|
Waste Input-output Model
The Waste Input-Output (WIO) model is an innovative extension of the Environmentally extended input-output analysis, environmentally extended input-output (EEIO) model. It enhances the traditional Input-Output (IO) model by incorporating physical waste flows generated and treated alongside monetary flows of products and services. In a WIO model, each waste flow is traced from its generation to its treatment, facilitated by an allocation matrix. Additionally, the model accounts for the transformation of waste during treatment into secondary waste and residues, as well as recycling and final disposal processes. By including the end-of-life (EoL) stage of products, the WIO model enables a comprehensive consideration of the entire product life cycle, encompassing production, use, and disposal stages within the IO analysis framework. As such, it serves as a valuable tool for life cycle assessment (LCA). Background With growing concerns about environmental issues, the EEIO model evolv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Environmentally Extended Input-output Analysis
Environment most often refers to: __NOTOC__ * Natural environment, referring respectively to all living and non-living things occurring naturally and the physical and biological factors along with their chemical interactions that affect an organism or a group of organisms Other physical and cultural environments *Ecology, the branch of ethology that deals with the relations of organisms to one another and to their physical surroundings *Environment (systems), the surroundings of a physical system that may interact with the system by exchanging mass, energy, or other properties. *Built environment, constructed surroundings that provide the settings for human activity, ranging from the large-scale civic surroundings to the personal places *Social environment, the culture that an individual lives in, and the people and institutions with whom they interact *Market environment, business term Arts, entertainment and publishing * Environment (magazine), ''Environment'' (magazine), a p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Material Flow Accounting
Material flow accounting (MFA) is the study of material flows on a national or regional scale. It is therefore sometimes also referred to as regional, national or economy-wide material flow analysis. Introduction Material flow accounting provides economy-wide data on material use. Through international standardization, this data has become reliable and comparable across countries. Increasingly, the data are also being made available in medium- to long-term time series allowing for the analysis of past trends as well as potential future developments. Material flow accounts provide information on the material inputs into, the changes in material stock within, and the material outputs in the form of exports to other economies or discharges to the environment of an economy. Material flow accounting can be used in national planning, especially for scarce resources, and also allows for forecasting. The method can be used to assess environmental burdens associated with the economic activi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economic Planning
Economic planning is a resource allocation mechanism based on a computational procedure for solving a constrained maximization problem with an iterative process for obtaining its solution. Planning is a mechanism for the allocation of resources between and within organizations contrasted with the Market (economics), market mechanism. As an allocation mechanism for socialism, economic planning replaces factor markets with a procedure for direct allocations of resources within an interconnected group of Social ownership, socially owned organizations which together comprise the productive apparatus of the economy. There are various forms of economic planning that vary based on their specific procedures and approach. The level of centralization or decentralization in decision-making depends on the specific type of planning mechanism employed. In addition, one can distinguish between centralized planning and decentralized planning. An economy primarily based on planning is referred to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economics Models
Economics () is a behavioral science that studies the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. Economics focuses on the behaviour and interactions of economic agents and how economies work. Microeconomics analyses what is viewed as basic elements within economies, including individual agents and markets, their interactions, and the outcomes of interactions. Individual agents may include, for example, households, firms, buyers, and sellers. Macroeconomics analyses economies as systems where production, distribution, consumption, savings, and investment expenditure interact; and the factors of production affecting them, such as: labour, capital, land, and enterprise, inflation, economic growth, and public policies that impact these elements. It also seeks to analyse and describe the global economy. Other broad distinctions within economics include those between positive economics, describing "what is", and normative economics, advocating "wha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematical And Quantitative Methods (economics)
Mathematics is a field of study that discovers and organizes methods, theories and theorems that are developed and proved for the needs of empirical sciences and mathematics itself. There are many areas of mathematics, which include number theory (the study of numbers), algebra (the study of formulas and related structures), geometry (the study of shapes and spaces that contain them), analysis (the study of continuous changes), and set theory (presently used as a foundation for all mathematics). Mathematics involves the description and manipulation of abstract objects that consist of either abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicspurely abstract entities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. Mathematics uses pure reason to prove properties of objects, a ''proof'' consisting of a succession of applications of deductive rules to already established results. These results include previously proved theorems, axioms, andin case of abstracti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecological Economics
Ecological economics, bioeconomics, ecolonomy, eco-economics, or ecol-econ is both a transdisciplinary and an interdisciplinary field of academic research addressing the interdependence and coevolution of human economy, economies and natural ecosystems, both intertemporally and spatially. By treating the economy as a subsystem of Earth's larger ecosystem, and by emphasizing the preservation of natural capital, the field of ecological economics is differentiated from environmental economics, which is the mainstream economics, mainstream economic analysis of the environment. One survey of German economists found that ecological and environmental economics are different schools of economic thought, with ecological economists emphasizing strong sustainability and rejecting the proposition that Physical capital, physical (human-made) capital can substitute for natural capital (see the section on #Weak versus strong sustainability, weak versus strong sustainability below). Ecological ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Ministry Of The Environment
The is a Cabinet-level ministry of the government of Japan responsible for global environmental conservation, pollution control, and nature conservation. The ministry was formed in 2001 from the sub-cabinet level Environmental Agency established in 1971. The Minister of the Environment is a member of the Cabinet of Japan and is chosen by the Prime Minister, usually from among members of the Diet. In March 2006, the then-Minister of the Environment Yuriko Koike, created a ''furoshiki'' cloth to promote its use in the modern world. In August 2011, the Cabinet of Japan approved a plan to establish a new energy watchdog under the Environment Ministry, and the Nuclear Regulation Authority was founded on September 19, 2012. Organization * Minister's Secretariat (大臣官房) * (総合環境政策統括官) * Global Environment Bureau (地球環境局) * Environment Management Bureau (水・大気環境局) * Nature Conservation Bureau (自然環境局) * (環境再生・資源� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waste Treatment Technologies
There are a number of different waste treatment technologies for the disposal, recycling, storage, or energy recovery from different waste types. Each type has its own associated methods of waste management. Landfill Municipal solid waste consists mainly of household and commercial waste which is disposed of by or on behalf of a local authority. Landfills waste are categorized by either being hazardous, non-hazardous or inert waste. In order for a landfill design to be considered it must abide by the following requirements: final landforms profile, site capacity, settlement, waste density, materials requirements and drainage. Incineration The advantages of the incineration are reduction of volume and mass by burning, reduction to a percentage of sterile ash, source of energy, increase of income by selling bottom ash, and is also environmentally acceptable. The disadvantages of incineration are the following: * higher cost and longer payback period due to high capital investment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urban Metabolism
Urban metabolism (UM) is a model to facilitate the description and analysis of the flows of the materials and energy within cities, such as undertaken in a material flow analysis of a city. It provides researchers with a metaphorical framework to study the interactions of natural and human systems in specific regions.Pincetl, S., Bunje, P., & Holmes, T. (2012). An expanded urban metabolism method: Toward a systems approach for assessing urban energy processes and causes. Landscape and Urban Planning, 193-202. From the beginning, researchers have tweaked and altered the parameters of the urban metabolism model. C. Kennedy and fellow researchers have produced a clear definition in the 2007 paper ''The Changing Metabolism of Cities'' claiming that urban metabolism is "the sum total of the technical and socio-economic process that occur in cities, resulting in growth, production of energy and elimination of waste."Kennedy, C., Cuddihy, J., & Engel-Yan, J. (2007). The changing metabolis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
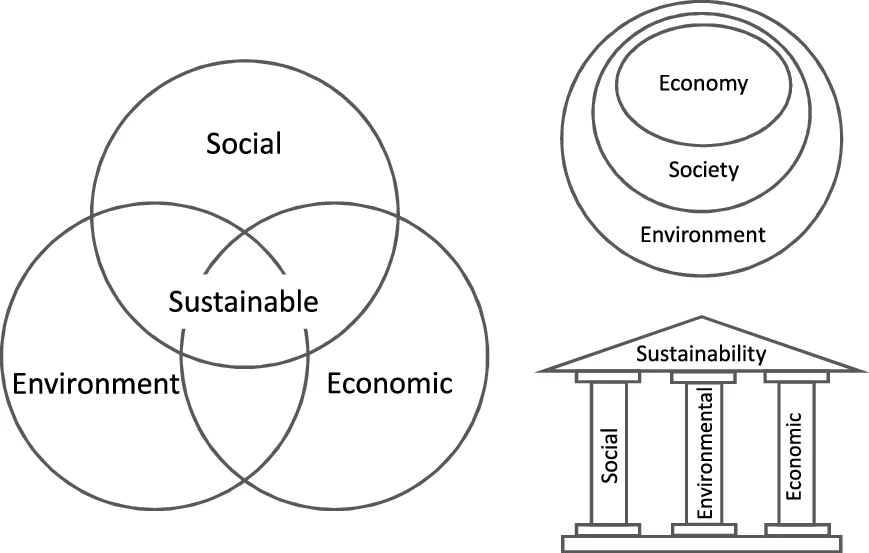
Sustainability
Sustainability is a social goal for people to co-exist on Earth over a long period of time. Definitions of this term are disputed and have varied with literature, context, and time. Sustainability usually has three dimensions (or pillars): environmental, economic, and social. Many definitions emphasize the environmental dimension. This can include addressing key environmental problems, including climate change and biodiversity loss. The idea of sustainability can guide decisions at the global, national, organizational, and individual levels. A related concept is that of sustainable development, and the terms are often used to mean the same thing. UNESCO distinguishes the two like this: "''Sustainability'' is often thought of as a long-term goal (i.e. a more sustainable world), while ''sustainable development'' refers to the many processes and pathways to achieve it." Details around the economic dimension of sustainability are controversial. Scholars have discussed this under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Metabolism
Social metabolism or socioeconomic metabolism is the set of flows of materials and energy that occur between nature and society, between different societies, and within societies. These human-controlled material and energy flows are a basic feature of all societies but their magnitude and diversity largely depend on specific cultures, or sociometabolic regimes. El metabolismo social: una nueva teoría socioecológica. Relaciones. 2013. Social or socioeconomic metabolism is also described as "the self-reproduction and evolution of the biophysical structures of human society. It comprises those biop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
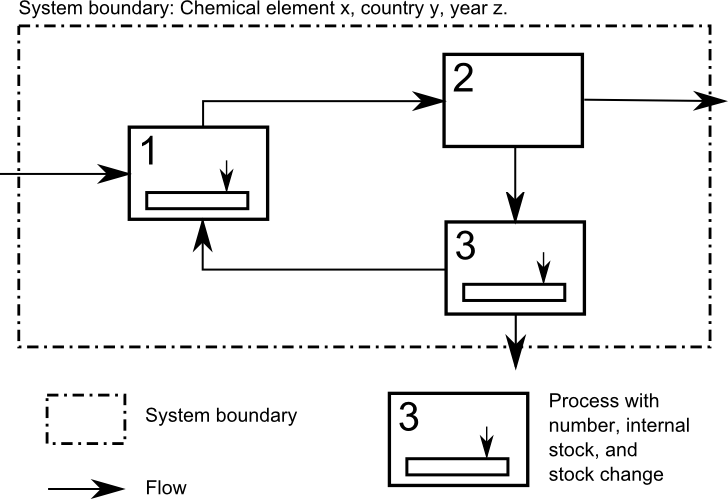
Material Flow Analysis
Material flow analysis (MFA), also referred to as substance flow analysis (SFA), is an analytical method to quantify flows and stocks of materials or substances in a well-defined system. MFA is an important tool to study the bio-physical aspects of human activity on different spatial and temporal scales. It is considered a core method of industrial ecology or anthropogenic metabolism, anthropogenic, urban metabolism, urban, social metabolism, social and industrial metabolism. MFA is used to study material, substance, or product flows across different industrial sectors or within ecosystems. MFA can also be applied to a single industrial installation, for example, for tracking nutrient flows through a waste water treatment plant. When combined with an assessment of the costs associated with material flows this business-oriented application of MFA is called material flow cost accounting. MFA is an important tool to study the circular economy and to devise material flow management. Sinc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |