|
WPP Domain
The WPP domain is a protein domain thought to be exclusively found in plants, first identified in 2000. The domain is about 90 amino acid residues long. The domain is known to direct RanGAP to the nuclear envelope. Non-RanGAP nuclear envelope proteins are also known to encode WPP domains, such as MFP1 attachment factor 1 (MAF1), WPP1{{cite journal , vauthors=Patel S, Rose A, Meulia T, Dixit R, Cyr RJ, Meier I , title=Arabidopsis WPP-domain proteins are developmentally associated with the nuclear envelope and promote cell division , journal=The Plant Cell , volume=16 , issue=12 , pages=3260–73 , date=December 2004 , pmid=15548735 , pmc=535872 , doi=10.1105/tpc.104.026740 and WPP2. The WPP stands for a tryptophan-proline-proline motif that is highly conserved in the domain. Either deletion of the WPP domain or mutation of both the namesake tryptophan and first proline residues into alanine Alanine (symbol Ala or A), or α-alanine, is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Domain
In molecular biology, a protein domain is a region of a protein's polypeptide chain that is self-stabilizing and that folds independently from the rest. Each domain forms a compact folded three-dimensional structure. Many proteins consist of several domains, and a domain may appear in a variety of different proteins. Molecular evolution uses domains as building blocks and these may be recombined in different arrangements to create proteins with different functions. In general, domains vary in length from between about 50 amino acids up to 250 amino acids in length. The shortest domains, such as zinc fingers, are stabilized by metal ions or disulfide bridges. Domains often form functional units, such as the calcium-binding EF hand domain of calmodulin. Because they are independently stable, domains can be "swapped" by genetic engineering between one protein and another to make chimeric proteins. Background The concept of the domain was first proposed in 1973 by Wetlaufer aft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plant Physiology (journal)
''Plant Physiology'' is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal that covers research on physiology, biochemistry, cellular and molecular biology, genetics, biophysics, and environmental biology of plants. The journal has been published since 1926 by the American Society of Plant Biologists. The current editor-in-chief is Yunde Zhao (University of California San Diego. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2021 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published in the last two years in a given journal, as i ... of 8.005. References External links * {{Authority control Botany journals Publications established in 1926 Monthly journals English-language journals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RanGAP
RanGAP is a protein involved in the transport of other proteins from the cytosol to the nucleus in eukaryotic cells. In model species such as the yeast ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'', the primate ''Homo sapiens'' (See RANGAP1) and the plant ''Arabidopsis thaliana,'' it acts as a GTPase-activating protein, catalysing the conversion of cytosolically-bound RanGTP to RanGDP. It has the opposite function of the RCC1, a nuclear-located protein that converts RanGDP to RanGTP. Together, RanGAP and RCC1 maintain what is known as the ran gradient, where RanGDP is in higher concentrations in the cytosol, while RanGTP is in higher concentrations in the nucleus. It is this ran gradient which provides the energy necessary for the transport of proteins into and out of the nucleus by karyopherin proteins. Location in cell In mammalian and plant cells, RanGAP is located at the nuclear envelope during interphase. Animal RanGAP is bound to the nuclear pore component RANBP2 (Nup358). Plant RanGAP protei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Envelope
The nuclear envelope, also known as the nuclear membrane, is made up of two lipid bilayer membranes that in eukaryotic cells surround the nucleus, which encloses the genetic material. The nuclear envelope consists of two lipid bilayer membranes: an inner nuclear membrane and an outer nuclear membrane. The space between the membranes is called the perinuclear space. It is usually about 10–50 nm wide. The outer nuclear membrane is continuous with the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. The nuclear envelope has many nuclear pores that allow materials to move between the cytosol and the nucleus. Intermediate filament proteins called lamins form a structure called the nuclear lamina on the inner aspect of the inner nuclear membrane and give structural support to the nucleus. Structure The nuclear envelope is made up of two lipid bilayer membranes, an inner nuclear membrane and an outer nuclear membrane. These membranes are connected to each other by nuclear pores. Two sets of in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proceedings Of The National Academy Of Sciences Of The United States Of America
''Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America'' (often abbreviated ''PNAS'' or ''PNAS USA'') is a peer-reviewed multidisciplinary scientific journal. It is the official journal of the National Academy of Sciences, published since 1915, and publishes original research, scientific reviews, commentaries, and letters. According to ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2021 impact factor of 12.779. ''PNAS'' is the second most cited scientific journal, with more than 1.9 million cumulative citations from 2008 to 2018. In the mass media, ''PNAS'' has been described variously as "prestigious", "sedate", "renowned" and "high impact". ''PNAS'' is a delayed open access journal, with an embargo period of six months that can be bypassed for an author fee ( hybrid open access). Since September 2017, open access articles are published under a Creative Commons license. Since January 2019, ''PNAS'' has been online-only, although print issues are ava ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Plant Cell
''The Plant Cell'' is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal of plant sciences, especially the areas of cell and molecular biology, genetics, development, and evolution. It is published by the American Society of Plant Biologists. The editor-in-chief is Blake Meyers (Donald Danforth Plant Science Center). The journal was established in 1989, with Robert (Bob) Goldberg (University of California, Los Angeles) as founding editor-in-chief. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2020 impact factor of 11.277. In October 2009, ''The Plant Cell'' introduced Teaching Tools in Plant Biology, a new online feature consisting of materials to help instructors teach plant biology courses. Each topic includes a short essay introducing the topic, with suggested further reading, and a PowerPoint Microsoft PowerPoint is a presentation program, created by Robert Gaskins and Dennis Austin at a software company named Forethought, Inc. It was released on April 20, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tryptophan
Tryptophan (symbol Trp or W) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Tryptophan contains an α-amino group, an α- carboxylic acid group, and a side chain indole, making it a polar molecule with a non-polar aromatic beta carbon substituent. It is essential in humans, meaning that the body cannot synthesize it and it must be obtained from the diet. Tryptophan is also a precursor to the neurotransmitter serotonin, the hormone melatonin, and vitamin B3. It is encoded by the codon UGG. Like other amino acids, tryptophan is a zwitterion at physiological pH where the amino group is protonated (–; pKa = 9.39) and the carboxylic acid is deprotonated ( –COO−; pKa = 2.38). Humans and many animals cannot synthesize tryptophan: they need to obtain it through their diet, making it an essential amino acid. Function Amino acids, including tryptophan, are used as building blocks in protein biosynthesis, and proteins are required to sustain life. Man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proline
Proline (symbol Pro or P) is an organic acid classed as a proteinogenic amino acid (used in the biosynthesis of proteins), although it does not contain the amino group but is rather a secondary amine. The secondary amine nitrogen is in the protonated form (NH2+) under biological conditions, while the carboxyl group is in the deprotonated −COO− form. The "side chain" from the α carbon connects to the nitrogen forming a pyrrolidine loop, classifying it as a aliphatic amino acid. It is non-essential in humans, meaning the body can synthesize it from the non-essential amino acid L-glutamate. It is encoded by all the codons starting with CC (CCU, CCC, CCA, and CCG). Proline is the only proteinogenic secondary amino acid which is a secondary amine, as the nitrogen atom is attached both to the α-carbon and to a chain of three carbons that together form a five-membered ring. History and etymology Proline was first isolated in 1900 by Richard Willstätter who obtained the amino ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
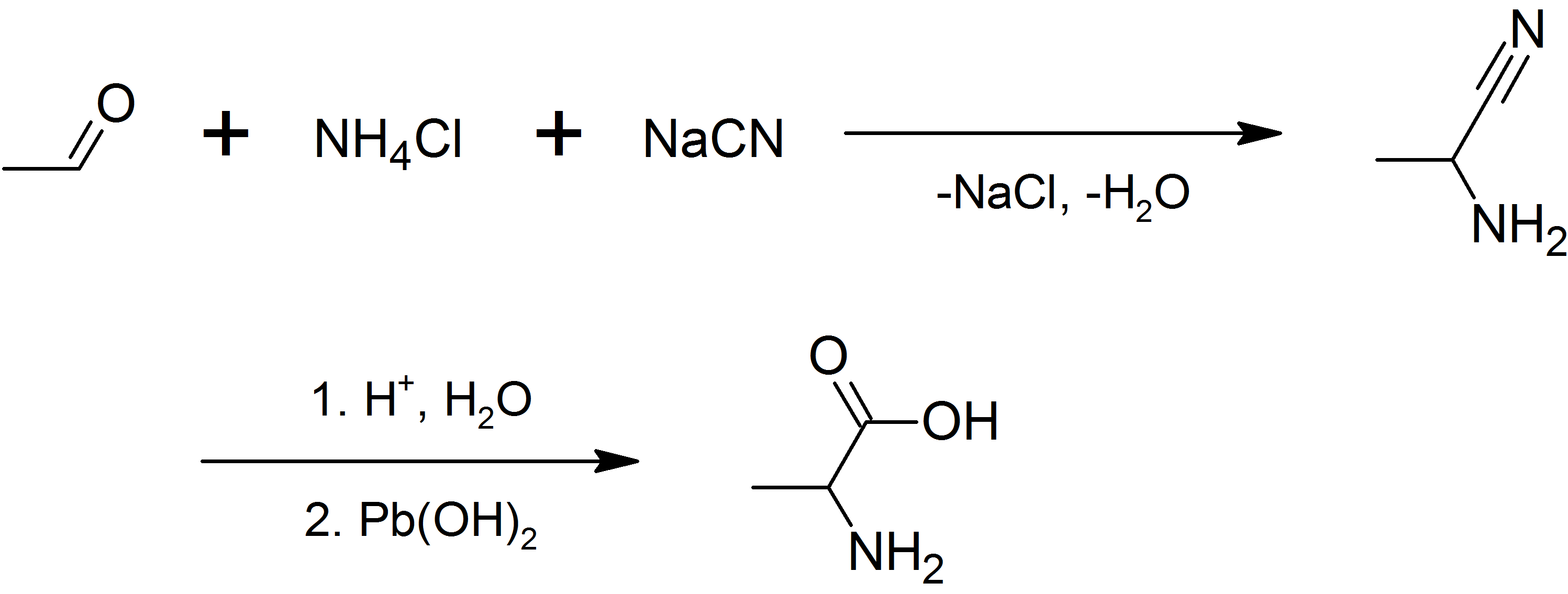
Alanine
Alanine (symbol Ala or A), or α-alanine, is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an amine group and a carboxylic acid group, both attached to the central carbon atom which also carries a methyl group side chain. Consequently, its IUPAC systematic name is 2-aminopropanoic acid, and it is classified as a nonpolar, aliphatic α-amino acid. Under biological conditions, it exists in its zwitterionic form with its amine group protonated (as −NH3+) and its carboxyl group deprotonated (as −CO2−). It is non-essential to humans as it can be synthesised metabolically and does not need to be present in the diet. It is encoded by all codons starting with GC (GCU, GCC, GCA, and GCG). The L-isomer of alanine (left-handed) is the one that is incorporated into proteins. L-alanine is second only to leucine in rate of occurrence, accounting for 7.8% of the primary structure in a sample of 1,150 proteins. The right-handed form, D-alanine, occurs in p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WPP Domain Alignment , holder of an annual press photography contest
{{disambiguation ...
WPP may refer to: * WPP plc, a British multinational advertising and public relations company * WPP domain, a protein domain found in plants * Wavefront parallel processing, a video coding technique * White Patriot Party, a former American white supremacist paramilitary political party * Windows software trace preprocessor * United States Federal Witness Protection Program * Woman's Peace Party, an American pacifist organization established in 1915 * World Press Photo World Press Photo Foundation is an independent, non-profit organization based in Amsterdam, Netherlands. Founded in 1955, the organization is known for holding an annual press photography contest. Since 2011, World Press Photo has organized a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |