fractional part on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
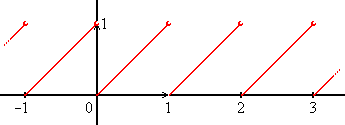 The fractional part or decimal part of a non‐negative
The fractional part or decimal part of a non‐negative
/ref> : with as the smallest integer not less than , also called the ceiling of . By consequence, we may get, for example, three different values for the fractional part of just one : let it be −1.3, its fractional part will be 0.7 according to the first definition, 0.3 according to the second definition, and −0.3 according to the third definition, whose result can also be obtained in a straightforward way by :. The and the "odd function" definitions permit for unique decomposition of any real number to the addition, sum of its integer and fractional parts, where "integer part" refers to or respectively. These two definitions of fractional-part function also provide idempotence. The fractional part defined via difference from floor function, ⌊ ⌋ is usually denoted by curly braces: :
 The fractional part or decimal part of a non‐negative
The fractional part or decimal part of a non‐negative real number
In mathematics, a real number is a number that can be used to measure a continuous one- dimensional quantity such as a duration or temperature. Here, ''continuous'' means that pairs of values can have arbitrarily small differences. Every re ...
is the excess beyond that number's integer part. The latter is defined as the largest integer not greater than , called ''floor
A floor is the bottom surface of a room or vehicle. Floors vary from wikt:hovel, simple dirt in a cave to many layered surfaces made with modern technology. Floors may be stone, wood, bamboo, metal or any other material that can support the ex ...
'' of or . Then, the fractional part can be formulated as a difference:
:.
The fractional part of logarithms
In mathematics, the logarithm of a number is the exponent by which another fixed value, the base, must be raised to produce that number. For example, the logarithm of to base is , because is to the rd power: . More generally, if , the ...
, specifically, is also known as the mantissa; by contrast with the mantissa, the integral part of a logarithm is called its ''characteristic''. The word ''mantissa'' was introduced by Henry Briggs.
For a positive number
In mathematics, the sign of a real number is its property of being either positive, negative, or 0. Depending on local conventions, zero may be considered as having its own unique sign, having no sign, or having both positive and negative sign. ...
written in a conventional positional numeral system
Positional notation, also known as place-value notation, positional numeral system, or simply place value, usually denotes the extension to any base of the Hindu–Arabic numeral system (or decimal system). More generally, a positional system ...
(such as binary or decimal
The decimal numeral system (also called the base-ten positional numeral system and denary or decanary) is the standard system for denoting integer and non-integer numbers. It is the extension to non-integer numbers (''decimal fractions'') of th ...
), its fractional part hence corresponds to the digits appearing after the radix point
alt=Four types of separating decimals: a) 1,234.56. b) 1.234,56. c) 1'234,56. d) ١٬٢٣٤٫٥٦., Both a full_stop.html" ;"title="comma and a full stop">comma and a full stop (or period) are generally accepted decimal separators for interna ...
, such as the decimal point
FIle:Decimal separators.svg, alt=Four types of separating decimals: a) 1,234.56. b) 1.234,56. c) 1'234,56. d) ١٬٢٣٤٫٥٦., Both a comma and a full stop (or period) are generally accepted decimal separators for international use. The apost ...
in English. The result is a real number in the half-open interval x, -\lfloor , x, \rfloor , or by the Weisstein, Eric W. "Fractional Part." From MathWorld--A Wolfram Web Resource/ref> : with as the smallest integer not less than , also called the ceiling of . By consequence, we may get, for example, three different values for the fractional part of just one : let it be −1.3, its fractional part will be 0.7 according to the first definition, 0.3 according to the second definition, and −0.3 according to the third definition, whose result can also be obtained in a straightforward way by :. The and the "odd function" definitions permit for unique decomposition of any real number to the addition, sum of its integer and fractional parts, where "integer part" refers to or respectively. These two definitions of fractional-part function also provide idempotence. The fractional part defined via difference from floor function, ⌊ ⌋ is usually denoted by curly braces: :
Relation to continued fractions
Every real number can be essentially uniquely represented as asimple continued fraction
A simple or regular continued fraction is a continued fraction with numerators all equal one, and denominators built from a sequence \ of integer numbers. The sequence can be finite or infinite, resulting in a finite (or terminated) continued fr ...
, namely as the sum of its integer part and the reciprocal of its fractional part which is written as the sum of ''its'' integer part and the reciprocal of ''its'' fractional part, and so on.
See also
* Circle group * Equidistributed sequence * One-parameter group * Pisot–Vijayaraghavan number * Poussin proof *Significand
The significand (also coefficient, sometimes argument, or more ambiguously mantissa, fraction, or characteristic) is the first (left) part of a number in scientific notation or related concepts in floating-point representation, consisting of its s ...
References
{{Reflist Arithmetic Unary operations