Coastal reservoir on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Coastal reservoir is a type of
Coastal reservoir is a type of
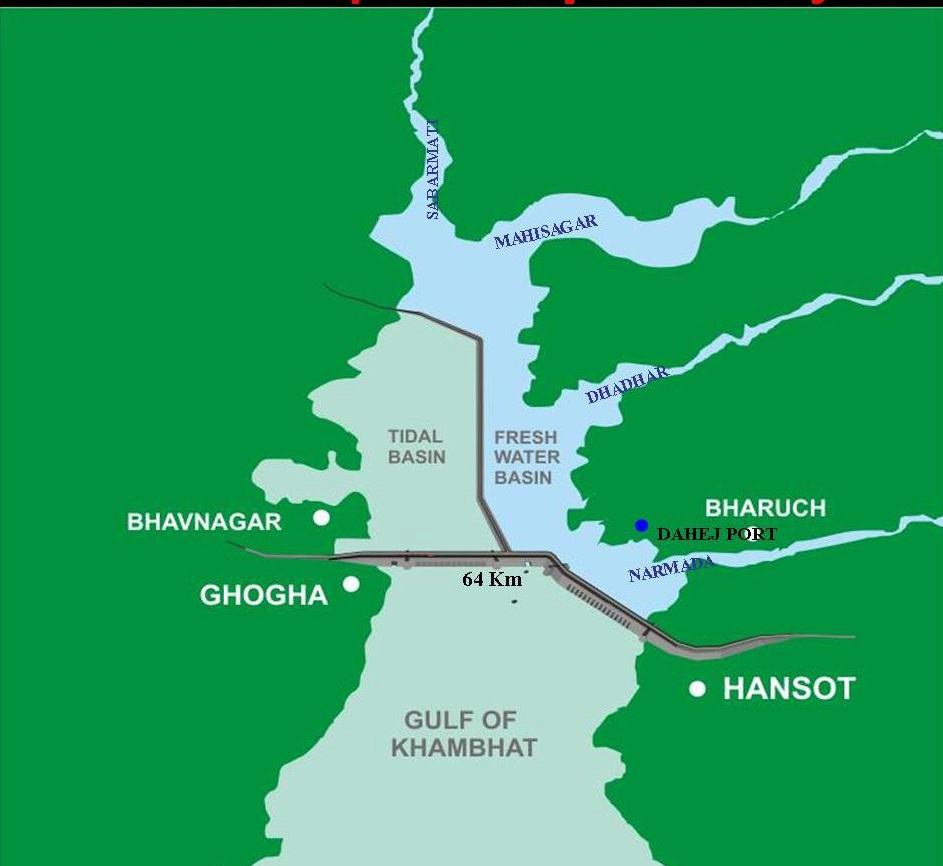 The coastal reservoir's earth dikes extending up to 8 m msl high, is in the form of two parallel dikes separated by 1000 meters gap. The main purpose of the twin dikes is to prevent any sea water seepage into coastal reservoirs as its water level is below the sea water level. The water level between the dikes is always maintained up to 2 m above sea level by pumping fresh water from the coastal reservoir to the 1000 m gap between the dikes. The higher level freshwater barrier between the two dikes fully eliminates any sea water seepage into the coastal reservoir by establishing freshwater seepage to the sea. The rainwater falling on the coastal reservoir area and the runoff water from the catchment area of its minor coastal rivers are adequate to cater to the seepage and evaporation losses from the coastal reservoir. The 1000 m gap between the two dikes is also used as deep water mega harbor for shipping, ship breaking, shipbuilding, safe berthing of crude oil, LPG,
The coastal reservoir's earth dikes extending up to 8 m msl high, is in the form of two parallel dikes separated by 1000 meters gap. The main purpose of the twin dikes is to prevent any sea water seepage into coastal reservoirs as its water level is below the sea water level. The water level between the dikes is always maintained up to 2 m above sea level by pumping fresh water from the coastal reservoir to the 1000 m gap between the dikes. The higher level freshwater barrier between the two dikes fully eliminates any sea water seepage into the coastal reservoir by establishing freshwater seepage to the sea. The rainwater falling on the coastal reservoir area and the runoff water from the catchment area of its minor coastal rivers are adequate to cater to the seepage and evaporation losses from the coastal reservoir. The 1000 m gap between the two dikes is also used as deep water mega harbor for shipping, ship breaking, shipbuilding, safe berthing of crude oil, LPG,
reservoir
A reservoir (; from French ''réservoir'' ) is an enlarged lake behind a dam. Such a dam may be either artificial, built to store fresh water or it may be a natural formation.
Reservoirs can be created in a number of ways, including contro ...
to store fresh water on sea coast area near a river delta
A river delta is a landform shaped like a triangle, created by deposition (geology), deposition of sediment that is carried by a river and enters slower-moving or stagnant water. This occurs where a river enters an ocean, sea, estuary, lake, res ...
. Saemanguem in South Korea, Marina Barrage
Marina Barrage is a dam in southern Singapore built at the confluence of five rivers, across the Marina Channel between Marina East and Marina South.
First conceptualised in 1987 by then prime minister Lee Kuan Yew to help achieve greater self-s ...
in Singapore, Qingcaosha and Plover Cove
Plovers ( , ) are a widely distributed group of wading birds belonging to the subfamily Charadriinae.
Description
There are about 66 species in the subfamily, most of them called "plover" or "dotterel". The closely related lapwing subf ...
in China, Delta Works
The Delta Works ( nl, Deltawerken) is a series of construction projects in the southwest of the Netherlands to protect a large area of land around the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta from the sea. Constructed between 1954 and 1997, the works con ...
in Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
, Thanneermukkom Bund
The Thanneermukkom Bund (Thannermukkom Salt Water Barrier) was constructed as a part of the Kuttanad Development Scheme to prevent tidal action and intrusion of salt water into the Kuttanad low-lands across Vembanad Lake between Thannermukkom on ...
in India etc. are a few existing coastal reservoirs.
Advantages
Unlike land-based water reservoirs, there is no land submergence in the case of coastal reservoirs. They store water without disturbing people and natural habitat by replacing standing salt water on the sea area by river flood water. The coastal reservoir area is separated from the sea by building earthdike
Dyke (UK) or dike (US) may refer to:
General uses
* Dyke (slang), a slang word meaning "lesbian"
* Dike (geology), a subvertical sheet-like intrusion of magma or sediment
* Dike (mythology), ''Dikē'', the Greek goddess of moral justice
* Dikes ...
s by dredging
Dredging is the excavation of material from a water environment. Possible reasons for dredging include improving existing water features; reshaping land and water features to alter drainage, navigability, and commercial use; constructing da ...
. Water is pumped from these reservoirs for irrigation, municipal and industrial purposes. Sometimes used for flood control and land reclamation
Land reclamation, usually known as reclamation, and also known as land fill (not to be confused with a waste landfill), is the process of creating new land from oceans, seas, riverbeds or lake beds. The land reclaimed is known as reclamati ...
from the sea coast. The social and environmental impacts of coastal reservoirs are negligible compared to land-based water reservoirs. The construction cost is a few times less than the cost of land-based reservoirs since there is no expenditure for acquiring the vast land area, the submerged immovable properties and the rehabilitation of displaced people. The sea side of the coastal reservoir can also be used for locating the deep sea harbor
A harbor (American English), harbour (British English; see spelling differences), or haven is a sheltered body of water where ships, boats, and barges can be docked. The term ''harbor'' is often used interchangeably with ''port'', which is a ...
.
Construction
 The coastal reservoir's earth dikes extending up to 8 m msl high, is in the form of two parallel dikes separated by 1000 meters gap. The main purpose of the twin dikes is to prevent any sea water seepage into coastal reservoirs as its water level is below the sea water level. The water level between the dikes is always maintained up to 2 m above sea level by pumping fresh water from the coastal reservoir to the 1000 m gap between the dikes. The higher level freshwater barrier between the two dikes fully eliminates any sea water seepage into the coastal reservoir by establishing freshwater seepage to the sea. The rainwater falling on the coastal reservoir area and the runoff water from the catchment area of its minor coastal rivers are adequate to cater to the seepage and evaporation losses from the coastal reservoir. The 1000 m gap between the two dikes is also used as deep water mega harbor for shipping, ship breaking, shipbuilding, safe berthing of crude oil, LPG,
The coastal reservoir's earth dikes extending up to 8 m msl high, is in the form of two parallel dikes separated by 1000 meters gap. The main purpose of the twin dikes is to prevent any sea water seepage into coastal reservoirs as its water level is below the sea water level. The water level between the dikes is always maintained up to 2 m above sea level by pumping fresh water from the coastal reservoir to the 1000 m gap between the dikes. The higher level freshwater barrier between the two dikes fully eliminates any sea water seepage into the coastal reservoir by establishing freshwater seepage to the sea. The rainwater falling on the coastal reservoir area and the runoff water from the catchment area of its minor coastal rivers are adequate to cater to the seepage and evaporation losses from the coastal reservoir. The 1000 m gap between the two dikes is also used as deep water mega harbor for shipping, ship breaking, shipbuilding, safe berthing of crude oil, LPG, LNG
Liquefied natural gas (LNG) is natural gas (predominantly methane, CH4, with some mixture of ethane, C2H6) that has been cooled down to liquid form for ease and safety of non-pressurized storage or transport. It takes up about 1/600th the volu ...
, etc. ships with floating storage options, etc. For shipping purposes, the breakwater
Breakwater may refer to:
* Breakwater (structure), a structure for protecting a beach or harbour
Places
* Breakwater, Victoria, a suburb of Geelong, Victoria, Australia
* Breakwater Island
Breakwater Island () is a small island in the Palme ...
outer dike facing the sea is envisaged with a few locks
Lock(s) may refer to:
Common meanings
*Lock and key, a mechanical device used to secure items of importance
*Lock (water navigation), a device for boats to transit between different levels of water, as in a canal
Arts and entertainment
* ''Lock ...
fitted with twin gates for access to the open sea. The top surface of the inner dike would serve as access to the mainland from the mega harbor
A harbor (American English), harbour (British English; see spelling differences), or haven is a sheltered body of water where ships, boats, and barges can be docked. The term ''harbor'' is often used interchangeably with ''port'', which is a ...
with rail and road links. The coastal reservoir whose full reservoir water level (FRL) is at 0.0 m MSL, would also drastically reduce the cyclone damage and flooding in coastal areas. It would also greatly improve the irrigated coastal lands drainage. The dikes of coastal reservoirs would also reclaim coastal lands by giving protection from tsunami
A tsunami ( ; from ja, 津波, lit=harbour wave, ) is a series of waves in a water body caused by the displacement of a large volume of water, generally in an ocean or a large lake. Earthquakes, volcanic eruptions and other underwater explo ...
s, storm surge
A storm surge, storm flood, tidal surge, or storm tide is a coastal flood or tsunami-like phenomenon of rising water commonly associated with low-pressure weather systems, such as cyclones. It is measured as the rise in water level above the n ...
s and tidal bore
Tidal is the adjectival form of tide.
Tidal may also refer to:
* ''Tidal'' (album), a 1996 album by Fiona Apple
* Tidal (king), a king involved in the Battle of the Vale of Siddim
* TidalCycles, a live coding environment for music
* Tidal (servic ...
s. The coastal reservoir area can also be used for locating floating solar
Floating solar or floating photovoltaics (FPV), sometimes called floatovoltaics, is solar panels mounted on a structure that floats on a body of water, typically a reservoir or a lake.
The market for this renewable energy technology has grown rap ...
power plants to generate the needed water pumping power. Also top surface of the inner dike of the coastal reservoirs can be used as transnational highway
A highway is any public or private road or other public way on land. It is used for major roads, but also includes other public roads and public tracks. In some areas of the United States, it is used as an equivalent term to controlled-access ...
s & railways
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a pre ...
. Coastal reservoirs are truly multi-purpose infrastructure projects with shipping & transport, land reclamation
Land reclamation, usually known as reclamation, and also known as land fill (not to be confused with a waste landfill), is the process of creating new land from oceans, seas, riverbeds or lake beds. The land reclaimed is known as reclamati ...
, irrigation, renewable power generation, etc. facilities.
The dikes are built by dredging
Dredging is the excavation of material from a water environment. Possible reasons for dredging include improving existing water features; reshaping land and water features to alter drainage, navigability, and commercial use; constructing da ...
sand and clay from the nearby shallow sea bed using dredgers fueled by LNG or Hydrogen fuel cells
A fuel cell is an electrochemical cell that converts the chemical energy of a fuel (often hydrogen fuel, hydrogen) and an oxidizing agent (often oxygen) into electricity through a pair of redox reactions. Fuel cells are different from most bat ...
or battery power
An electric battery is a source of electric power consisting of one or more electrochemical cells with external connections for powering electrical devices.
When a battery is supplying power, its positive terminal is the cathode and its negati ...
to reduce the construction cost. Major river water would be diverted in a controlled manner to the coastal reservoirs from their delta channels or by flood flow canals by constructing barrages across the major rivers. Their excessive flood flows are directly routed to the sea. The coastal reservoirs located on either side of a major river course/path are interconnected by submarine ducts/pipes of suitable length. Wherever existing ports/waterways and famous beach resorts are to be preserved, the long coastal reservoir is broken into parts and interconnected by submarine ducts of suitable length. During lean flow periods, minimum environmental flows would be maintained in medium and major rivers up to sea by letting water into the sea directly or via submarine ducts of suitable length. It would also prevent deterioration of water quality in coastal reservoirs by preventing the inflow of inferior quality river waters with higher salt load. For inland shipping, the deep water ports (1000 m wide) would be connected with locks arrangement to the major rivers via delta channels and to the adjacent coastal reservoir. Fish migration to and fro to the sea or rivers is possible as the rivers are not completely blocked. Navigation paths from sea to the river via deep sea port will also serve as fish migration routes. However the negative aspects of these man-made lagoons are to be evaluated in detail and proper remedial steps shall be incorporated to minimize the damage to the coastal ecosystem by the presence of freshwater lagoon as a barrier to the sea.
Proposed projects
There are vast deserts on all continents (western part of South America, northern and southwestern Africa, middle east in Asia, southwestern part of USA, Australia, etc.) and also water surplus regions nearer to these deserts. It is technically and economically feasible to construct man-made freshwater coastal reservoirs/lagoons on thecontinental shelf
A continental shelf is a portion of a continent that is submerged under an area of relatively shallow water, known as a shelf sea. Much of these shelves were exposed by drops in sea level during glacial periods. The shelf surrounding an island ...
of the sea up to 20 meters depth from the coastline to supply fresh water to desert areas from nearby water surplus/high rainfall areas. Excess water from the high rainfall regions will be collected in the coastal reservoirs at sea level and this fresh water is pumped to irrigate desert lands from the other end of the lengthy coastal reservoirs. In other words, the proposal is interconnecting rivers with a sea level / sub-sea level contour canal A contour canal is an artificially-dug navigable canal which closely follows the contour line of the land it traverses in order to avoid costly engineering works such as boring a tunnel through higher ground, building an embankment over lower ground ...
(at least five km wide) to facilitate water transfer.
The following are the proposed projects:
* The Reber plan
The Reber Plan was a late 1940s plan to fill in parts of the San Francisco Bay. It was designed and advocated by John Reber—an actor, theatrical producer, and schoolteacher.
San Francisco Bay Project
Under the plan, which was also known as the ...
involved damming the San Francisco Bay
San Francisco Bay is a large tidal estuary in the U.S. state of California, and gives its name to the San Francisco Bay Area. It is dominated by the big cities of San Francisco, San Jose, and Oakland.
San Francisco Bay drains water from a ...
near the Golden Gate
The Golden Gate is a strait on the west coast of North America that connects San Francisco Bay to the Pacific Ocean. It is defined by the headlands of the San Francisco Peninsula and the Marin Peninsula, and, since 1937, has been spanned by th ...
, in order to transform the San Francisco Bay into a giant freshwater reservoir that could be used to provide potable water and irrigation for the entire state of California
California is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States, located along the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the List of states and territori ...
.
* Hangzhou Bay
Hangzhou Bay, or the Bay of Hangzhou (), is a funnel-shaped inlet of the East China Sea, bordered by the province of Zhejiang and the municipality of Shanghai, which lies north of the Bay. The Bay extends from the East China Sea to its head a ...
area in south eastern China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
can be used for a coastal reservoir to store flood water of Yangtze River
The Yangtze or Yangzi ( or ; ) is the longest list of rivers of Asia, river in Asia, the list of rivers by length, third-longest in the world, and the longest in the world to flow entirely within one country. It rises at Jari Hill in th ...
for the needs of agriculture, city water supply, etc. in entire China.
* Water transfer from the west central Africa (Congo River
The Congo River ( kg, Nzâdi Kôngo, french: Fleuve Congo, pt, Rio Congo), formerly also known as the Zaire River, is the second longest river in Africa, shorter only than the Nile, as well as the second largest river in the world by discharge ...
basin, etc.) to Northern Africa (Sahara desert
, photo = Sahara real color.jpg
, photo_caption = The Sahara taken by Apollo 17 astronauts, 1972
, map =
, map_image =
, location =
, country =
, country1 =
, ...
) and South West Africa (Namibia
Namibia (, ), officially the Republic of Namibia, is a country in Southern Africa. Its western border is the Atlantic Ocean. It shares land borders with Zambia and Angola to the north, Botswana to the east and South Africa to the south and ea ...
and South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the north by the neighbouring countri ...
deserts)
* Water transfer from the south east Africa (Zambezi River
The Zambezi River (also spelled Zambeze and Zambesi) is the fourth-longest river in Africa, the longest east-flowing river in Africa and the largest flowing into the Indian Ocean from Africa. Its drainage basin covers , slightly less than hal ...
basin, etc.) to North east Africa (Somalia
Somalia, , Osmanya script: 𐒈𐒝𐒑𐒛𐒐𐒘𐒕𐒖; ar, الصومال, aṣ-Ṣūmāl officially the Federal Republic of SomaliaThe ''Federal Republic of Somalia'' is the country's name per Article 1 of thProvisional Constituti ...
, Ethiopia
Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ኢትዮጵያ, Ítiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the ...
, Sudan
Sudan ( or ; ar, السودان, as-Sūdān, officially the Republic of the Sudan ( ar, جمهورية السودان, link=no, Jumhūriyyat as-Sūdān), is a country in Northeast Africa. It shares borders with the Central African Republic t ...
, Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediter ...
, etc.).
* Water transfer from the northern part of the South America continent from Venezuela
Venezuela (; ), officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela ( es, link=no, República Bolivariana de Venezuela), is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in th ...
, Colombia
Colombia (, ; ), officially the Republic of Colombia, is a country in South America with insular regions in North America—near Nicaragua's Caribbean coast—as well as in the Pacific Ocean. The Colombian mainland is bordered by the Car ...
and Panama
Panama ( , ; es, link=no, Panamá ), officially the Republic of Panama ( es, República de Panamá), is a transcontinental country spanning the southern part of North America and the northern part of South America. It is bordered by Cos ...
to desert lands of Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in the western part of South America. It is the southernmost country in the world, and the closest to Antarctica, occupying a long and narrow strip of land between the Andes to the east a ...
and Peru
, image_flag = Flag of Peru.svg
, image_coat = Escudo nacional del Perú.svg
, other_symbol = Great Seal of the State
, other_symbol_type = Seal (emblem), National seal
, national_motto = "Fi ...
by interconnecting Atrato
Atrato is a municipality and town in the Chocó Department near the Pacific Ocean, Colombia.
Climate
Atrato has an extremely wet tropical rainforest climate
A tropical rainforest climate, humid tropical climate or equatorial climate is a trop ...
and Tuira rivers to lift/transfer water from the side of Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean.
* Water transfer from Fly
Flies are insects of the Order (biology), order Diptera, the name being derived from the Ancient Greek, Greek δι- ''di-'' "two", and πτερόν ''pteron'' "wing". Insects of this order use only a single pair of wings to fly, the hindwing ...
, Kikori
Kikori is a small town in the Gulf Province of Papua New Guinea.
Kikori lies in the delta of the Kikori River at the head of the Gulf of Papua. This area is particularly biologically rich with a diversity of ecosystems and densely forested, wit ...
, Purari, etc. rivers of the Papua New Guinea
Papua New Guinea (abbreviated PNG; , ; tpi, Papua Niugini; ho, Papua Niu Gini), officially the Independent State of Papua New Guinea ( tpi, Independen Stet bilong Papua Niugini; ho, Independen Stet bilong Papua Niu Gini), is a country i ...
island to Northern Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, sma ...
by blocking the shallow depth sea of Torres Strait
The Torres Strait (), also known as Zenadh Kes, is a strait between Australia and the Melanesian island of New Guinea. It is wide at its narrowest extent. To the south is Cape York Peninsula, the northernmost extremity of the Australian mai ...
between southern Papua New Guinea and Northern tip of Australia. For navigation purposes, a freshwater sea level navigation channel (20 m water depth and 500 m wide) is provided with locks at the entry to the sea to cross the coastal reservoir which is blocking the Torres Strait. The divided coastal reservoir into two parts is connected by underpass water tunnels for water transport.
* Water transfer from the north and south coastal areas of the western 'North America continent' to the southwestern region of the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
and central parts of Mexico
Mexico (Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the southeast by Guatema ...
.
* East to west Water transfer from a coastal reservoir on the Bay of Bengal sea to water deficit parts of India from Ganga
The Ganges ( ) (in India: Ganga ( ); in Bangladesh: Padma ( )). "The Ganges Basin, known in India as the Ganga and in Bangladesh as the Padma, is an international river to which India, Bangladesh, Nepal and China are the riparian states." is ...
and Bramhaputra flood waters.
* Water transfer from Andhra Pradesh
Andhra Pradesh (, abbr. AP) is a state in the south-eastern coastal region of India. It is the seventh-largest state by area covering an area of and tenth-most populous state with 49,386,799 inhabitants. It is bordered by Telangana to the ...
state in India from Krishna
Krishna (; sa, कृष्ण ) is a major deity in Hinduism. He is worshipped as the eighth avatar of Vishnu and also as the Supreme god in his own right. He is the god of protection, compassion, tenderness, and love; and is one ...
and Godavari
The Godavari ( IAST: ''Godāvarī'' �od̪aːʋəɾiː is India's second longest river after the Ganga river and drains into the third largest basin in India, covering about 10% of India's total geographical area. Its source is in Trimbakesh ...
rivers flood waters to Tamil Nadu
Tamil Nadu (; , TN) is a States and union territories of India, state in southern India. It is the List of states and union territories of India by area, tenth largest Indian state by area and the List of states and union territories of India ...
state in India with a coastal reservoir on Bay of Bengal
The Bay of Bengal is the northeastern part of the Indian Ocean, bounded on the west and northwest by India, on the north by Bangladesh, and on the east by Myanmar and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands of India. Its southern limit is a line between ...
sea.
* Water transfer from India and Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka (, ; si, ශ්රී ලංකා, Śrī Laṅkā, translit-std=ISO (); ta, இலங்கை, Ilaṅkai, translit-std=ISO ()), formerly known as Ceylon and officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, is an ...
to Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 24 ...
and Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
with lengthy coastal reservoir on Arabian sea
The Arabian Sea ( ar, اَلْبَحرْ ٱلْعَرَبِيُّ, Al-Bahr al-ˁArabī) is a region of the northern Indian Ocean bounded on the north by Pakistan, Iran and the Gulf of Oman, on the west by the Gulf of Aden, Guardafui Channel ...
along the west coast of India from Rameshwaram
Rameswaram (; also transliterated as Ramesvaram, Rameshwaram) is a municipality in the Ramanathapuram district of the Indian state of Tamil Nadu. It is on Pamban Island separated from mainland India by the Pamban channel and is about 40 kilo ...
to Strait of Hormuz
The Strait of Hormuz ( fa, تنگه هرمز ''Tangeh-ye Hormoz'' ar, مَضيق هُرمُز ''Maḍīq Hurmuz'') is a strait between the Persian Gulf and the Gulf of Oman. It provides the only sea passage from the Persian Gulf to the ...
.
The above gigantic coastal reservoir projects would cover most of the desert areas of the world except the high lands of central Asian deserts. Water needs of these areas can be fully met by diverting water of Siberian rivers. Thus most of the lands which are not available for cultivation and forestry can be turned in to a habitat to copious greenery which would help to mitigate the global warming process. With the advent of cheap renewable energy
Renewable energy is energy that is collected from renewable resources that are naturally replenished on a human timescale. It includes sources such as sunlight, wind, the movement of water, and geothermal heat. Although most renewable energy ...
like solar and wind power, availability of energy sources is not an ongoing issue but water availability is still a major issue that can be solved by coastal reservoirs to a major extent.
See also
*List of rivers by discharge
This is a list of rivers by their average discharge (that is, their water flow rate). Here, only those rivers whose discharge is more than are shown, as this list does not concern itself with rivers having a water flow rate of less than .
For c ...
* List of largest unfragmented rivers
This is a list of the largest river basins without fragmentation by dams in their catchments, ordered by average annual discharge.
To qualify for inclusion, a river must not only have no dams on its “main” stem, but also no dams on any tributa ...
* Polavaram Project
The ''Polavaram Project'' is an under construction multi-purpose irrigation project on the Godavari River in the Eluru District and East Godavari District in Andhra Pradesh. The project has been accorded National Project of India, National pro ...
* Pollution of the Ganges
Pollution of the Ganges, the largest river in India, poses significant threats to human health and the larger environment. The river, which is severely polluted with human waste and industrial contaminants, provides water to about 40% of In ...
* Water export
Water exports involve exporting freshwater from one country to another. Large increases in human population and economic growth throughout the world during the twentieth century placed a huge stress on the world’s freshwater resources. Combine ...
References
{{reflist Reservoirs Lakes by type Bodies of water