|
Waring Problem
In number theory, Waring's problem asks whether each natural number ''k'' has an associated positive integer ''s'' such that every natural number is the sum of at most ''s'' natural numbers raised to the power ''k''. For example, every natural number is the sum of at most 4 squares, 9 cubes, or 19 fourth powers. Waring's problem was proposed in 1770 by Edward Waring, after whom it is named. Its affirmative answer, known as the Hilbert–Waring theorem, was provided by Hilbert in 1909. Waring's problem has its own Mathematics Subject Classification, 11P05, "Waring's problem and variants". Relationship with Lagrange's four-square theorem Long before Waring posed his problem, Diophantus had asked whether every positive integer could be represented as the sum of four perfect squares greater than or equal to zero. This question later became known as Bachet's conjecture, after the 1621 translation of Diophantus by Claude Gaspard Bachet de Méziriac, and it was solved by Joseph-Louis La ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Number Theory
Number theory is a branch of pure mathematics devoted primarily to the study of the integers and arithmetic functions. Number theorists study prime numbers as well as the properties of mathematical objects constructed from integers (for example, rational numbers), or defined as generalizations of the integers (for example, algebraic integers). Integers can be considered either in themselves or as solutions to equations (Diophantine geometry). Questions in number theory can often be understood through the study of Complex analysis, analytical objects, such as the Riemann zeta function, that encode properties of the integers, primes or other number-theoretic objects in some fashion (analytic number theory). One may also study real numbers in relation to rational numbers, as for instance how irrational numbers can be approximated by fractions (Diophantine approximation). Number theory is one of the oldest branches of mathematics alongside geometry. One quirk of number theory is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aubrey J
Aubrey () is a traditionally male English language, English name. It was quite common in the Middle Ages, but had lost favour for a time before experiencing a resurgence of popularity in the 19th century. In the United States, following the 1973 release of the song Aubrey (song), "Aubrey", by the band Bread (band), Bread, ''Aubrey'' began to be commonly used as a given name for girls, potentially influenced by its similarity to ''Audrey''. In 2023, ''Aubrey'' was the 101st most popular girls' name in the United States. Etymology ''Aubrey'' is from the Norman language, Norman French derivation ''Aubry'' of the Germanic languages, Germanic given name ''Alberic'' / Old High German given name ''Alberich'', which consists of the elements ''alb'' 'elf' and ''ric'' 'power' or 'ruler', Before being largely replaced by ''Aubrey'' after the Norman Conquest, Norman Conquest of England, the Anglo-Saxons used the native form Ælfric, ''Ælfrīc''. The mediaeval feminine name ''Aubrée'', in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kurt Mahler
Kurt Mahler FRS (26 July 1903 – 25 February 1988) was a German mathematician who worked in the fields of transcendental number theory, diophantine approximation, ''p''-adic analysis, and the geometry of numbers.The Kurt Mahler Archive available from CARMA research center at carmamaths.org Career Mahler was a student at the universities in and , graduating with a Ph.D. from |
American Journal Of Mathematics
The ''American Journal of Mathematics'' is a bimonthly mathematics journal published by the Johns Hopkins University Press. History The ''American Journal of Mathematics'' is the oldest continuously published mathematical journal in the United States, established in 1878 at the Johns Hopkins University by James Joseph Sylvester, an English-born mathematician who also served as the journal's editor-in-chief from its inception through early 1884. Initially W. E. Story was associate editor in charge; he was replaced by Thomas Craig (mathematician), Thomas Craig in 1880. For volume 7 Simon Newcomb became chief editor with Craig managing until 1894. Then with volume 16 it was "Edited by Thomas Craig with the Co-operation of Simon Newcomb" until 1898. Other notable mathematicians who have served as editors or editorial associates of the journal include Frank Morley, Oscar Zariski, Lars Ahlfors, Hermann Weyl, Wei-Liang Chow, S. S. Chern, André Weil, Harish-Chandra, Jean Dieudonné, Hen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ivan M
Ivan () is a Slavic male given name, connected with the variant of the Greek name (English: John) from Hebrew meaning 'God is gracious'. It is associated worldwide with Slavic countries. The earliest person known to bear the name was the Bulgarian Saint Ivan of Rila. It is very popular in Russia, Ukraine, Croatia, Serbia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Slovenia, Bulgaria, Belarus, North Macedonia, and Montenegro and has also become more popular in Romance-speaking countries since the 20th century. Etymology Ivan is the common Slavic Latin spelling, while Cyrillic spelling is two-fold: in Bulgarian, Russian, Macedonian, Serbian and Montenegrin it is , while in Belarusian and Ukrainian it is . The Old Church Slavonic (or Old Cyrillic) spelling is . It is the Slavic relative of the Latin name , corresponding to English '' John''. This Slavic version of the name originates from New Testament Greek (''Iōánnēs'') rather than from the Latin . The Greek name is in tur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leonard Eugene Dickson
Leonard Eugene Dickson (January 22, 1874 – January 17, 1954) was an American mathematician. He was one of the first American researchers in abstract algebra, in particular the theory of finite fields and classical groups, and is also remembered for a three-volume history of number theory, '' History of the Theory of Numbers''. The L. E. Dickson instructorships at the University of Chicago Department of Mathematics are named after him. Life Dickson considered himself a Texan by virtue of having grown up in Cleburne, where his father was a banker, merchant, and real estate investor. He attended the University of Texas at Austin, where George Bruce Halsted encouraged his study of mathematics. Dickson earned a B.S. in 1893 and an M.S. in 1894, under Halsted's supervision. Dickson first specialised in Halsted's own specialty, geometry. A. A. Albert (1955Leonard Eugene Dickson 1874–1954from National Academy of Sciences Both the University of Chicago and Harvard University ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euler
Leonhard Euler ( ; ; ; 15 April 170718 September 1783) was a Swiss polymath who was active as a mathematician, physicist, astronomer, logician, geographer, and engineer. He founded the studies of graph theory and topology and made influential discoveries in many other branches of mathematics, such as analytic number theory, complex analysis, and infinitesimal calculus. He also introduced much of modern mathematical terminology and notation, including the notion of a mathematical function. He is known for his work in mechanics, fluid dynamics, optics, astronomy, and music theory. Euler has been called a "universal genius" who "was fully equipped with almost unlimited powers of imagination, intellectual gifts and extraordinary memory". He spent most of his adult life in Saint Petersburg, Russia, and in Berlin, then the capital of Prussia. Euler is credited for popularizing the Greek letter \pi (lowercase pi) to denote the ratio of a circle's circumference to its diameter, as we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Euler
Johann Albrecht Euler (27 November 1734 – 17 September 1800) was a Swiss-Russian astronomer and mathematician who made contributions to electrostatics. The eldest son of the renowned mathematician Leonhard Euler, he served as professor of physics at the Imperial Academy of Sciences in Saint Petersburg and later as secretary of conferences overseeing the Academy's correspondence. His work ''Disquisitio de Causa Physica Electricitatis'' represented one of the earliest attempts to mathematize electrical theory through a mechanical framework based on compressible, elastic aether. Biography Also known as ''Johann Albert Euler'' or ''John-Albert Euler'', Johann Albrecht Euler was the first child born to the great Swiss mathematician Leonhard Euler (1707–1783), who had emigrated (for the first time) to Saint-Petersburg on 17 May 1727. His mother was Katharina Gsell (1707–1773) whose maternal grandmother was the famous scientific illustrator Maria Sibylla Merian (1647–1717). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
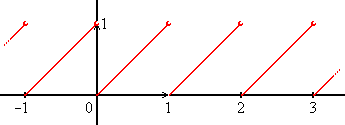
Fractional Part
The fractional part or decimal part of a non‐negative real number x is the excess beyond that number's integer part. The latter is defined as the largest integer not greater than , called ''floor'' of or \lfloor x\rfloor. Then, the fractional part can be formulated as a difference: :\operatorname (x)=x - \lfloor x \rfloor,\; x > 0. The fractional part of logarithms, specifically, is also known as the mantissa; by contrast with the mantissa, the integral part of a logarithm is called its ''characteristic''. The word ''mantissa'' was introduced by Henry Briggs. For a positive number written in a conventional positional numeral system (such as binary or decimal), its fractional part hence corresponds to the digits appearing after the radix point, such as the decimal point in English. The result is a real number in the half-open interval x, -\lfloor , x, \rfloor , or by the [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integral Part
In mathematics, an integral is the continuous analog of a sum, which is used to calculate areas, volumes, and their generalizations. Integration, the process of computing an integral, is one of the two fundamental operations of calculus,Integral calculus is a very well established mathematical discipline for which there are many sources. See and , for example. the other being differentiation. Integration was initially used to solve problems in mathematics and physics, such as finding the area under a curve, or determining displacement from velocity. Usage of integration expanded to a wide variety of scientific fields thereafter. A definite integral computes the signed area of the region in the plane that is bounded by the graph of a given function between two points in the real line. Conventionally, areas above the horizontal axis of the plane are positive while areas below are negative. Integrals also refer to the concept of an '' antiderivative'', a function whose d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subbayya Sivasankaranarayana Pillai
Subbayya Sivasankaranarayana Pillai (5 April 1901 – 31 August 1950) was an Indian mathematician specialising in number theory. His contribution to Waring's problem was described in 1950 by K. S. Chandrasekharan as "almost certainly his best piece of work and one of the very best achievements in Indian Mathematics since Ramanujan". Biography Subbayya Sivasankaranarayana Pillai was born to parents Subbayya Pillai and Gomati Ammal. His mother died a year after his birth and his father when Pillai was in his last year at school. Pillai did his intermediate course and B.Sc. Mathematics in the Scott Christian College at Nagercoil and managed to earn a B.A. degree from Maharaja's college, Trivandrum. In 1927, Pillai was awarded a research fellowship at the University of Madras to work among professors K. Ananda Rau and Ramaswamy S. Vaidyanathaswamy. He was from 1929 to 1941 at Annamalai University where he worked as a lecturer. It was in Annamalai University that he did his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |