|
Wabash Confederacy
The Wabash Confederacy, also referred to as the Wabash Indians or the Wabash tribes, was a number of 18th century Native American villagers in the area of the Wabash River in what are now the U.S. states of Illinois, Indiana, and Ohio. The Wabash Indians were primarily the Miami, Weas and Piankashaws, but also included Kickapoos, Mascoutens, and others. In that time and place, Native American tribes were smaller political units, and the villages along the Wabash were multi-tribal settlements with no centralized government. The confederacy, then, was a loose alliance of influential village leaders (sometimes called headmen or chiefs). In the 1780s, headmen of the Wabash Confederacy allied themselves with a larger, loose confederacy of Native American leaders in the Ohio Country and Illinois Country known as the Northwestern Confederacy, in order to collectively resist U.S. expansion after the American Revolutionary War. In 1786, a Wyandot messenger named Scotosh warned Congress ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
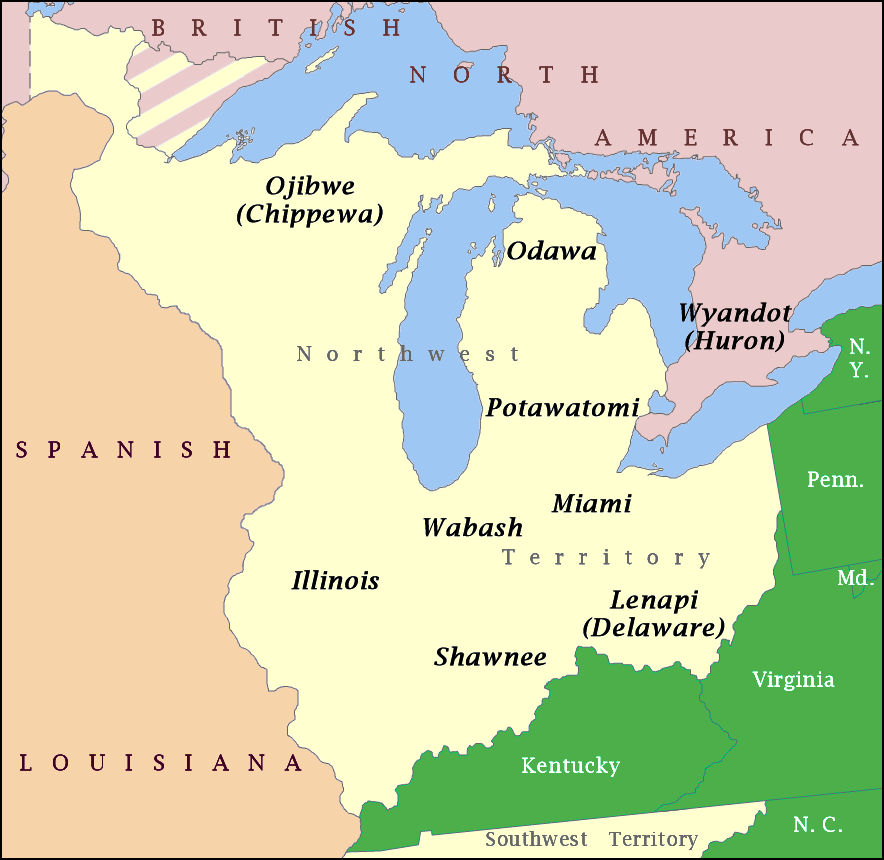
NW Native Tribes, 1792
NW may refer to: Arts and entertainment * ''NW'' (novel), by Zadie Smith * Nat Wolff, a singer and actor * New wave music, a genre * ''New Weekly'', an Australian celebrity magazine * Nintendo Wii, a video game console Geography * Northwest (other), multiple articles * NW postcode area, northwest London, UK * Nidwalden, a canton of Switzerland * North Rhine-Westphalia, the most populous state of Germany * North West (South African province) Technology * Nanowire, a nanostructure with a diameter on the order of a nanometer * NetWare, in file and protocol names of the Novell NetWare family * Nuclear warfare, the use of nuclear weapons in war * An ISO-specified vacuum flange fitting (code NW) Other uses * No worries, an expression * Norfolk and Western Railroad, a U.S. class I railroad * ''North Western Reporter The ''North Western Reporter'' and ''North Western Reporter, Second Series'' are United States regional case law reporters. It is part of the Nation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Native American History Of Indiana
Native may refer to: People * Jus soli, citizenship by right of birth * Indigenous peoples, peoples with a set of specific rights based on their historical ties to a particular territory ** Native Americans (other) In arts and entertainment * Native (band), a French R&B band * Native (comics), a character in the X-Men comics universe * ''Native'' (album), a 2013 album by OneRepublic * ''Native'' (2016 film), a British science fiction film * ''The Native'', a Nigerian music magazine In science * Native (computing), software or data formats supported by a certain system * Native language, the language(s) a person has learned from birth * Native metal, any metal that is found in its metallic form, either pure or as an alloy, in nature * Native species, a species whose presence in a region is the result of only natural processes Other uses * Northeast Arizona Technological Institute of Vocational Education (NATIVE), a technology school district in the Arizona portion o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indiana In The Northwest Indian War
Indiana () is a U.S. state in the Midwestern United States. It is the 38th-largest by area and the 17th-most populous of the 50 States. Its capital and largest city is Indianapolis. Indiana was admitted to the United States as the 19th state on December 11, 1816. It is bordered by Lake Michigan to the northwest, Michigan to the north, Ohio to the east, the Ohio River and Kentucky to the south and southeast, and the Wabash River and Illinois to the west. Various indigenous peoples inhabited what would become Indiana for thousands of years, some of whom the U.S. government expelled between 1800 and 1836. Indiana received its name because the state was largely possessed by native tribes even after it was granted statehood. Since then, settlement patterns in Indiana have reflected regional cultural segmentation present in the Eastern United States; the state's northernmost tier was settled primarily by people from New England and New York, Central Indiana by migrants from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northwest Indian War
The Northwest Indian War (1786–1795), also known by other names, was an armed conflict for control of the Northwest Territory fought between the United States and a united group of Native American nations known today as the Northwestern Confederacy. The United States Army considers it the first of the American Indian Wars. Following centuries of conflict for control of this region, it was granted to the new United States by the Kingdom of Great Britain in article 2 of the Treaty of Paris, which ended the American Revolutionary War. The treaty used the Great Lakes as a border between British territory and the United States. This granted significant territory to the United States, initially known as the Ohio Country and the Illinois Country, which had previously been prohibited to new settlements. However, numerous Native American peoples inhabited this region, and the British maintained a military presence and continued policies that supported their Native allies. Wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congress Of The Confederation
The Congress of the Confederation, or the Confederation Congress, formally referred to as the United States in Congress Assembled, was the governing body of the United States of America during the Confederation period, March 1, 1781 – March 4, 1789. A unicameral body with legislative and executive function, it was composed of delegates appointed by the legislatures of the several states. Each state delegation had one vote. It was preceded by the Second Continental Congress (1775–1781) and was created by the Articles of Confederation and Perpetual Union in 1781. The Congress continued to refer itself as the Continental Congress throughout its eight-year history, although modern historians separate it from the two earlier congresses, which operated under slightly different rules and procedures until the later part of American Revolutionary War. The membership of the Second Continental Congress automatically carried over to the Congress of the Confederation when the la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wyandot People
The Wyandot people, or Wyandotte and Waⁿdát, are Indigenous peoples of the Northeastern Woodlands. The Wyandot are Iroquoian Indigenous peoples of North America who emerged as a confederacy of tribes around the north shore of Lake Ontario with their original homeland extending to Georgian Bay of Lake Huron and Lake Simcoe in Ontario, Canada and occupying some territory around the western part of the lake. The Wyandot, not to be mistaken for the Huron-Wendat, predominantly descend from the Tionontati tribe. The Tionontati (or Tobacco/Petun people) never belonged to the Huron (Wendat) Confederacy. However, the Wyandot(te) have connections to the Wendat-Huron through their lineage from the Attignawantan, the founding tribe of the Huron. The four Wyandot(te) Nations are descended from remnants of the Tionontati, Attignawantan and Wenrohronon (Wenro), that were "all unique independent tribes, who united in 1649-50 after being defeated by the Iroquois Confederacy." After th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of the United States, fighting began on April 19, 1775, followed by the Lee Resolution on July 2, 1776, and the Declaration of Independence on July 4, 1776. The American Patriots were supported by the Kingdom of France and, to a lesser extent, the Dutch Republic and the Spanish Empire, in a conflict taking place in North America, the Caribbean, and the Atlantic Ocean. Established by royal charter in the 17th and 18th centuries, the American colonies were largely autonomous in domestic affairs and commercially prosperous, trading with Britain and its Caribbean colonies, as well as other European powers via their Caribbean entrepôts. After British victory over the French in the Seven Years' War in 1763, tensions between the motherla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northwestern Confederacy
The Northwestern Confederacy, or Northwestern Indian Confederacy, was a loose confederacy of Native Americans in the Great Lakes region of the United States created after the American Revolutionary War. Formally, the confederacy referred to itself as the United Indian Nations, at their Confederate Council. It was known infrequently as the Miami Confederacy since many contemporaneous federal officials overestimated the influence and numerical strength of the Miami tribes based on the size of their principal city, Kekionga. The confederacy, which had its roots in pan-tribal movements dating to the 1740s, formed in an attempt to resist the expansion of the United States and the encroachment of American settlers into the Northwest Territory after Great Britain ceded the region to the U.S. in the 1783 Treaty of Paris. American expansion resulted in the Northwest Indian War (1785–1795), in which the Confederacy won significant victories over the United States, but concluded wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Illinois Country
The Illinois Country (french: Pays des Illinois ; , i.e. the Illinois people)—sometimes referred to as Upper Louisiana (french: Haute-Louisiane ; es, Alta Luisiana)—was a vast region of New France claimed in the 1600s in what is now the Midwestern United States. While these names generally referred to the entire Upper Mississippi River watershed, French colonial settlement was concentrated along the Mississippi and Illinois Rivers in what is now the U.S. states of Illinois and Missouri, with outposts in Indiana. Explored in 1673 from Green Bay to the Arkansas River by the ''Canadien'' expedition of Louis Jolliet and Jacques Marquette, the area was claimed by France. It was settled primarily from the '' Pays d'en Haut'' in the context of the fur trade, and in the establishment of missions by French Catholic religious orders. Over time, the fur trade took some French to the far reaches of the Rocky Mountains, especially along the branches of the broad Missouri R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tribe
The term tribe is used in many different contexts to refer to a category of human social group. The predominant worldwide usage of the term in English is in the discipline of anthropology. This definition is contested, in part due to conflicting theoretical understandings of social and kinship structures, and also reflecting the problematic application of this concept to extremely diverse human societies. The concept is often contrasted by anthropologists with other social and kinship groups, being hierarchically larger than a lineage or clan, but smaller than a chiefdom, nation or state. These terms are equally disputed. In some cases tribes have legal recognition and some degree of political autonomy from national or federal government, but this legalistic usage of the term may conflict with anthropological definitions. In the United States, Native American tribes are legally considered to have "domestic dependent nation" status within the territorial United States, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Native Americans Of The United States
Native Americans, also known as American Indians, First Americans, Indigenous Americans, and other terms, are the Indigenous peoples of the mainland United States (Indigenous peoples of Hawaii, Alaska and territories of the United States are generally known by other terms). There are 574 federally recognized tribes living within the US, about half of which are associated with Indian reservations. As defined by the United States Census, "Native Americans" are Indigenous tribes that are originally from the contiguous United States, along with Alaska Natives. Indigenous peoples of the United States who are not listed as American Indian or Alaska Native include Native Hawaiians, Samoan Americans, and the Chamorro people. The US Census groups these peoples as " Native Hawaiian and other Pacific Islanders". European colonization of the Americas, which began in 1492, resulted in a precipitous decline in Native American population because of new diseases, wars, ethnic cleansin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |