formative (550 BC to 400 AD). The Pukara engaged in agriculture, herding and fishing, domesticating the alpaca and constructing ridges and furrows that allowed agriculture in floodable lands on the shores of Lake Titicaca, which ensured intensive high-altitude agriculture. During that time comple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Coipasa
__NOTOC__ Lago Coipasa or Salar de Coipasa is a lake in Sabaya Province, Oruro Department, Bolivia. At an elevation of 3657 m, its surface area is 806 km². It is on the western part of Altiplano, 20 km north of Salar de Uyuni and south of the main road linking Oruro and Huara (Chile). Lake Coipasa is a tectonic saline lake with a depth of 3.5 metres that is surrounded by the Coipasa salt flat (''Salar de Coipasa''), and the volcanic cone of Wila Pukarani. Thousands of flamingos have settled on the shores of Lake Coipasa. Gallery Coipasa lake map of the shape and depth (bathymetry) 2020.jpg, Map of the shape and depth (bathymetry) of the Coipasa lake, 2020 Lago Uru Uru Chipaya 4.jpg, The lake Poblacion Chipaya.jpg, The village of Chipaya, Oruro, Bolivia, near the lake See also * Chipaya * Ouki Ouki was an ancient lake in the Bolivian Altiplano. Its existence was postulated in 2006 by a group of scientists which had subdivided the Lake Minchin lake cycle in sev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Altiplano
The Altiplano (Spanish for "high plain"), Collao (Quechua and Aymara: Qullaw, meaning "place of the Qulla") or Andean Plateau, in west-central South America, is the most extensive high plateau on Earth outside Tibet. The plateau is located at the latitude of the widest part of the north-south-trending Andes. The bulk of the Altiplano lies in Bolivia, but its northern parts lie in Peru, and its southwestern fringes lie in Chile. There are on the plateau several cities in each of these three nations, including El Alto, La Paz, Oruro, and Puno. The northeastern part of the Altiplano is more humid than the southwestern part, which has several salares (salt flats), due to its aridity. At the Bolivia–Peru border lies Lake Titicaca, the largest lake in South America. Farther south, in Bolivia, there was until recently a lake, Lake Poopó, but by December 2015 it had completely dried up, and was declared defunct. It is unclear whether that lake, which had been the second-largest in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coipasa Municipality
Coipasa is a rural municipality in Sabaya Province, Oruro Department, Bolivia. It is surrounded by Coipasa Lake on three directions, and has an average elevation of 3,709 meters above the sea level. The municipality was created by Law of 8 June 1966, during the presidency of Alfredo Ovando Candía. As of 2020, there are 951 residents within Coipasa. Climate Coipasa has a Semi-arid Climate (BSk). It sees the most rainfall in January, with an average precipitation of 130 mm; and the least rainfall in June, with an average precipitation of 1 mm. See also * Coipasa Lake * Salar de Uyuni * Eduardo Avaroa Andean Fauna National Reserve The Eduardo Avaroa Andean Fauna National Reserve (''Reserva Nacional de Fauna Andina Eduardo Avaroa''; Spanish acronym: REA) is located in Sur Lípez Province. Situated in the far southwestern region of Bolivia, it is the country's most visite ... References {{Reflist Municipalities of Oruro Department Populated places in Oruro Departme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological Epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was finally confirmed in 2009 by the International Union of Geological Sciences, the cutoff of the Pleistocene and the preceding Pliocene was regarded as being 1.806 million years Before Present (BP). Publications from earlier years may use either definition of the period. The end of the Pleistocene corresponds with the end of the last glacial period and also with the end of the Paleolithic age used in archaeology. The name is a combination of Ancient Greek grc, label=none, πλεῖστος, pleīstos, most and grc, label=none, καινός, kainós (latinized as ), 'new'. At the end of the preceding Pliocene, the previously isolated North and South American continents were joined by the Isthmus of Panama, causing Great American Interchang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salar De Coipasa
__NOTOC__ Lago Coipasa or Salar de Coipasa is a lake in Sabaya Province, Oruro Department, Bolivia. At an elevation of 3657 m, its surface area is 806 km². It is on the western part of Altiplano, 20 km north of Salar de Uyuni and south of the main road linking Oruro and Huara (Chile). Lake Coipasa is a tectonic saline lake with a depth of 3.5 metres that is surrounded by the Coipasa salt flat (''Salar de Coipasa''), and the volcanic cone of Wila Pukarani. Thousands of flamingo Flamingos or flamingoes are a type of wading bird in the family Phoenicopteridae, which is the only extant family in the order Phoenicopteriformes. There are four flamingo species distributed throughout the Americas (including the Caribbea ...s have settled on the shores of Lake Coipasa. Gallery Coipasa lake map of the shape and depth (bathymetry) 2020.jpg, Map of the shape and depth (bathymetry) of the Coipasa lake, 2020 Lago Uru Uru Chipaya 4.jpg, The lake Poblacion Chipaya.jpg, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lauca River
The Lauca River is a binational river. It originates in the Chilean Altiplano of the Arica and Parinacota Region, crosses the Andes and empties into Coipasa Lake in Bolivia. The upper reach of the river lies within the boundaries of Lauca National Park in the Parinacota Province. Lauca River receives waters from a group of lakes known as Quta Qutani through the ''Desaguadero River''. In this area there is a type of marsh known as Parinacota wetlands, in which converge several streams, being the more important the river just mentioned, which has a variable flow rate ranging from 100 to 560 L/s, and an average of 260 L/s. From its source in the Parinacota wetlands the river flows west. The spurs of the ''Cordillera Central'' (also known as ''Chapiquiña'') form an obstacle impossible to pass through, forcing the river's course southward. In the vicinity of Wallatiri volcano, the Lauca turns again, now eastward crossing from Chile into Bolivia at the latitude of ''Macaya'', at an e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)