|
West Of Scotland Coronary Prevention Study
The West of Scotland Coronary Prevention Study, also known as WOSCOPS, was a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial, published in 1995. It compared 40mg of the lipid-lowering drug pravastatin to placebo in 6, 595 men who had a mean cholesterol of 7 mmol/L but no previous history of a heart attack. The study concluded that statin treatment for primary prevention reduced coronary heart disease (CHD) events by 31% after nearly five years of treatment. See also * Heart Protection Study * Scandinavian Simvastatin Survival Study The Scandinavian Simvastatin Survival Study (also known as the 4S study), was a multicentre, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial, which provided the initial data that supported the use of the cholesterol-lowering drug, sim ... References Epidemiological study projects Clinical trials related to cardiology Statins Cardiology {{Treatment-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Randomized Controlled Trial
A randomized controlled trial (or randomized control trial; RCT) is a form of scientific experiment used to control factors not under direct experimental control. Examples of RCTs are clinical trials that compare the effects of drugs, surgical techniques, medical devices, diagnostic procedures or other medical treatments. Participants who enroll in RCTs differ from one another in known and unknown ways that can influence study outcomes, and yet cannot be directly controlled. By Random assignment, randomly allocating participants among compared treatments, an RCT enables ''statistical control'' over these influences. Provided it is designed well, conducted properly, and enrolls enough participants, an RCT may achieve sufficient control over these confounding factors to deliver a useful comparison of the treatments studied. Definition and examples An RCT in clinical research typically compares a proposed new treatment against an existing Standard of care#Medical standard of care, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treatment And Control Groups
In the design of experiments, hypotheses are applied to experimental units in a treatment group. In comparative experiments, members of a control group receive a standard treatment, a placebo, or no treatment at all. There may be more than one treatment group, more than one control group, or both. A placebo control group can be used to support a double-blind study, in which some subjects are given an ineffective treatment (in medical studies typically a sugar pill) to minimize differences in the experiences of subjects in the different groups; this is done in a way that ensures no participant in the experiment (subject or experimenter) knows to which group each subject belongs. In such cases, a third, non-treatment control group can be used to measure the placebo effect directly, as the difference between the responses of placebo subjects and untreated subjects, perhaps paired by age group or other factors (such as being twins). For the conclusions drawn from the results of an e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statin
Statins, also known as HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, are a class of lipid-lowering medications that reduce illness and mortality in those who are at high risk of cardiovascular disease. They are the most common cholesterol-lowering drugs. Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) carriers of cholesterol play a key role in the development of atherosclerosis and coronary heart disease via the mechanisms described by the lipid hypothesis. Statins are effective in lowering LDL cholesterol and so are widely used for primary prevention in people at high risk of cardiovascular disease, as well as in secondary prevention for those who have developed cardiovascular disease. Side effects of statins include muscle pain, increased risk of diabetes mellitus, and abnormal blood levels of liver enzymes. Additionally, they have rare but severe adverse effects, particularly muscle damage. They inhibit the enzyme HMG-CoA reductase which plays a central role in the production of cholesterol. High cholester ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pravastatin
Pravastatin, sold under the brand name Pravachol among others, is a statin medication, used for preventing cardiovascular disease in those at high risk and treating abnormal lipids. It should be used together with diet changes, exercise, and weight loss. It is taken by mouth. Common side effects include joint pain, diarrhea, nausea, headaches, and muscle pains. Serious side effects may include rhabdomyolysis, liver problems, and diabetes. Use during pregnancy may harm the baby. Like all statins, pravastatin works by inhibiting HMG-CoA reductase, an enzyme found in liver that plays a role in producing cholesterol. Pravastatin was patented in 1980 and approved for medical use in 1989. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. It is available as a generic medication. In 2020, it was the 34th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 17million prescriptions. Medical uses Pravastatin is primarily used for the treatment o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Placebo
A placebo ( ) is a substance or treatment which is designed to have no therapeutic value. Common placebos include inert tablets (like sugar pills), inert injections (like Saline (medicine), saline), sham surgery, and other procedures. In general, placebos can affect how patients perceive their condition and encourage the body's chemical processes for relieving pain and a few other symptoms, but have no impact on the disease itself. Improvements that patients experience after being treated with a placebo can also be due to unrelated factors, such as regression to the mean (a statistical effect where an unusually high or low measurement is likely to be followed by a less extreme one). The use of placebos in clinical medicine raises ethical concerns, especially if they are disguised as an active treatment, as this introduces dishonesty into the doctor–patient relationship and bypasses informed consent. While it was once assumed that this deception was necessary for placebos to have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myocardial Infarction
A myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when blood flow decreases or stops to the coronary artery of the heart, causing damage to the heart muscle. The most common symptom is chest pain or discomfort which may travel into the shoulder, arm, back, neck or jaw. Often it occurs in the center or left side of the chest and lasts for more than a few minutes. The discomfort may occasionally feel like heartburn. Other symptoms may include shortness of breath, nausea, feeling faint, a cold sweat or feeling tired. About 30% of people have atypical symptoms. Women more often present without chest pain and instead have neck pain, arm pain or feel tired. Among those over 75 years old, about 5% have had an MI with little or no history of symptoms. An MI may cause heart failure, an irregular heartbeat, cardiogenic shock or cardiac arrest. Most MIs occur due to coronary artery disease. Risk factors include high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primary Prevention
Preventive healthcare, or prophylaxis, consists of measures taken for the purposes of disease prevention.Hugh R. Leavell and E. Gurney Clark as "the science and art of preventing disease, prolonging life, and promoting physical and mental health and efficiency. Leavell, H. R., & Clark, E. G. (1979). Preventive Medicine for the Doctor in his Community (3rd ed.). Huntington, NY: Robert E. Krieger Publishing Company. Disease and disability are affected by environmental factors, genetic predisposition, disease agents, and lifestyle choices, and are dynamic processes which begin before individuals realize they are affected. Disease prevention relies on anticipatory actions that can be categorized as primal, primary, secondary, and tertiary prevention. Each year, millions of people die of preventable deaths. A 2004 study showed that about half of all deaths in the United States in 2000 were due to preventable behaviors and exposures. Leading causes included cardiovascular disease, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
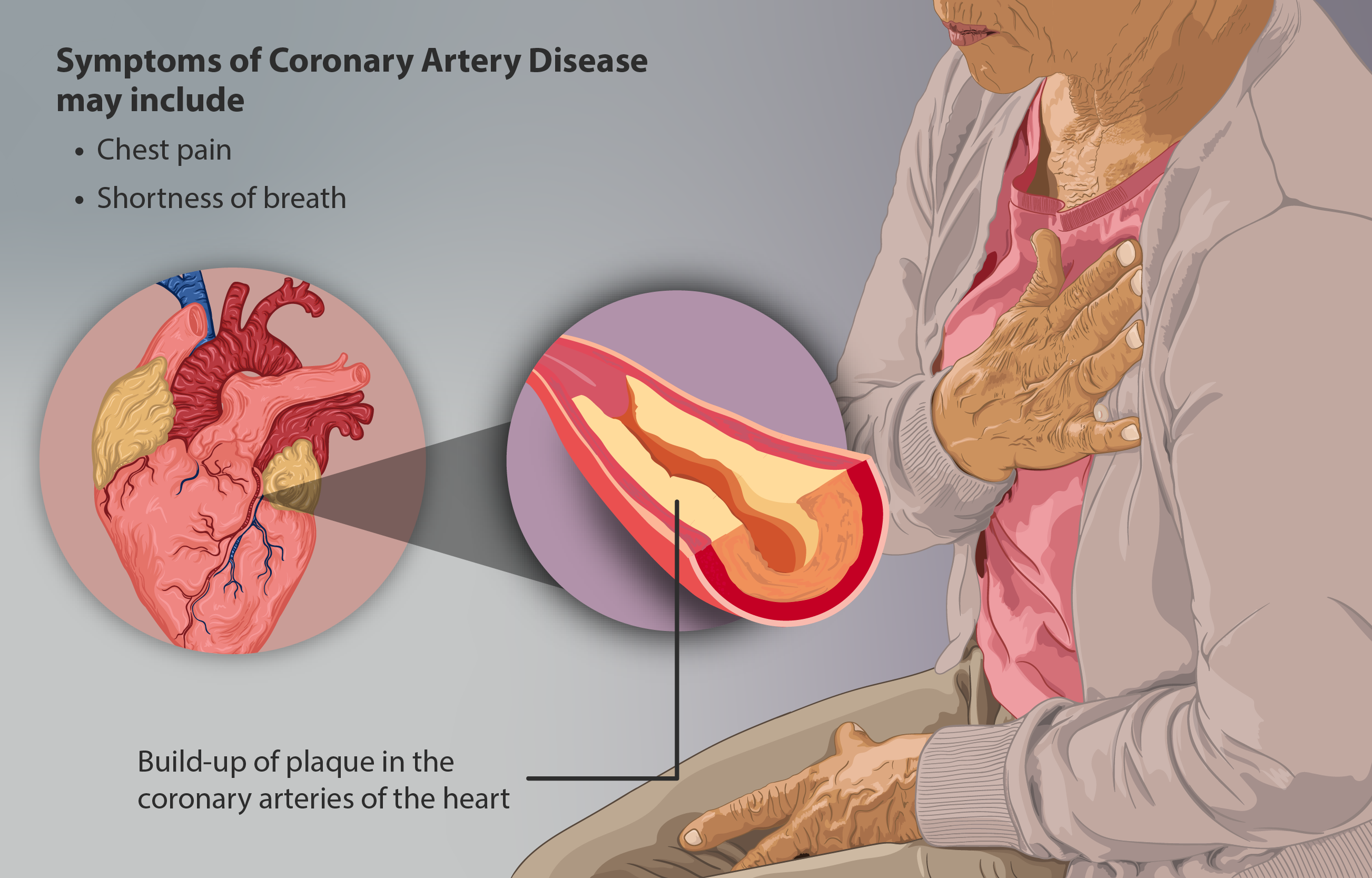
Coronary Heart Disease
Coronary artery disease (CAD), also called coronary heart disease (CHD), ischemic heart disease (IHD), myocardial ischemia, or simply heart disease, involves the reduction of blood flow to the heart muscle due to build-up of atherosclerotic plaque in the arteries of the heart. It is the most common of the cardiovascular diseases. Types include stable angina, unstable angina, myocardial infarction, and sudden cardiac death. A common symptom is chest pain or discomfort which may travel into the shoulder, arm, back, neck, or jaw. Occasionally it may feel like heartburn. Usually symptoms occur with exercise or emotional stress, last less than a few minutes, and improve with rest. Shortness of breath may also occur and sometimes no symptoms are present. In many cases, the first sign is a heart attack. Other complications include heart failure or an abnormal heartbeat. Risk factors include high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes, lack of exercise, obesity, high blood cholesterol, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxford University Press
Oxford University Press (OUP) is the university press of the University of Oxford. It is the largest university press in the world, and its printing history dates back to the 1480s. Having been officially granted the legal right to print books by decree in 1586, it is the second oldest university press after Cambridge University Press. It is a department of the University of Oxford and is governed by a group of 15 academics known as the Delegates of the Press, who are appointed by the vice-chancellor of the University of Oxford. The Delegates of the Press are led by the Secretary to the Delegates, who serves as OUP's chief executive and as its major representative on other university bodies. Oxford University Press has had a similar governance structure since the 17th century. The press is located on Walton Street, Oxford, opposite Somerville College, in the inner suburb of Jericho. For the last 500 years, OUP has primarily focused on the publication of pedagogical texts and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heart Protection Study
The Heart Protection Study was a randomized controlled trial run by the Clinical Trial Service Unit, and funded by the Medical Research Council (UK), Medical Research Council (MRC) and the British Heart Foundation (BHF) in the United Kingdom. It studied the use of the statin, cholesterol lowering drug, simvastatin 40 mg and vitamin supplementation (vitamin E, vitamin C and carotene, beta carotene) in people who were at risk of cardiovascular disease. It was led by Jane Armitage, an epidemiologist at the Clinical Trial Service Unit. Results An outline of the study protocol was published in 1999. Initial results were published in 2002, which indicated that vitamins made little difference in modifying cardiovascular risk, but that simvastatin could significantly reduce the risk of cardiovascular events. Further publications, from 2003 and 2004, were concerned with the efficacy of simvastatin in diabetes patients and preventing stroke. A 2005 paper analyses the cost-effectiveness o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scandinavian Simvastatin Survival Study
The Scandinavian Simvastatin Survival Study (also known as the 4S study), was a multicentre, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial, which provided the initial data that supported the use of the cholesterol-lowering drug, simvastatin, in people with a moderately raised cholesterol and coronary heart disease (CHD); that is people who had previously had a heart attack or angina. The study was sponsored by the pharmaceutical company Merck and enrolled 4,444 people from 94 centres in Scandinavia. Before the 4S study, it was not proven that lowering cholesterol could prolong life in people who had CHD. The study concluded that secondary prevention with simvastatin in a high risk group with CHD reduced overall mortality by 30%. Published in ''The Lancet'' in 1994, it is considered a "landmark paper". Objective The 4S multicentre, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial enrolled 4,444 people chosen from 7,027 people who had been followed up for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epidemiological Study Projects
Epidemiology is the study and analysis of the distribution (who, when, and where), patterns and determinants of health and disease conditions in a defined population. It is a cornerstone of public health, and shapes policy decisions and evidence-based practice by identifying risk factors for disease and targets for preventive healthcare. Epidemiologists help with study design, collection, and statistical analysis of data, amend interpretation and dissemination of results (including peer review and occasional systematic review). Epidemiology has helped develop methodology used in clinical research, public health studies, and, to a lesser extent, basic research in the biological sciences. Major areas of epidemiological study include disease causation, transmission, outbreak investigation, disease surveillance, environmental epidemiology, forensic epidemiology, occupational epidemiology, screening, biomonitoring, and comparisons of treatment effects such as in clinical trials. Epid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)

