|
Walter Seifert
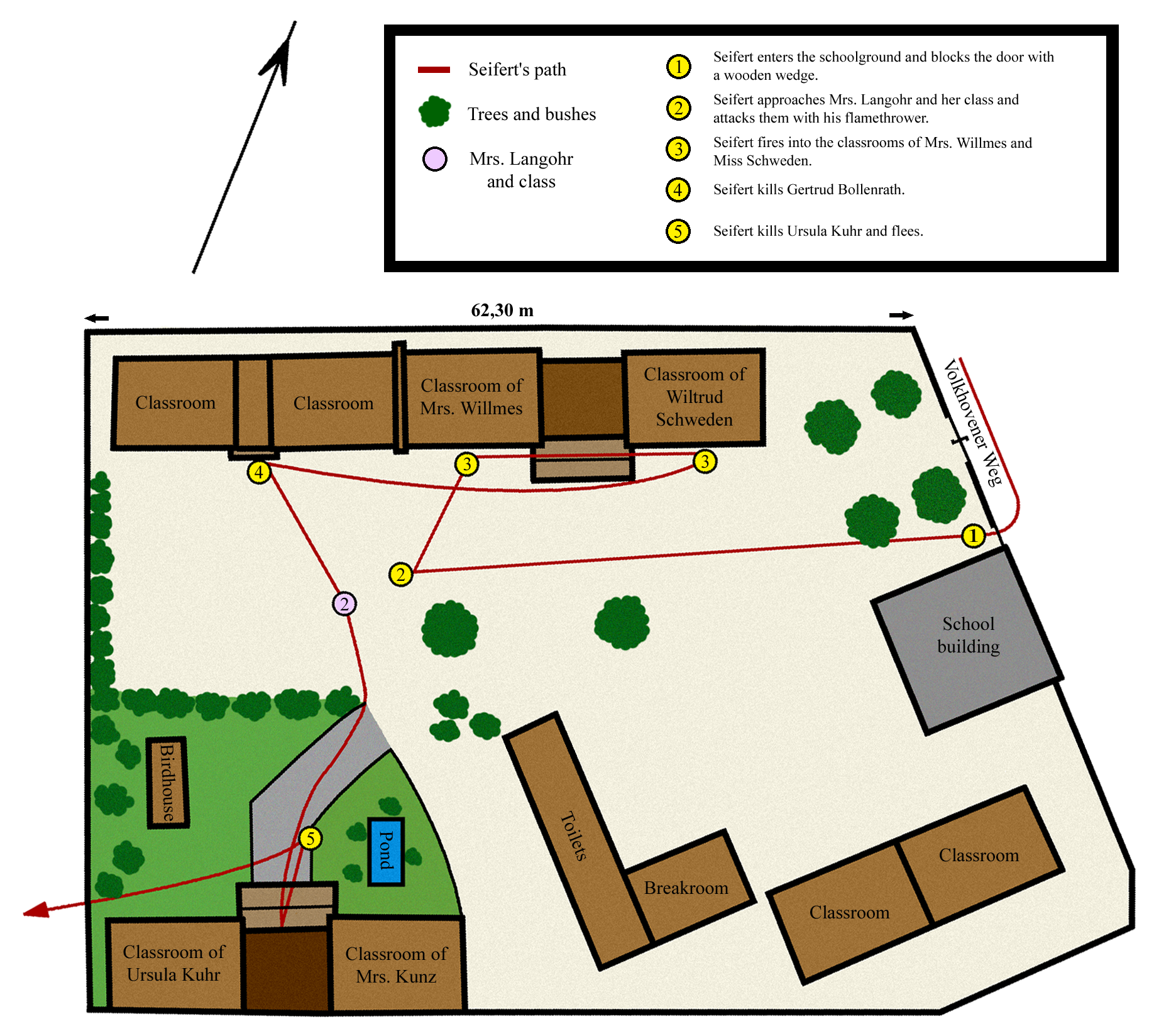
The Cologne school massacre was a mass murder that occurred at the Catholic elementary school () located in the suburb of Volkhoven in Cologne, West Germany on 11 June 1964. The perpetrator, Walter Seifert, also known as "" ("Firedevil of Volkhoven"), attacked the people at the school with a home-made flamethrower and a spear, killing eight pupils and two teachers, and wounding twenty-two others. When police arrived at the scene, he fled from the school compound and poisoned himself. He was taken to a hospital, where he died the same evening. Perpetrator Willi Walter Seifert (19 June 1921 – 11 June 1964) was born in Bickendorf, a district of Cologne. He was the son of a glass-grinder and had one brother. From 1927 to 1935 he attended the Volksschule in Ehrenfeld, and afterwards started an apprenticeship as metal worker at a machine factory, which he successfully finished in 1939. In 1941 he was drafted into the Luftwaffe and attended the Waffentechnische Schule der Luftwaffe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cologne
Cologne ( ; german: Köln ; ksh, Kölle ) is the largest city of the German western States of Germany, state of North Rhine-Westphalia (NRW) and the List of cities in Germany by population, fourth-most populous city of Germany with 1.1 million inhabitants in the city proper and 3.6 million people in the Cologne Bonn Region, urban region. Centered on the left bank of the Rhine, left (west) bank of the Rhine, Cologne is about southeast of NRW's state capital Düsseldorf and northwest of Bonn, the former capital of West Germany. The city's medieval Catholic Cologne Cathedral (), the third-tallest church and tallest cathedral in the world, constructed to house the Shrine of the Three Kings, is a globally recognized landmark and one of the most visited sights and pilgrimage destinations in Europe. The cityscape is further shaped by the Twelve Romanesque churches of Cologne, and Cologne is famous for Eau de Cologne, that has been produced in the city since 1709, and "col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apprenticeship
Apprenticeship is a system for training a new generation of practitioners of a Tradesman, trade or profession with on-the-job training and often some accompanying study (classroom work and reading). Apprenticeships can also enable practitioners to gain a license to practice in a regulated occupation. Most of their training is done while working for an employer who helps the apprentices learn their trade or profession, in exchange for their continued labor for an agreed period after they have achieved measurable competencies. Apprenticeship lengths vary significantly across sectors, professions, roles and cultures. In some cases, people who successfully complete an apprenticeship can reach the "journeyman" or professional certification level of competence. In other cases, they can be offered a permanent job at the company that provided the placement. Although the formal boundaries and terminology of the apprentice/journeyman/master system often do not extend outside guilds and tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paranoid Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a mental disorder characterized by continuous or relapsing episodes of psychosis. Major symptoms include hallucinations (typically Auditory hallucination#Schizophrenia, hearing voices), delusions, and disorganized thinking. Other symptoms include Solitude#Health effects, social withdrawal, Reduced affect display, decreased emotional expression, and apathy. Symptoms typically Prodrome, develop gradually, begin during young adulthood, and in many cases never become resolved. There is no objective diagnostic test; diagnosis is based on observed behavior, a psychiatric history, history that includes the person's reported experiences, and reports of others familiar with the person. To be diagnosed with schizophrenia, symptoms and functional impairment need to be present for six months (DSM-5) or one month (ICD-11). Many people with schizophrenia have other mental disorders, especially substance use disorders, Mood disorder, depressive disorders, anxiety disorders, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paranoid
Paranoia is an instinct or thought process that is believed to be heavily influenced by anxiety or fear, often to the point of delusion and irrationality. Paranoid thinking typically includes persecutory beliefs, or beliefs of conspiracy concerning a perceived threat towards oneself (i.e. ''"Everyone is out to get me"''). Paranoia is distinct from phobias, which also involve irrational fear, but usually no blame. Making false accusations and the general distrust of other people also frequently accompany paranoia. For example, a paranoid person might believe an incident was intentional when most people would view it as an accident or coincidence. Paranoia is a central symptom of psychosis.Green, C., Freeman, D., Kuipers, E., Bebbington, P., Fowler, D., Dunn, G., & Garety, P. (2008). Measuring ideas of persecution and social reference: the Green et al. Paranoid Thought Scales (GPTS). ''Psychological Medicine, 38'', 101 - 111. Signs and symptoms A common symptom of paranoia is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Train Of Thought
The train of thought or track of thought refers to the interconnection in the sequence of ideas expressed during a connected discourse or thought, as well as the sequence itself, especially in discussion how this sequence leads from one idea to another. When a reader or listener "loses the train of thought" (i.e., loses the relation between consecutive sentences or phrases, or the relation between non-verbal concepts in an argument or presentation), comprehension is lost of the expressed or unexpressed thought.Edward Parmelee Morris, "On Principles and Methods in Latin Syntax" (1901), Chapter VI: ''Parataxis'' The term "train of thoughts" was introduced and elaborated as early as in 1651 by Thomas Hobbes in his '' Leviathan'', though with a somewhat different meaning (similar to the meaning used by the British associationists): See also * Absent-mindedness * Association of Ideas * Associationism * Derailment (thought disorder) * Internal monologue * Mind-wandering Mind- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychiatry
Psychiatry is the medical specialty devoted to the diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of mental disorders. These include various maladaptations related to mood, behaviour, cognition, and perceptions. See glossary of psychiatry. Initial psychiatric assessment of a person typically begins with a case history and mental status examination. Physical examinations and psychological tests may be conducted. On occasion, neuroimaging or other neurophysiological techniques are used. Mental disorders are often diagnosed in accordance with clinical concepts listed in diagnostic manuals such as the ''International Classification of Diseases'' (ICD), edited and used by the World Health Organization (WHO) and the widely used '' Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders'' (DSM), published by the American Psychiatric Association (APA). The fifth edition of the DSM (DSM-5) was published in May 2013 which re-organized the larger categories of various diseases and expanded upon the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurology
Neurology (from el, wikt:νεῦρον, νεῦρον (neûron), "string, nerve" and the suffix wikt:-logia, -logia, "study of") is the branch of specialty (medicine), medicine dealing with the diagnosis and treatment of all categories of conditions and disease involving the brain, the spinal cord and the peripheral nerves. Neurological practice relies heavily on the field of neuroscience, the scientific study of the nervous system. A neurologist is a physician specializing in neurology and trained to investigate, diagnose and treat neurological disorders. Neurologists treat a myriad of neurologic conditions, including stroke, seizures, movement disorders such as Parkinson's disease, autoimmune neurologic disorders such as multiple sclerosis, headache disorders like migraine and dementias such as Alzheimer's disease. Neurologists may also be involved in clinical research, clinical trials, and basic research, basic or translational research. While neurology is a nonsurgical sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanatorium
A sanatorium (from Latin '' sānāre'' 'to heal, make healthy'), also sanitarium or sanitorium, are antiquated names for specialised hospitals, for the treatment of specific diseases, related ailments and convalescence. Sanatoriums are often located in a healthy climate, usually in the countryside. The idea of healing was an important reason for the historical wave of establishments of sanatoriums, especially at the end of the 19th- and early 20th centuries. One sought for instance the healing of consumptives, especially tuberculosis (before the discovery of antibiotics) or alcoholism, but also of more obscure addictions and longings, of hysteria, masturbation, fatigue and emotional exhaustion. Facility operators were often charitable associations such as the Order of St. John and the newly founded social welfare insurance companies. Sanatoriums should not be confused with the Russian sanatoriums from the time of the Soviet Union, which were a type of sanatorium resort r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regimen
A regimen is a plan, or course of action such as a diet, exercise or medical treatment. A low-salt diet is a regimen. A course of penicillin is a regimen, and there are many chemotherapy regimens in the treatment of cancer. History The work, ''Regimen in Acute Diseases'', attributed to the ancient Greek physician, Hippocrates of Cos, describes the types and usage of medical regimens in his era (400 BCE). This is perhaps the first appearance of the term. PubMed at the US National Library of Medicine lists over 220,000 articles using the term "regimen" from 1892 to January 2013. In the context of medieval medicine, regimen referred to the careful management of habits, diet, and schedule to keep the four humors in equilibrium. By manipulating the six non-naturals (airs, diet, sleep, exercise, evacuation, and emotion) a person could keep track of their physical and mental wellbeing by attending to regimen. Usage in statistics In economic statistics, a regimen refers to the sele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
War Pension
War pensions are almost certainly the most ancient type of social security. Plutarch's Life of Solon mentions a law which provides that those who are maimed in war shall be maintained at the public charge. Halsbury's Laws of England traced their history back to the days of King Alfred. Until 1978 the British War Pension scheme was run entirely under the Royal Prerogative and completely without legislation. See also * Veterans' benefits The US Department of Veterans Affairs provides a wide variety of benefits, e.g., educational assistance (GI Bill), healthcare, assisted living, home loans, insurance, and burial and memorial services, for retired or separated United States armed f ... (United States) References {{reflist External linksPensions for veterans War Social security in the United Kingdom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease usually caused by '' Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections show no symptoms, in which case it is known as latent tuberculosis. Around 10% of latent infections progress to active disease which, if left untreated, kill about half of those affected. Typical symptoms of active TB are chronic cough with blood-containing mucus, fever, night sweats, and weight loss. It was historically referred to as consumption due to the weight loss associated with the disease. Infection of other organs can cause a wide range of symptoms. Tuberculosis is spread from one person to the next through the air when people who have active TB in their lungs cough, spit, speak, or sneeze. People with Latent TB do not spread the disease. Active infection occurs more often in people with HIV/AIDS and in those who smoke. Diagnosis of active TB is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catarrh
Catarrh is an exudate of inflamed mucous membranes in one of the airways or cavities of the body, usually with reference to the throat and paranasal sinuses. It can result in a thick exudate of mucus and white blood cells caused by the swelling of the mucous membranes in the head in response to an infection. It is a symptom usually associated with the common cold, pharyngitis, and chesty coughs, but it can also be found in patients with adenoiditis, otitis media, sinusitis or tonsillitis. The phlegm produced by catarrh may either discharge or cause a blockage that may become chronic. The word "catarrh" was widely used in medicine since before the era of medical science, which explains why it has various senses and in older texts may be synonymous with, or vaguely indistinguishable from, common cold, nasopharyngitis, pharyngitis, rhinitis, or sinusitis. The word is no longer as widely used in American medical practice, mostly because more precise words are available for any part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |