|
Water In India
Water resources in India includes information on precipitation, surface and groundwater storage and hydropower potential. India experiences an average precipitation of per year, or about of rains annually or about of fresh water ''per person'' every year. India accounts for 18% of the world population and about 4% of the world's water resources. One of the proposed solutions to solve the country's water woes is the Indian rivers interlinking project. Some 80 percent of its area experiences rains of or more a year. However, this rain is not uniform in time or geography. Most of the rains occur during its monsoon seasons (June to September), with the north east and north receiving far more rains than India's west and south. Other than rains, the melting of snow over the Himalayas after winter season feeds the northern rivers to varying degrees. The southern rivers, however experience more flow variability over the year. For the Himalayan basin, this leads to flooding in some mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Precipitation
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls under gravitational pull from clouds. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, sleet, snow, ice pellets, graupel and hail. Precipitation occurs when a portion of the atmosphere becomes saturated with water vapor (reaching 100% relative humidity), so that the water condenses and "precipitates" or falls. Thus, fog and mist are not precipitation but colloids, because the water vapor does not condense sufficiently to precipitate. Two processes, possibly acting together, can lead to air becoming saturated: cooling the air or adding water vapor to the air. Precipitation forms as smaller droplets coalesce via collision with other rain drops or ice crystals within a cloud. Short, intense periods of rain in scattered locations are called showers. Moisture that is lifted or otherwise forced to rise over a layer of sub-freezing air at the surface may be condensed into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potential Evaporation
Potential evaporation (PE) or potential evapotranspiration (PET) is defined as the amount of evaporation that would occur if a sufficient water source were available. If the actual evapotranspiration is considered the net result of atmospheric demand for moisture from a surface and the ability of the surface to supply moisture, then PET is a measure of the demand side. Surface and air temperatures, insolation, and wind all affect this. A dryland is a place where annual potential evaporation exceeds annual precipitation. Estimates of potential evaporation Thornthwaite equation (1948) PET = 16 \left(\frac\right) \left(\frac\right) \left(\frac\right)^ Where PET is the estimated potential evapotranspiration (mm/month) T_d is the average daily temperature (degrees Celsius; if this is negative, use 0) of the month being calculated N is the number of days in the month being calculated L is the average day length (hours) of the month being calculated \alpha = (6.75 \times 10 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brahmaputra
The Brahmaputra is a trans-boundary river which flows through Tibet, northeast India, and Bangladesh. It is also known as the Yarlung Tsangpo in Tibetan, the Siang/Dihang River in Arunachali, Luit in Assamese, and Jamuna River in Bangla. It is the 9th largest river in the world by discharge, and the 15th longest. With its origin in the Manasarovar Lake region, near Mount Kailash, on the northern side of the Himalayas in Burang County of Tibet where it is known as the Yarlung Tsangpo River, It flows along southern Tibet to break through the Himalayas in great gorges (including the Yarlung Tsangpo Grand Canyon) and into Arunachal Pradesh. It flows southwest through the Assam Valley as the Brahmaputra and south through Bangladesh as the Jamuna (not to be confused with the Yamuna of India). In the vast Ganges Delta, it merges with the Ganges, popularly known as the Padma in Bangladesh, and becomes the Meghna and ultimately empties into the Bay of Bengal. About long, the Bra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bay Of Bengal
The Bay of Bengal is the northeastern part of the Indian Ocean, bounded on the west and northwest by India, on the north by Bangladesh, and on the east by Myanmar and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands of India. Its southern limit is a line between Sangaman Kanda, Sri Lanka, and the north westernmost point of Sumatra, Indonesia. It is the largest water region called a bay in the world. There are countries dependent on the Bay of Bengal in South Asia and Southeast Asia. During the existence of British India, it was named as the Bay of Bengal after the historic Bengal region. At the time, the Port of Kolkata served as the gateway to the Crown rule in India. Cox's Bazar, the longest sea beach in the world and Sundarbans, the largest mangrove forest and the natural habitat of the Bengal tiger, are located along the bay. The Bay of Bengal occupies an area of . A number of large rivers flow into the Bay of Bengal: the Ganges– Hooghly, the Padma, the Brahmaputra–Yamuna, the Barak� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
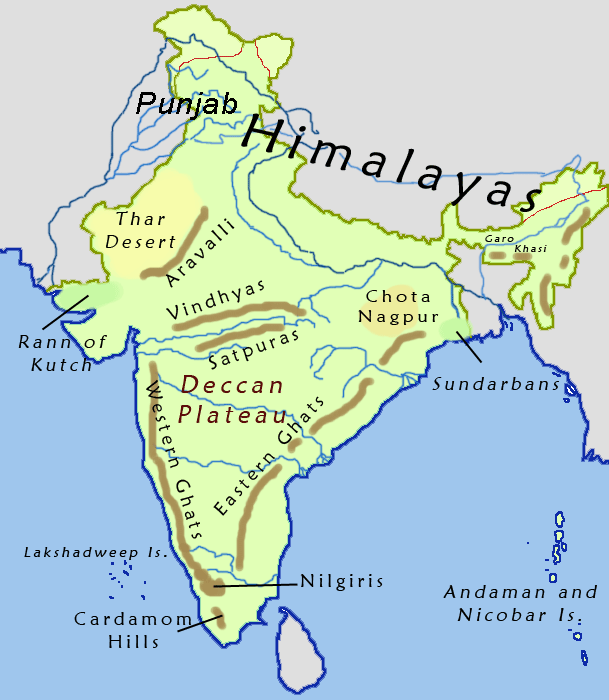
India Map Based On Survey Of India Rivers
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the south, the Arabian Sea on the southwest, and the Bay of Bengal on the southeast, it shares land borders with Pakistan to the west; China, Nepal, and Bhutan to the north; and Bangladesh and Myanmar to the east. In the Indian Ocean, India is in the vicinity of Sri Lanka and the Maldives; its Andaman and Nicobar Islands share a maritime border with Thailand, Myanmar, and Indonesia. Modern humans arrived on the Indian subcontinent from Africa no later than 55,000 years ago., "Y-Chromosome and Mt-DNA data support the colonization of South Asia by modern humans originating in Africa. ... Coalescence dates for most non-European populations average to between 73–55 ka.", "Modern human beings—''Homo sapiens''—originated in Africa. Then, interm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Ghats
The Eastern Ghats are a discontinuous range of mountains along India's eastern coast. The Eastern Ghats pass through Odisha, Andhra Pradesh to Tamil Nadu in the south passing some parts of Karnataka as well as Telangana. They are eroded and cut through by four major rivers of peninsular India, viz., Mahanadi, Godavari, Krishna, and Kaveri. Deomali with 1672 m height is the tallest point in Odisha. Arma Konda/Jindhagada Peak with 1680 m is the highest point in Andhra Pradesh. BR hill range located in Karnataka is the tallest hill range in Eastern Ghats with many peaks above 1750 m height. Kattahi betta in BR hills with the height of 1822 m is the tallest peak in Eastern Ghats. Thalamalai hill range in Tamil Nadu is the second tallest hill range. Araku range is the third tallest hill range. Geology The Eastern Ghats are made up of charnockites, granite gneiss, khondalites, metamorphic gneisses and quartzite rock formations. The structure of the Eastern Ghats i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vindhya Mountains
The Vindhya Range (also known as Vindhyachal) () is a complex, discontinuous chain of mountain ridges, hill ranges, highlands and plateau escarpments in west-central India. Technically, the Vindhyas do not form a single mountain range in the geological sense. The exact extent of the Vindhyas is loosely defined, and historically, the term covered a number of distinct hill systems in central India, including the one that is now known as the Satpura Range. Today, the term principally refers to the escarpment and its hilly extensions that runs north of and roughly parallel to the Narmada River in Madhya Pradesh. Depending on the definition, the range extends up to Gujarat in the west, Uttar Pradesh and Bihar in the north, and Chhattisgarh in the east. The Vindhyas have a great significance in Indian mythology and history. Several ancient texts mention the Vindhyas as the southern boundary of the ''Āryāvarta'', the territory of the ancient Indo-Aryan peoples. Although today I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aravali Range
The Aravalli Range (also spelled ''Aravali'') is a mountain range in Northern-Western India, running approximately in a south-west direction, starting near Delhi, passing through southern Haryana, Rajasthan, and ending in Ahmedabad Gujarat. The highest peak is Guru Shikhar on Mount Abu at . The Aravalli Range is arguably the oldest geological feature on Earth, having its origin in the Proterozoic era. The Aravalli Range is rich in natural resources and serves as check to the growth of the western desert. Etymology Aravalli, a composite Sanskrit word from the roots ''"ara"'' and ''"vali"'', literally means the ''"line of peaks"''. Natural history Geology The Aravalli Range, an eroded stub of ancient mountains, is believed to be the oldest range of fold mountains in India.Roy, A. B. (1990). Evolution of the Precambrian crust of the Aravalli Range. Developments in Precambrian Geology, 8, 327–347. The natural history of the Aravalli Range dates back to times when ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Himalayas
The Himalayas, or Himalaya (; ; ), is a mountain range in Asia, separating the plains of the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau. The range has some of the planet's highest peaks, including the very highest, Mount Everest. Over 100 peaks exceeding in elevation lie in the Himalayas. By contrast, the highest peak outside Asia (Aconcagua, in the Andes) is tall. The Himalayas abut or cross five countries: Bhutan, India, Nepal, China, and Pakistan. The sovereignty of the range in the Kashmir region is disputed among India, Pakistan, and China. The Himalayan range is bordered on the northwest by the Karakoram and Hindu Kush ranges, on the north by the Tibetan Plateau, and on the south by the Indo-Gangetic Plain. Some of the world's major rivers, the Indus, the Ganges, and the Tsangpo–Brahmaputra, rise in the vicinity of the Himalayas, and their combined drainage basin is home to some 600 million people; 53 million people live in the Himalayas. The Himalayas have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coastal Reservoir
Coastal reservoir is a type of reservoir to store fresh water on sea coast area near a river delta. Saemanguem in South Korea, Marina Barrage in Singapore, Qingcaosha and Plover Cove in China, Delta Works in Netherlands, Thanneermukkom Bund in India etc. are a few existing coastal reservoirs. Advantages Unlike land-based water reservoirs, there is no land submergence in the case of coastal reservoirs. They store water without disturbing people and natural habitat by replacing standing salt water on the sea area by river flood water. The coastal reservoir area is separated from the sea by building earth dikes by dredging. Water is pumped from these reservoirs for irrigation, municipal and industrial purposes. Sometimes used for flood control and land reclamation from the sea coast. The social and environmental impacts of coastal reservoirs are negligible compared to land-based water reservoirs. The construction cost is a few times less than the cost of land-based reservoirs since ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Groundwater Resources
Water resources are natural resources of water that are potentially useful for humans, for example as a source of drinking water supply or irrigation water. 97% of the water on the Earth is salt water and only three percent is fresh water; slightly over two thirds of this is frozen in glaciers and polar ice caps. The remaining unfrozen freshwater is found mainly as groundwater, with only a small fraction present above ground or in the air. Natural sources of fresh water include surface water, under river flow, groundwater and frozen water. Artificial sources of fresh water can include treated wastewater (wastewater reuse) and desalinated seawater. Human uses of water resources include agricultural, industrial, household, recreational and environmental activities. Water resources are under threat from water scarcity, water pollution, water conflict and climate change. Fresh water is a renewable resource, yet the world's supply of groundwater is steadily decreasing, with depletion o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |