material flow analysis on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Material flow analysis (MFA), also referred to as substance flow analysis (SFA), is an analytical method to quantify flows and stocks of materials or substances in a well-defined
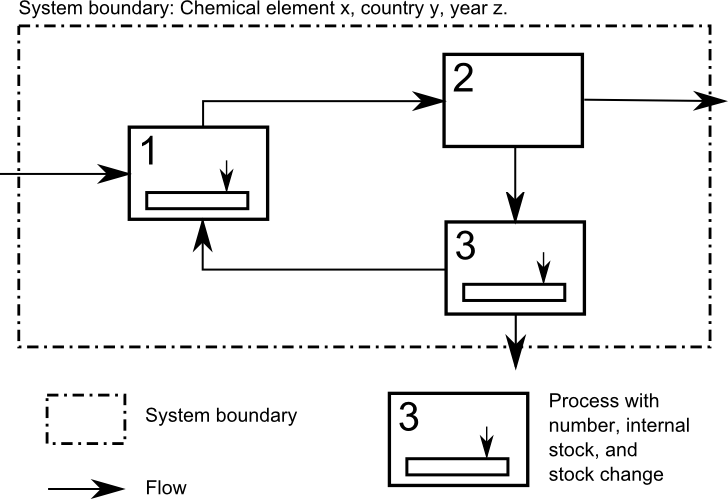
 An MFA system is a model of an industrial plant, an industrial sector or a region of concern. The level of detail of the system model is chosen to fit the purpose of the study. An MFA system always consists of the system boundary, one or more processes, material flows between processes, and stocks of materials within processes. Physical exchange between the system and its environment happens via flows that cross the system boundary. Contrary to the preconceived notion that a system represents a specific industrial installation, systems and processes in MFA can represent much larger and more abstract entities as long as they are well-defined. The explicit system definition helps the practitioner to locate the available quantitative information in the system, either as stocks within certain processes or as flows between processes. An MFA system description can be refined by disaggregating processes or simplified by aggregating processes.
Next to specifying the arrangement of processes, stocks, and flows in the system definition, the practitioner also needs to indicate the scale and the indicator element or material of the system studied.
The spatial scale describes the geographic entity that is covered by the system. A system representing a certain industrial sector can be applied to the USA, China, certain world regions, or the world as a whole.
The temporal scale describes the point in time or the time span for which the system is quantified.
The indicator element or material of the system is the physical entity that is measured and for which the mass balance holds. As the name says, an indicator element is a certain
An MFA system is a model of an industrial plant, an industrial sector or a region of concern. The level of detail of the system model is chosen to fit the purpose of the study. An MFA system always consists of the system boundary, one or more processes, material flows between processes, and stocks of materials within processes. Physical exchange between the system and its environment happens via flows that cross the system boundary. Contrary to the preconceived notion that a system represents a specific industrial installation, systems and processes in MFA can represent much larger and more abstract entities as long as they are well-defined. The explicit system definition helps the practitioner to locate the available quantitative information in the system, either as stocks within certain processes or as flows between processes. An MFA system description can be refined by disaggregating processes or simplified by aggregating processes.
Next to specifying the arrangement of processes, stocks, and flows in the system definition, the practitioner also needs to indicate the scale and the indicator element or material of the system studied.
The spatial scale describes the geographic entity that is covered by the system. A system representing a certain industrial sector can be applied to the USA, China, certain world regions, or the world as a whole.
The temporal scale describes the point in time or the time span for which the system is quantified.
The indicator element or material of the system is the physical entity that is measured and for which the mass balance holds. As the name says, an indicator element is a certain 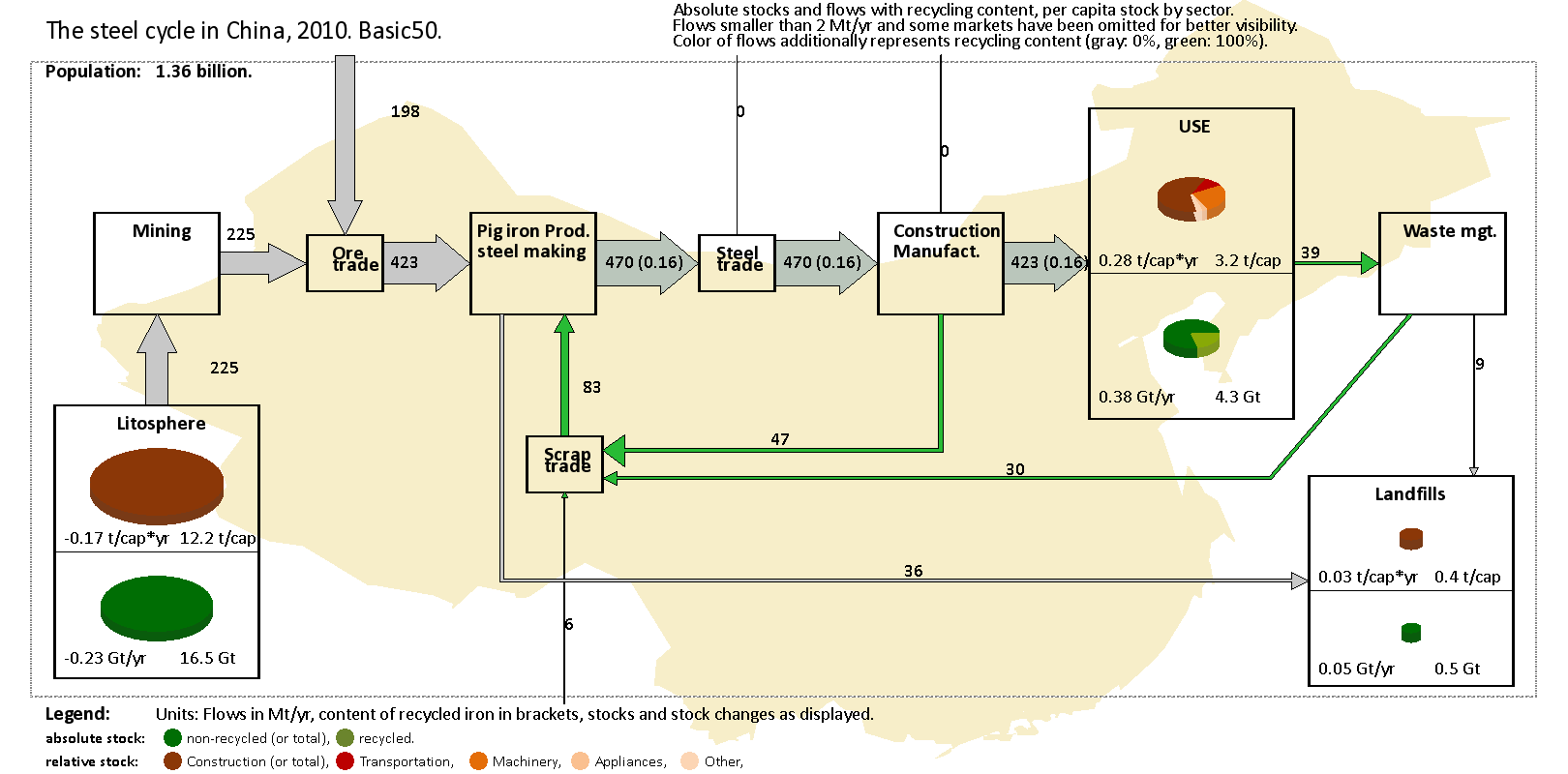
 The process balance is a first order physical principle that turns MFA into a powerful accounting and analysis tool. The nature of the processes in the system determine which balances apply. For a process '
The process balance is a first order physical principle that turns MFA into a powerful accounting and analysis tool. The nature of the processes in the system determine which balances apply. For a process '
Stefan Bringezu
specified this concept in economy-wide material flow analysis, as screening tool for product life-cycle assessment within a cross-scale framework. He defined indicators such as Total Material Requirement (formerly Total Material Input) and Raw Material Input, which are used to quantify the Material Footprint of products, infrastructures and countries. * The
CSIRO and UNEP Material Flow and Resource Productivity Database for Asia and the Pacific
materialflows.net
online portal for material flow data, providing access to material flow data sets on the national level * MFA is described in great detail and published on 166 pages in the first of four paper volumes co-edited with assistance from UNEP and in online form by th
Economy-wide Material Flow Analysis and Indicators
Material flow analysis in the context of environmental accounting
Online Material Flow Analysis Tool (OMAT)
online software to administer a Material Flow Analysis {{Systems science Environmental impact assessment Industrial ecology Environmental social science concepts
system
A system is a group of interacting or interrelated elements that act according to a set of rules to form a unified whole. A system, surrounded and influenced by its open system (systems theory), environment, is described by its boundaries, str ...
. MFA is an important tool to study the bio-physical aspects of human activity on different spatial and temporal scales. It is considered a core method of industrial ecology
Industrial ecology (IE) is the study of material and energy flows through industrial systems. The global industrial economy can be modelled as a network of industrial processes that extract resources from the Earth and transform those resource ...
or anthropogenic
Anthropogenic ("human" + "generating") is an adjective that may refer to:
* Anthropogeny, the study of the origins of humanity
Anthropogenic may also refer to things that have been generated by humans, as follows:
* Human impact on the enviro ...
, urban, social
Social organisms, including human(s), live collectively in interacting populations. This interaction is considered social whether they are aware of it or not, and whether the exchange is voluntary or not.
Etymology
The word "social" derives fro ...
and industrial metabolism. MFA is used to study material, substance, or product flows across different industrial sectors or within ecosystem
An ecosystem (or ecological system) is a system formed by Organism, organisms in interaction with their Biophysical environment, environment. The Biotic material, biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and en ...
s. MFA can also be applied to a single industrial installation, for example, for tracking nutrient
A nutrient is a substance used by an organism to survive, grow and reproduce. The requirement for dietary nutrient intake applies to animals, plants, fungi and protists. Nutrients can be incorporated into cells for metabolic purposes or excret ...
flows through a waste water treatment plant
Water treatment is any process that improves the quality of water to make it appropriate for a specific end-use. The end use may be drinking, industrial water supply, irrigation, river flow maintenance, water recreation or many other uses, inc ...
. When combined with an assessment of the costs associated with material flows this business-oriented application of MFA is called material flow cost accounting. MFA is an important tool to study the circular economy
A circular economy (also referred to as circularity or CE) is a model of resource Production (economics), production and Resource consumption, consumption in any economy that involves sharing, leasing, Reuse, reusing, repairing, refurbishing, and ...
and to devise material flow management. Since the 1990s, the number of publications related to material flow analysis has grown steadily. Peer-reviewed journals that publish MFA-related work include the '' Journal of Industrial Ecology'', ''Ecological Economics
Ecological economics, bioeconomics, ecolonomy, eco-economics, or ecol-econ is both a transdisciplinary and an interdisciplinary field of academic research addressing the interdependence and coevolution of human economy, economies and natural ec ...
'', '' Environmental Science and Technology'', and ''Resources, Conservation, and Recycling''.
Methodology
Motivation
Human needs such as shelter, food, transport, or communication require materials like wood, starch, sugar, iron and steel, copper, or semiconductors. As society develops and economic activity expands, material production, use, and disposal increase to a level where unwanted impacts on environment and society cannot beneglected
''Xestia castanea'', the grey rustic or neglected, is a moth of the family Noctuidae. It is found from central Europe to Morocco, Turkey, Lebanon, Israel, Jordan and Syria.
Technical description and variation
The wingspan is 36–42 mm. F ...
anymore, neither locally nor globally. Material flows are at the core of local environmental problems such as leaching from landfill
A landfill is a site for the disposal of waste materials. It is the oldest and most common form of waste disposal, although the systematic burial of waste with daily, intermediate and final covers only began in the 1940s. In the past, waste was ...
s or oil spill
An oil spill is the release of a liquid petroleum hydrocarbon into the environment, especially the marine ecosystem, due to human activity, and is a form of pollution. The term is usually given to marine oil spills, where oil is released into th ...
s. Rising concern about global warming
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes ...
puts a previously unimportant waste flow, carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalent bond, covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in a gas state at room temperature and at norma ...
, on top of the political and scientific agenda.
The gradual shift from primary material production to urban mining in developed countries requires a detailed assessment of in-use and obsolete stocks of materials within human society.
Scientists, industries, government bodies, and NGOs therefore need a tool that complements economic accounting and modelling. They need a systematic method to keep track of and display stocks and flows of the materials entering, staying within, and leaving the different processes in the anthroposphere
The anthroposphere refers to that part of the Earth system that is made or modified by humans for use in human activities and human habitats. The term has been suggested for inclusion as one of the Earth's spheres, while others use the related te ...
. Material flow analysis is such a method.
Basic principles
MFA is based on two fundamental and well-established scientific principles, thesystem
A system is a group of interacting or interrelated elements that act according to a set of rules to form a unified whole. A system, surrounded and influenced by its open system (systems theory), environment, is described by its boundaries, str ...
s approach and mass balance
In physics, a mass balance, also called a material balance, is an application of conservation of mass to the analysis of physical systems. By accounting for material entering and leaving a system, mass flows can be identified which might have ...
.
The system definition is the starting point of every MFA study.
System definition

 An MFA system is a model of an industrial plant, an industrial sector or a region of concern. The level of detail of the system model is chosen to fit the purpose of the study. An MFA system always consists of the system boundary, one or more processes, material flows between processes, and stocks of materials within processes. Physical exchange between the system and its environment happens via flows that cross the system boundary. Contrary to the preconceived notion that a system represents a specific industrial installation, systems and processes in MFA can represent much larger and more abstract entities as long as they are well-defined. The explicit system definition helps the practitioner to locate the available quantitative information in the system, either as stocks within certain processes or as flows between processes. An MFA system description can be refined by disaggregating processes or simplified by aggregating processes.
Next to specifying the arrangement of processes, stocks, and flows in the system definition, the practitioner also needs to indicate the scale and the indicator element or material of the system studied.
The spatial scale describes the geographic entity that is covered by the system. A system representing a certain industrial sector can be applied to the USA, China, certain world regions, or the world as a whole.
The temporal scale describes the point in time or the time span for which the system is quantified.
The indicator element or material of the system is the physical entity that is measured and for which the mass balance holds. As the name says, an indicator element is a certain
An MFA system is a model of an industrial plant, an industrial sector or a region of concern. The level of detail of the system model is chosen to fit the purpose of the study. An MFA system always consists of the system boundary, one or more processes, material flows between processes, and stocks of materials within processes. Physical exchange between the system and its environment happens via flows that cross the system boundary. Contrary to the preconceived notion that a system represents a specific industrial installation, systems and processes in MFA can represent much larger and more abstract entities as long as they are well-defined. The explicit system definition helps the practitioner to locate the available quantitative information in the system, either as stocks within certain processes or as flows between processes. An MFA system description can be refined by disaggregating processes or simplified by aggregating processes.
Next to specifying the arrangement of processes, stocks, and flows in the system definition, the practitioner also needs to indicate the scale and the indicator element or material of the system studied.
The spatial scale describes the geographic entity that is covered by the system. A system representing a certain industrial sector can be applied to the USA, China, certain world regions, or the world as a whole.
The temporal scale describes the point in time or the time span for which the system is quantified.
The indicator element or material of the system is the physical entity that is measured and for which the mass balance holds. As the name says, an indicator element is a certain chemical element
A chemical element is a chemical substance whose atoms all have the same number of protons. The number of protons is called the atomic number of that element. For example, oxygen has an atomic number of 8: each oxygen atom has 8 protons in its ...
such as cadmium or a substance such as CO2. In general, a material or a product can also be used as indicator as long as a process balance can be established for it. Examples of more general indicators are goods such as passenger cars, materials like steel, or other physical quantities such as energy
Energy () is the physical quantity, quantitative physical property, property that is transferred to a physical body, body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of Work (thermodynamics), work and in the form of heat and l ...
.
MFA requires practitioners to make precise use of the terms 'material', 'substance', or 'good', as laid out, for example, in chapter 2.1 of Brunner and Rechberger, one of the main references for the MFA method.
* A chemical element
A chemical element is a chemical substance whose atoms all have the same number of protons. The number of protons is called the atomic number of that element. For example, oxygen has an atomic number of 8: each oxygen atom has 8 protons in its ...
is "a pure chemical substance consisting of one type of atom distinguished by its atomic number".
* A substance is "any (chemical) element or compound composed of uniform units. All substances are characterised by a unique and identical constitution and are thus homogeneous." From chapter 2.1.1 in Brunner&Rechberger.
* A good is defined as "economic entity of matter with a positive or negative economic value. Goods are made up of one or several substances". From chapter 2.1.2 in Brunner and Rechberger.
* The term material in MFA "serves as an umbrella term for both substances and goods". From chapter 2.1.3 in Brunner&Rechberger.

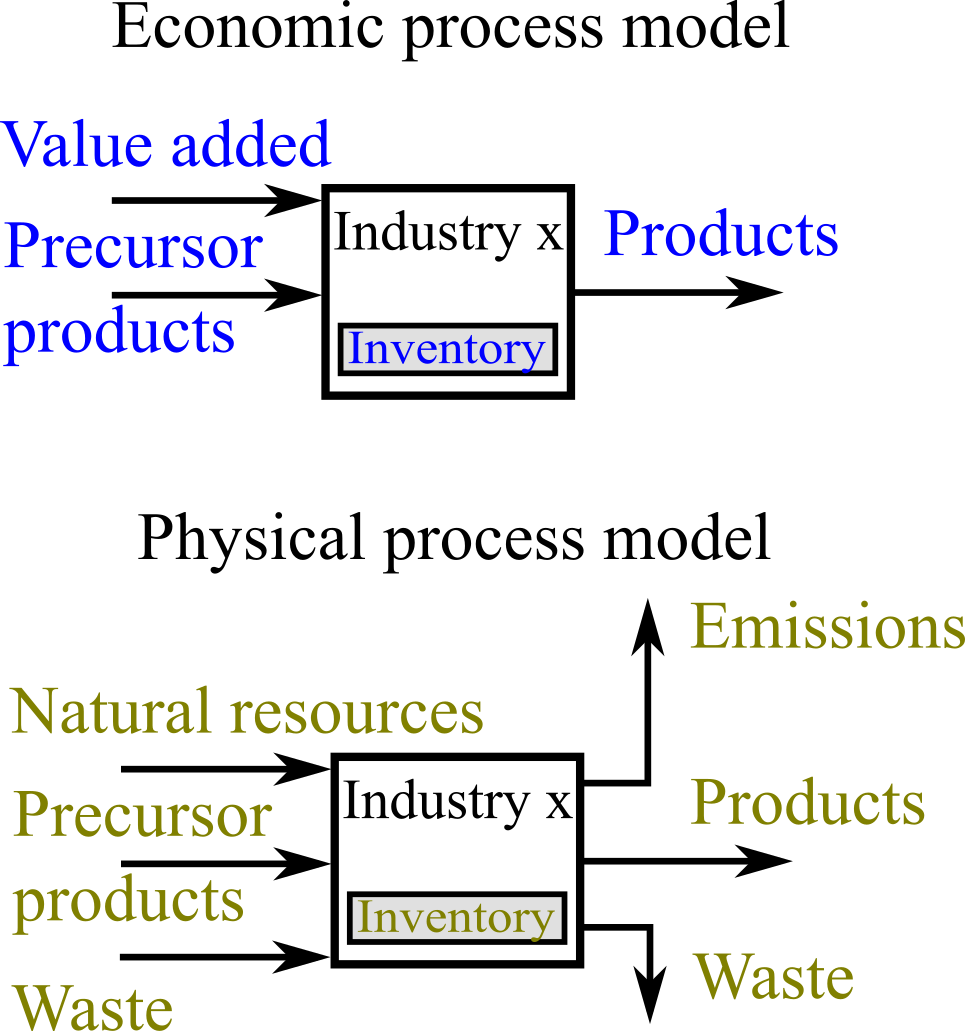
Process balance
One of the main purposes of MFA is to quantify themetabolism
Metabolism (, from ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cellular processes; the co ...
of the elements of the system. Unlike economic accounting, MFA also covers non-economic waste flows, emissions to the environment, and non-market natural resources.
 The process balance is a first order physical principle that turns MFA into a powerful accounting and analysis tool. The nature of the processes in the system determine which balances apply. For a process '
The process balance is a first order physical principle that turns MFA into a powerful accounting and analysis tool. The nature of the processes in the system determine which balances apply. For a process 'oil refinery
An oil refinery or petroleum refinery is an industrial processes, industrial process Factory, plant where petroleum (crude oil) is transformed and refining, refined into products such as gasoline (petrol), diesel fuel, Bitumen, asphalt base, ...
', for example, one can establish a mass balance for each chemical element, while this is not possible for a nuclear power station. A car manufacturing plant respects the balance for steel, but a steel mill does not.
When quantifying MFA systems either by measurements or from statistical data, mass and other process balances have to be checked to ensure the correctness of the quantification and to reveal possible data inconsistencies or even misconceptions in the system such as the omission of a flow or a process. Conflicting information can be reconciled using data validation and reconciliation
Industrial process data validation and reconciliation, or more briefly, process data reconciliation (PDR), is a technology that uses process information and mathematical methods in order to automatically ensure data validation and reconciliation by ...
, and the STAN-software offers basic reconciliation functionality that is suitable for many MFA application.
Examples of applications on different spatial and temporal scales
MFA studies are conducted on various spatial and temporal scales and for a variety of elements, substances, and goods. They cover a wide range of process chains and material cycles. Several examples: * ''MFA on a national or regional scale'' (also referred to asmaterial flow accounting Material flow accounting (MFA) is the study of material flows on a national or regional scale. It is therefore sometimes also referred to as regional, national or economy-wide material flow analysis.
Introduction
Material flow accounting provides ...
): In this type of study, the material exchanges between an economy and the natural environment are analyzed. Several indicators are calculated in order to assess the level of resource intensity of the system.
* ''Corporate material flow analysis'', or MFA along an ''industrial supply chain'' involves a number of companies: The goal of material flow analysis within a company is to quantify and then optimize the production processes so that materials and energy are used more efficiently manner, e.g., by recycling
Recycling is the process of converting waste materials into new materials and objects. This concept often includes the recovery of energy from waste materials. The recyclability of a material depends on its ability to reacquire the propert ...
and waste
Waste are unwanted or unusable materials. Waste is any substance discarded after primary use, or is worthless, defective and of no use. A by-product, by contrast is a joint product of relatively minor Value (economics), economic value. A wast ...
reduction. Companies can use the results obtained by Material Flow Cost Accounting to reduce their operational costs and improve environmental performance.
* In the ''life cycle of a product'': The life cycle inventory, whose compilation is at the core of life cycle assessment, follows the MFA methodology as it is based on an explicit system definition and process balances.
Historical development
* Mass balance or the conservation of matter has been postulated already in ancient Greece, and it was introduced into modern chemistry byAntoine Lavoisier
Antoine-Laurent de Lavoisier ( ; ; 26 August 17438 May 1794), When reduced without charcoal, it gave off an air which supported respiration and combustion in an enhanced way. He concluded that this was just a pure form of common air and that i ...
(cf. chapter 2.1.3 in Brunner&Rechberger,), from where it found its way to chemical engineering and finally to environmental science.
* Other seminal contributions were made by Sanctorius and Theodor Weyl.
* Dennis Meadows made a wide audience aware of the physical foundation of the economy when he co-authored the bestseller ''Limits to Growth
''The Limits to Growth'' (''LTG'') is a 1972 report that discussed the possibility of exponential economic and population growth with finite supply of resources, studied by computer simulation. The study used the World3 computer model to simula ...
'' in 1971. Meadows et al. based their predictions on an analysis of resource stocks; see in the glossary of environmental science
This is a glossary of environmental science.
Environmental science is the study of interactions among physical, chemical, and biological components of the environment. Environmental science provides an integrated, quantitative, and interdisciplin ...
.
* The methodology of MFA was developed during the 1980s and 1990s. Development happened simultaneously in different research groups. Central publications on the MFA methodology include Baccini and Bader (1996), Brunner and Rechberger (2004), Baccini and Brunner (2012), and van der Voet et al. (2002).
* Friedrich Schmidt-Bleek, who worked at the Wuppertal Institute, developed the MFA-related concept of Material Input Per Service unit (MIPS).
Stefan Bringezu
specified this concept in economy-wide material flow analysis, as screening tool for product life-cycle assessment within a cross-scale framework. He defined indicators such as Total Material Requirement (formerly Total Material Input) and Raw Material Input, which are used to quantify the Material Footprint of products, infrastructures and countries. * The
UNEP
The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) is responsible for coordinating responses to environmental issues within the United Nations system. It was established by Maurice Strong, its first director, after the Declaration of the United Nati ...
Resource Panel was set up in 2007 by the United Nations Environment Program. In analogy to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) is an intergovernmental body of the United Nations. Its job is to "provide governments at all levels with scientific information that they can use to develop climate policies". The World M ...
) it brings together experts from many disciplines and institutions to review the current state of research on societal metabolism and to communicate the latest findings to policymakers and stakeholders.
Recent development
* MFA concepts have been or are being incorporated in national accounts in several countries and regions such as the EU and Japan. MFA is also used in theSystem of Integrated Environmental and Economic Accounting
System of Environmental-Economic Accounting (SEEA)System of Environmental-Economic Accounting 2012: Central Framework – final, official publication 2012, UN, EC, IMF, OECD and World Ban"System of Integrated Environmental and Economic Accounting" ...
.
* Several international conferences or other meetings provide a platform for researchers and policymakers to meet and exchange results and ideas, including the World Resources Forum
The World Resources Forum (WRF) is a non-profit organisation for knowledge sharing, sharing knowledge about the economic, political, social and environmental implications of global resource use. WRF promotes resource productivity among researc ...
, a bi-annual international conference on material flow analysis and sustainable development.
* Waste Input-Output ( WIO)-MFA is an approach designed to establish a comprehensive MFA system for the entire economy. This is achieved by utilizing monetary Input-Output (IO) tables and incorporating physical information related to material inputs. The method seamlessly integrates MFA with Input-Output models, offering a straightforward means to transform monetary flows within an Input-Output table into distinct physical flows categorized by materials. WIO-MFA serves as an illustrative example of MFA based on economic Input-Output analysis.
* The Sustainable Europe Research Institute (SERI) in Vienna, Austria, has developed a database called material flows.net.
* Dynamic MFA aims for long-term quantification of MFA systems and uses historic development patterns of physical stocks and flows to create robust scenarios for the years and decades to come.
* The MaTrace model, a variant of dynamic Material Flow Analysis (MFA), is designed to track the trajectory of materials through time and across different products within open-loop recycling systems. This model explicitly accounts for losses and the quality of scrap materials. MaTrace focuses on monitoring the journey of materials initially present in a final product, such as a passenger car. This tracking spans various life stages, including End-of-Life (EoL) processing, which involves collection, disassembling/demolition, and sorting/separation into scraps. Following this, there are metallurgical processes like remelting and/or smelting, where scraps are transformed into secondary materials. The materials then undergo fabrication into products, extending beyond passenger cars. Finally, the model considers the accumulation of these materials as stocks, with losses occurring at each transformation and use phase.
* Japan has developed into a hotspot for MFA research. The country has scarce mineral resources and therefore depends on imports of energy carriers, ores, and other raw materials. The Japanese government fosters research on material cycles and also inaugurated the 3-R concept.
Conducting a state-of-the-art MFA
A state-of-the-art MFA consists of the following steps: * Establish an explicit system definition: Specify the system boundary with geographical and temporal scope, processes (can contain stocks), and flows. Specify the material for which the system is to be quantified (product, substance, or indicator element). Make sure that each stock is associated with a process and that each flow connects one process to another. Flows can also begin or end outside the system boundary. * Define and name the system variables. The system variables include: All stocks within the processes, all flows between processes, and all flows coming from outside or going to outside the system boundaries. Sometimes, stocks are not considered and only the net stock changes are of interest. For each variable, it must be clear whether it is a stock or a flow, and this distinction needs to be reflected in the names and in the mathematical symbols chosen. * Quantify the system variables by linking them to literature, measurement, or modelled data. * Perform a mass balance check for all processes and the system as a whole. * Optional: Visualise your system by using the box-and-arrow scheme shown above or by using Sankey diagrams. * Document the MFA by reporting the explicit system definition along with the list of quantified system variables and the mass balance checks.The difference between material and substance flow analysis
While the term 'substance' in 'substance flow analysis (SFA) always refers to chemical substances, the term 'material' in 'material flow analysis (MFA)' has a much wider scope. According to Brunner and Rechberger the term 'material' comprises substances AND goods, and the reason for this wide scope is the wish to apply MFA not only to chemical elements or substances but also to materials like steel, timber, or products like cars or buildings. It is thus possible to conduct an MFA for the passenger vehicle fleet by recording the vehicles entering and leaving the use phase.Relation to other methods
MFA is complementary to the other coreindustrial ecology
Industrial ecology (IE) is the study of material and energy flows through industrial systems. The global industrial economy can be modelled as a network of industrial processes that extract resources from the Earth and transform those resource ...
methods life cycle assessment (LCA) and input-output (IO) models. Some overlaps between the different methods exist as they all share the system approach and to some extent the mass balance principle. The methods mainly differ in purpose, scope, and data requirements.
MFA studies often cover the entire cycle (mining, production, manufacturing, use, waste handling) of a certain substance within a given geographical boundary and time frame. Material stocks are explicit in MFA, which makes this method suitable for studies involving resource scarcity and recycling from old scrap. The common use of time series (dynamic modelling) and lifetime models makes MFA a suitable tool for assessing long-term trends in material use.
* Compared to IO analyses, the number of processes considered in MFA systems is usually much lower. On the other hand, mass balance ensures that flows of by-products or waste are not overlooked in MFA studies, whereas in IO tables these flows are often not included due to their lack of economic value. Physical IO models are much less common than economic tables. However, WIO-MFA makes it possible to transform monetary flows within an IO table into distinct physical flows categorized by materials, including the flow of byproducts and waste (refer to the section above for details on WIO-MFA). Material stocks are not covered by IO analysis, only the addition to stock can be included in form of capital accumulation
Capital accumulation is the dynamic that motivates the pursuit of profit, involving the investment of money or any financial asset with the goal of increasing the initial monetary value of said asset as a financial return whether in the form ...
.
* Life cycle inventories record the demand for many different materials associated with individual products, whereas MFA studies typically focus on a single material used in many different products.
See also
References
Further reading
*External links
CSIRO and UNEP Material Flow and Resource Productivity Database for Asia and the Pacific
materialflows.net
online portal for material flow data, providing access to material flow data sets on the national level * MFA is described in great detail and published on 166 pages in the first of four paper volumes co-edited with assistance from UNEP and in online form by th
Economy-wide Material Flow Analysis and Indicators
Material flow analysis in the context of environmental accounting
Online Material Flow Analysis Tool (OMAT)
online software to administer a Material Flow Analysis {{Systems science Environmental impact assessment Industrial ecology Environmental social science concepts