|
W. R. Galbraith
William Robert Galbraith (7 July 1829 – 5 October 1914)Marshall, 2003 was a civil engineer in the United Kingdom during the late 19th and early 20th centuries. He was employed by the London and South Western Railway as a consulting engineer for over 40 years, overseeing the design and construction of nearly all that company's new lines between 1862 and his retirement in 1907. In 1892 he formed an engineering consultancy with R. F. Church. As Galbraith & Church they undertook numerous projects for other railways besides the LSWR, including the Baker Street and Waterloo Railway which became known as London Underground's Bakerloo line. In total he designed and oversaw the construction of over 14 miles of London's underground railways). In the 1890s Galbraith was the North British Railway's Parliamentary Consultant, acting as a resident expert and adviser during Parliamentary hearings on the company's engineering projects). His projects include: * Kew railway bridge acro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Civil Engineer
A civil engineer is a person who practices civil engineering – the application of planning, designing, constructing, maintaining, and operating infrastructure while protecting the public and environmental health, as well as improving existing infrastructure that may have been neglected. Civil engineering is one of the oldest engineering disciplines because it deals with constructed environment including planning, designing, and overseeing construction and maintenance of building structures, and facilities, such as roads, railroads, airports, bridges, harbors, channels, dams, irrigation projects, pipelines, power plants, and water and sewage systems. The term "civil engineer" was established by John Smeaton in 1750 to contrast engineers working on civil projects with the military engineers, who worked on armaments and defenses. Over time, various sub-disciplines of civil engineering have become recognized and much of military engineering has been absorbed by civil engineering. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Act Of Parliament
Acts of Parliament, sometimes referred to as primary legislation, are texts of law passed by the Legislature, legislative body of a jurisdiction (often a parliament or council). In most countries with a parliamentary system of government, acts of parliament begin as a Bill (law), bill, which the legislature votes on. Depending on the structure of government, this text may then be subject to assent or approval from the Executive (government), executive branch. Bills A draft act of parliament is known as a Bill (proposed law), bill. In other words, a bill is a proposed law that needs to be discussed in the parliament before it can become a law. In territories with a Westminster system, most bills that have any possibility of becoming law are introduced into parliament by the government. This will usually happen following the publication of a "white paper", setting out the issues and the way in which the proposed new law is intended to deal with them. A bill may also be introduced in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Civil Engineers
British may refer to: Peoples, culture, and language * British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies. ** Britishness, the British identity and common culture * British English, the English language as spoken and written in the United Kingdom or, more broadly, throughout the British Isles * Celtic Britons, an ancient ethno-linguistic group * Brittonic languages, a branch of the Insular Celtic language family (formerly called British) ** Common Brittonic, an ancient language Other uses *''Brit(ish)'', a 2018 memoir by Afua Hirsch *People or things associated with: ** Great Britain, an island ** United Kingdom, a sovereign state ** Kingdom of Great Britain (1707–1800) ** United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland (1801–1922) See also * Terminology of the British Isles * Alternative names for the British * English (other) * Britannic (other) * British Isles * Brit (other) * Briton (d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calstock Railway Station
Calstock railway station is an unstaffed railway station on the Tamar Valley Line serving the village of Calstock in Cornwall, United Kingdom. It is situated at the north end of Calstock Viaduct which carries the railway at high level over the River Tamar. History The gauge East Cornwall Mineral Railway was opened to Kelly Quay at Calstock on 8 May 1872. Wagons with goods from the mines around Gunnislake and Callington were brought down the hillside on a cable-worked incline with a gradient of 1 in 6 (17%). The Plymouth, Devonport and South Western Junction Railway opened the station on 2 March 1908. This line was a branch from Bere Alston to Callington Road and crossed the River Tamar on Calstock Viaduct. A steam-powered lift was attached to the downstream side of the viaduct which could raise and lower wagons to the quays below, making it one of the highest such lifts in the country. It was connected to the station goods yard by a second parallel steel stub viad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
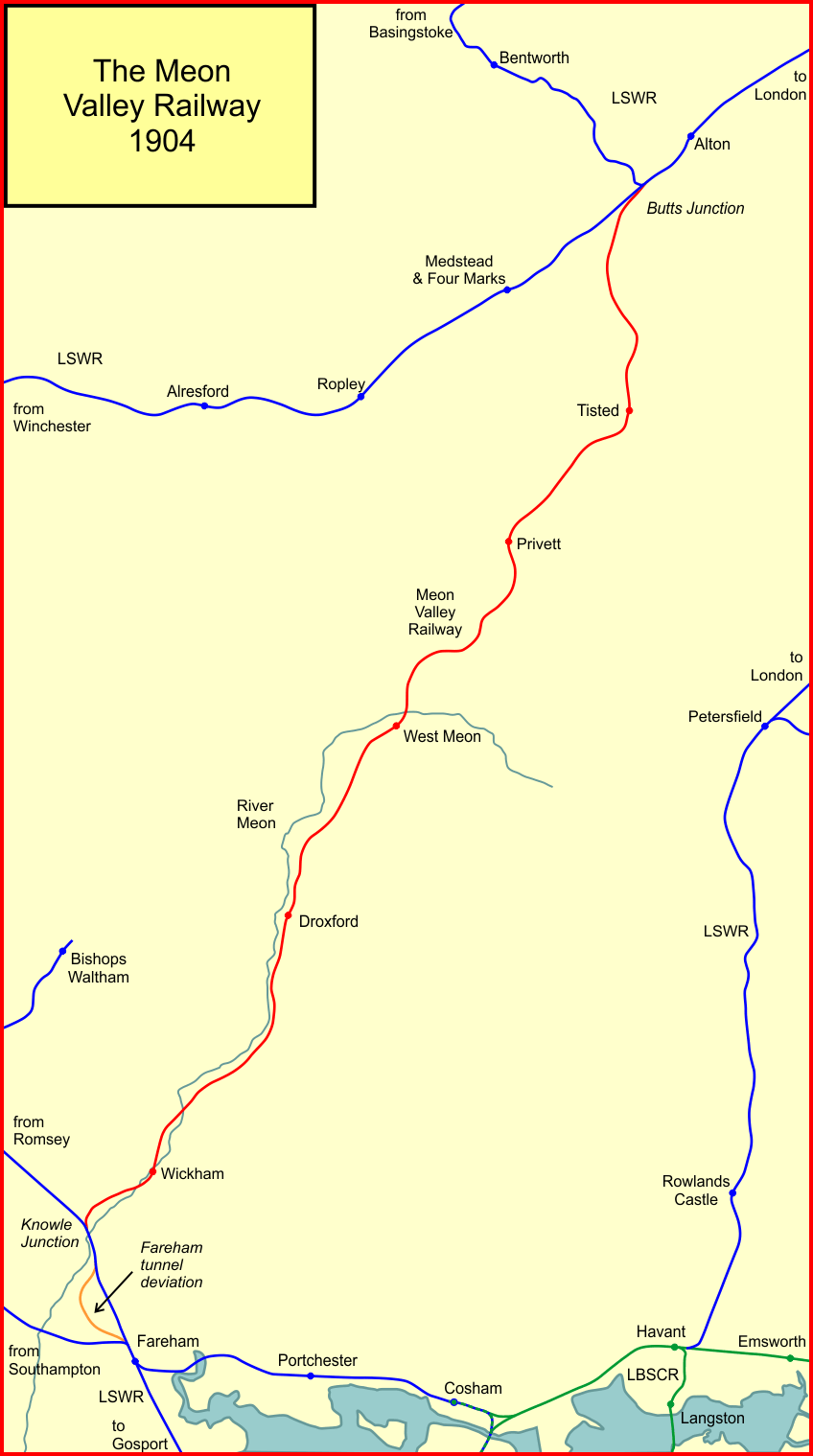
Meon Valley Railway
The Meon Valley Railway was a cross-country railway in Hampshire, England, that ran for 22 miles (36 km) between Alton and Fareham, closely following the course of the River Meon. At its northern (Alton) end, it joined with the Alton Line from London. It was conceived as an additional main line to the area around Gosport, and it was opened in 1903. It never fulfilled its planned potential, and remained a local line through sparsely populated agricultural areas, and it closed to passenger services in 1955; some local goods services continued until total closure in 1968. The name does not refer to an independent company; it was constructed and run by the London and South Western Railway (LSWR). History Background By the last decade of the nineteenth century, the railway map of Great Britain was already mature, and there were few gaps waiting to be filled by speculators. In 1852 the London and South Western Railway had reached Alton, from Brookwood on the London to Southampton ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waterloo & City Line
The Waterloo & City line, colloquially known as The Drain, is a London Underground shuttle line that runs between Waterloo and Bank with no intermediate stops. Its primary traffic consists of commuters from south-west London, Surrey and Hampshire arriving at Waterloo main line station and travelling forward to the City of London financial district. For this reason, the line has historically not operated on Sundays or public holidays, except in very limited circumstances. However, following the COVID-19 pandemic, the line is currently only open on weekdays. It is one of only two lines on the Underground network to run completely underground, the other being the Victoria line. Printed in turquoise on the Tube map, it is by far the shortest line on the Underground network, being long, with an end-to-end journey lasting just four minutes. In absolute terms, it is the least-used Tube line, carrying just over 15 million passengers annually. However, in terms of the average nu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southampton
Southampton () is a port city in the ceremonial county of Hampshire in southern England. It is located approximately south-west of London and west of Portsmouth. The city forms part of the South Hampshire built-up area, which also covers Portsmouth and the towns of Havant, Waterlooville, Eastleigh, Fareham and Gosport. A major port, and close to the New Forest, it lies at the northernmost point of Southampton Water, at the confluence of the River Test and Itchen, with the River Hamble joining to the south. Southampton is classified as a Medium-Port City . Southampton was the departure point for the and home to 500 of the people who perished on board. The Spitfire was built in the city and Southampton has a strong association with the ''Mayflower'', being the departure point before the vessel was forced to return to Plymouth. In the past century, the city was one of Europe's main ports for ocean liners and more recently, Southampton is known as the home port of some of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hockley Railway Viaduct
The Hockley Railway Viaduct is a disused railway viaduct to the south of Winchester in Hampshire, England. History The viaduct, originally called the Shawford Viaduct, was built in the late 1880s by the London and South Western Railway (LSWR). It provided a link over the River Itchen and water meadows, from the Didcot, Newbury and Southampton Railway (DN&SR), to the LSWR's main line. The DN&SR was originally intended to continue down the east side of the Itchen to Southampton, but had stalled at Winchester due to lack of funds. The viaduct crossed the valley to link the DN&SR to the LSWR, which ran (and still runs) down the west side of the valley. The viaduct was last used by the railway on 2 April 1966. The line it carried closed as a result of the Beeching Axe, although all of it, with the exception of a few bricks on the walls, is still standing and is open to walkers and cyclists. It forms part of the National Cycle Network Route 23. Construction The structure has 33 spa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Okehampton
Okehampton ( ) is a town and civil parishes in England, civil parish in West Devon in the English county of Devon. It is situated at the northern edge of Dartmoor, and had a population of 5,922 at the 2011 census. Two electoral wards are based in the town (east and west). Their joint population at the same census was 7,500. Okehampton is 21 miles (33 km) west of Exeter, 26 miles (42 km) north of Plymouth and 24 miles (38 km) south of Barnstaple. History Okehampton was founded by the Saxons. The earliest written record of the settlement is from 980 AD as , meaning settlement by the Ockment, a river which runs through the town. It was recorded as a place for slaves to be freed at cross roads. Like many towns in the West Country, Okehampton grew on the medieval wool trade. Notable buildings in the town include the 15th century chapel of James, son of Zebedee, St. James and Okehampton Castle, which was established by the Normans, Norman High Sheriff of Devon, Sherif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meldon Viaduct
Meldon Viaduct carried the London & South Western Railway (LSWR) across the West Okement River at Meldon (near Okehampton) on Dartmoor in Devon, South West England. The truss bridge, which was constructed from wrought iron and cast iron not stone or brick arches, was built under the direction of the LSWR's chief engineer, WR Galbraith. After taking three years to build, the dual-tracked bridge opened to rail traffic in 1874. Usage was limited to certain classes of locomotive because the viaduct had an axle load limit. Although regular services were withdrawn in 1968, the bridge was used for shunting by a local quarry. In the 1990s the remaining single line was removed after the viaduct was deemed to be too weak to carry rail traffic. The crossing is now used by The Granite Way, a long-distance cycle track across Dartmoor. The viaduct, which is a scheduled monument, is now one of only two such surviving railway bridges in the United Kingdom that uses wrought iron lattice piers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London
London is the capital and largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a major settlement for two millennia. The City of London, its ancient core and financial centre, was founded by the Romans as '' Londinium'' and retains its medieval boundaries.See also: Independent city § National capitals The City of Westminster, to the west of the City of London, has for centuries hosted the national government and parliament. Since the 19th century, the name "London" has also referred to the metropolis around this core, historically split between the counties of Middlesex, Essex, Surrey, Kent, and Hertfordshire, which largely comprises Greater London, governed by the Greater London Authority.The Greater London Authority consists of the Mayor of London and the London Assembly. The London Mayor is distinguished fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland. The United Kingdom includes the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland, and many smaller islands within the British Isles. Northern Ireland shares a land border with the Republic of Ireland; otherwise, the United Kingdom is surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, the North Sea, the English Channel, the Celtic Sea and the Irish Sea. The total area of the United Kingdom is , with an estimated 2020 population of more than 67 million people. The United Kingdom has evolved from a series of annexations, unions and separations of constituent countries over several hundred years. The Treaty of Union between the Kingdom of England (which included Wales, annexed in 1542) and the Kingdom of Scotland in 170 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |