|
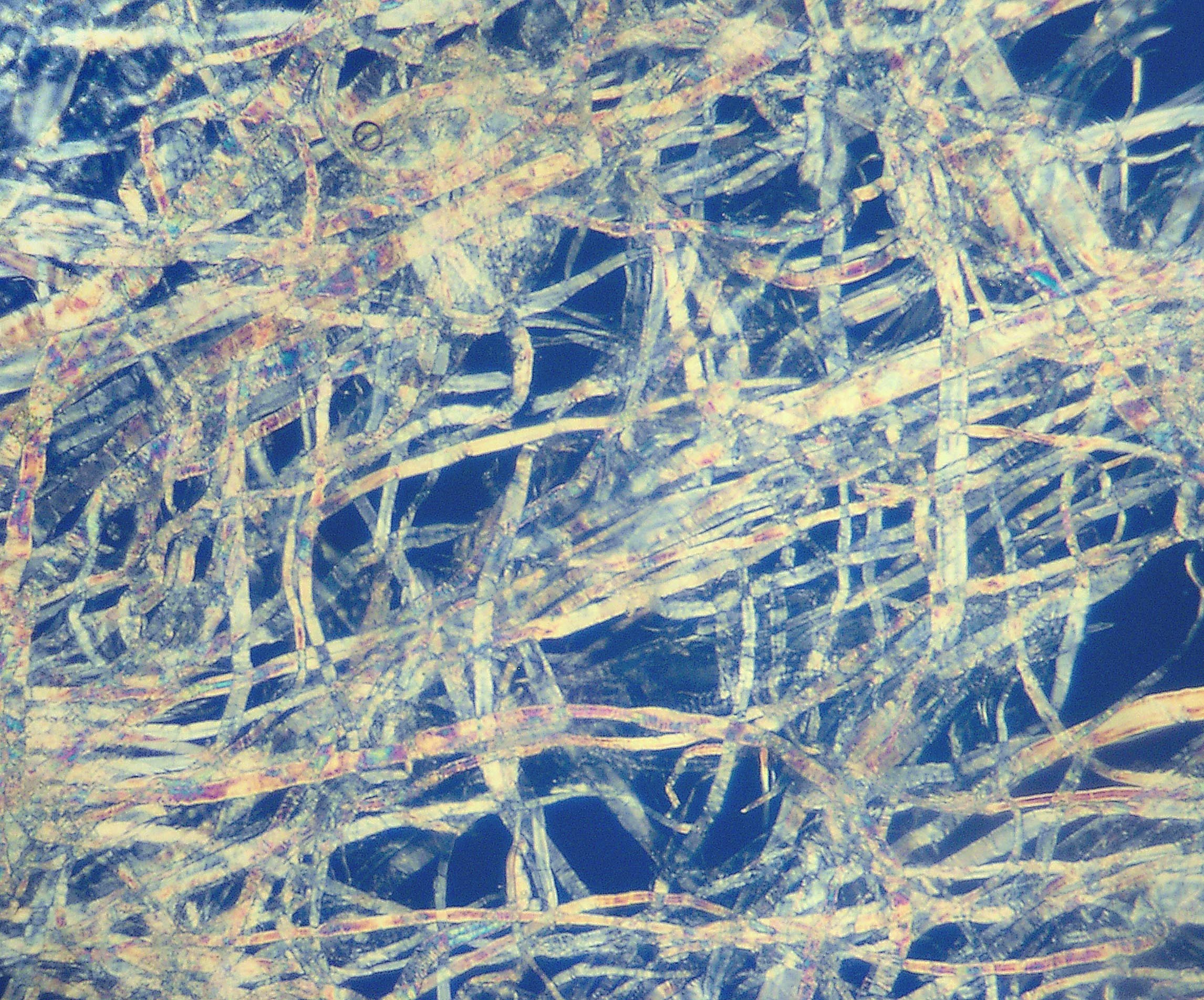
Voile
Voile is a soft, sheer fabric, usually made of 99% cotton or cotton blended with linen or polyester. The term is French for ''veil''. Because of its light weight, the fabric is mostly used in soft furnishing. In tropical climates, voile is used for window treatments and mosquito nets. When used as curtain material, voile is similar to net curtains. Voiles are available in a range of patterns and colours. Because of their semitransparent quality, voile curtains are made using heading tape that is less easily noticeable through the fabric. Voile fabric is also used in dressmaking, either in multiple layers or laid over a second material. It is similar to chiffon. Material types Light-penetrable sheer fabrics include voile, muslin, and lace. These can be broadly divided into two groups based on method of production. The first are the natural fibers such as cotton and silk. The second group is prepared from a man-made fiber. This kind of synthetic sheer is extracted from ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sheer Fabric
Sheer fabric is fabric which is made using thin thread or low density of knit. This results in a semi- transparent and flimsy cloth. Some fabrics become transparent when wet. Overview The sheerness of a fabric is expressed as a numerical denier which ranges from 3 (extremely rare, very thin, barely visible) to 15 (standard sheer for stockings) up to 30 (semi opaque) until 100 (opaque). The materials which can be made translucent include gossamer, silk, rayon or nylon. Sheer fabric comes in a wide variety of colors, but for curtains, white and shades of white, such as cream, winter white, eggshell, and ivory are popular. In some cases, sheer fabric is embellished with embroidered patterns or designs. A common use for sheer fabric is in curtains, which allows for sunlight to pass through during daylight, while maintaining a level of privacy. However, when it is lighter on the inside of a room than it is on the outside (such as at nighttime), then the inside of the room can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Fibers
Natural fibers or natural fibres (see spelling differences) are fibers that are produced by geological processes, or from the bodies of plants or animals. They can be used as a component of composite materials, where the orientation of fibers impacts the properties. Natural fibers can also be matted into sheets to make paper or felt. The earliest evidence of humans using fibers is the discovery of wool and dyed flax fibers found in a prehistoric cave in the Republic of Georgia that date back to 36,000 BP. Natural fibers can be used for high-tech applications, such as composite parts for automobiles and medical supplies. Compared to composites reinforced with glass fibers, composites with natural fibers have advantages such as lower density, better thermal insulation, and reduced skin irritation. Further, unlike glass fibers, natural fibers can be broken down by bacteria once they are no longer used. Natural fibers are good water absorbents and can be found in various ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organza
Organza is a thin, plain weave, sheer fabric traditionally made from silk. Many modern organzas are woven with synthetic filament fibers such as polyester or nylon. Silk organza is woven by a number of mills along the Yangtze River and in the province of Zhejiang in China. A coarser silk organza is woven in the Bangalore area of India. Deluxe silk organzas are woven in France and Italy. Organza is distinguished by its crisp hand, stiffness relative to weight, and slippery surface texture. Organza is used for bridalwear and eveningwear. Sometimes, it is used as a hidden structural element. Beginning in the 1980's, trends shifted and organza began seeing more use in day to day clothing. In the interiors market, it is used for effects in bedrooms and between rooms. Double-width organzas in viscose and acetate are used as sheer curtains. The term may derive from French ''organsin'', ultimately from the Central Asian city of Urgench, the midpoint of the Northern Silk Road. See al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marquisette
Marquisette is a lightweight, sheer fabric that has a structure similar to a mosquito net. Construction Marquisette is a very loose weave construction plain and sometimes with designs. Leno is one type of weaving the marquisette. Marquisette may be made with many natural or synthetic yarns, and the most common is nylon. The other variants are possible with cotton, silk, rayon, orlon and polyester. Use Marquisette is employed in certain undergarments, and is seen in dresses such as bridal wear and evening wear. It can commonly be seen in sheer draperies and curtains. See also * Ninon * Voile Voile is a soft, sheer fabric, usually made of 99% cotton or cotton blended with linen or polyester. The term is French for ''veil''. Because of its light weight, the fabric is mostly used in soft furnishing. In tropical climates, voile is used ... References External links * Net fabrics Textiles {{Textile-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Window Valance
A window valance (or pelmet in the UK) is a form of window treatment that covers the uppermost part of the window and can be hung alone or paired with other window blinds, or curtains. Valances are a popular decorative choice in concealing drapery hardware. Window valances were popular in Victorian interior design. In draping or bunting form they are commonly referred to as ''swag''. Types Window valances are also called window top treatments. The earliest recorded history of interior design is rooted in the renaissance Era, a time of great change and rebirth in the world of art and architecture, and much of this time saw understated, simple treatments, eventually moving towards more elaborate fabrics of multiple layers of treatments, including, towards the end of this period, valances, swags, jabots, and pelmets. By the Baroque and early Georgian period (1643-1730), elaborate and theatrical treatments placed high emphasis on the cornice and pelmet as a way to finish off the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Window Dressing
A display window, also a shop window (British English) or store window (American English), is a window in a shop displaying items for sale or otherwise designed to attract customers to the store. Usually, the term refers to larger windows in the front façade of the shop. History The first display windows in shops were installed in the late 18th century in London, where levels of conspicuous consumption were growing rapidly. Retailer Francis Place was one of the first to experiment with this new retailing method at his tailoring establishment in Charing Cross, where he fitted the shop-front with large plate glass windows. Although this was condemned by many, he defended his practice in his memoirs, claiming that he "sold from the window more goods...than paid journeymen's wages and the expenses of housekeeping. Display windows at boutiques usually have dressed-up mannequins in them. Window dressing Displaying merchandise in a store window is known as " window dressing", which is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petroleum
Petroleum, also known as crude oil, or simply oil, is a naturally occurring yellowish-black liquid mixture of mainly hydrocarbons, and is found in geological formations. The name ''petroleum'' covers both naturally occurring unprocessed crude oil and petroleum products that consist of refined crude oil. A fossil fuel, petroleum is formed when large quantities of dead organisms, mostly zooplankton and algae, are buried underneath sedimentary rock and subjected to both prolonged heat and pressure. Petroleum is primarily recovered by oil drilling. Drilling is carried out after studies of structural geology, sedimentary basin analysis, and reservoir characterisation. Recent developments in technologies have also led to exploitation of other unconventional reserves such as oil sands and oil shale. Once extracted, oil is refined and separated, most easily by distillation, into innumerable products for direct use or use in manufacturing. Products include fuels such as gasol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wood Pulp
Pulp is a lignocellulosic fibrous material prepared by chemically or mechanically separating cellulose fibers from wood, fiber crops, waste paper, or rags. Mixed with water and other chemical or plant-based additives, pulp is the major raw material used in papermaking and the industrial production of other paper products. History Before the widely acknowledged invention of papermaking by Cai Lun in China around 105 AD, paper-like writing materials such as papyrus and amate were produced by ancient civilizations using plant materials which were largely unprocessed. Strips of bark or bast material were woven together, beaten into rough sheets, dried, and polished by hand. Pulp used in modern and traditional papermaking is distinguished by the process which produces a finer, more regular slurry of cellulose fibers which are pulled out of solution by a screen and dried to form sheets or rolls. The earliest paper produced in China consisted of bast fibers from the paper mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Man-made Fibers
Fiber or fibre (from la, fibra, links=no) is a natural or artificial substance that is significantly longer than it is wide. Fibers are often used in the manufacture of other materials. The strongest engineering materials often incorporate fibers, for example carbon fiber and ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene. Synthetic fibers can often be produced very cheaply and in large amounts compared to natural fibers, but for clothing natural fibers can give some benefits, such as comfort, over their synthetic counterparts. Natural fibers Natural fibers develop or occur in the fiber shape, and include those produced by plants, animals, and geological processes. They can be classified according to their origin: *Vegetable fibers are generally based on arrangements of cellulose, often with lignin: examples include cotton, hemp, jute, flax, abaca, piña, ramie, sisal, bagasse, and banana. Plant fibers are employed in the manufacture of paper and textile (cloth), and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silk
Silk is a natural protein fiber, some forms of which can be woven into textiles. The protein fiber of silk is composed mainly of fibroin and is produced by certain insect larvae to form cocoons. The best-known silk is obtained from the cocoons of the larvae of the mulberry silkworm ''Bombyx mori'' reared in captivity ( sericulture). The shimmering appearance of silk is due to the triangular prism-like structure of the silk fibre, which allows silk cloth to refract incoming light at different angles, thus producing different colors. Silk is produced by several insects; but, generally, only the silk of moth caterpillars has been used for textile manufacturing. There has been some research into other types of silk, which differ at the molecular level. Silk is mainly produced by the larvae of insects undergoing complete metamorphosis, but some insects, such as webspinners and raspy crickets, produce silk throughout their lives. Silk production also occurs in hymenoptera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lace
Lace is a delicate fabric made of yarn or thread in an open weblike pattern, made by machine or by hand. Generally, lace is divided into two main categories, needlelace and bobbin lace, although there are other types of lace, such as knitted or crocheted lace. Other laces such as these are considered as a category of their specific craft. Knitted lace, therefore, is an example of knitting. This article considers both needle lace and bobbin lace. While some experts say both needle lace and bobbin lace began in Italy in the late 1500s, there are some questions regarding its origins. Originally linen, silk, gold, or silver threads were used. Now lace is often made with cotton thread, although linen and silk threads are still available. Manufactured lace may be made of synthetic fiber. A few modern artists make lace with a fine copper or silver wire instead of thread. Etymology The word lace is from Middle English, from Old French ''las'', noose, string, from Vulgar Latin *''l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cotton
Cotton is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus '' Gossypium'' in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is almost pure cellulose, and can contain minor percentages of waxes, fats, pectins, and water. Under natural conditions, the cotton bolls will increase the dispersal of the seeds. The plant is a shrub native to tropical and subtropical regions around the world, including the Americas, Africa, Egypt and India. The greatest diversity of wild cotton species is found in Mexico, followed by Australia and Africa. Cotton was independently domesticated in the Old and New Worlds. The fiber is most often spun into yarn or thread and used to make a soft, breathable, and durable textile. The use of cotton for fabric is known to date to prehistoric times; fragments of cotton fabric dated to the fifth millennium BC have been found in the Indus Valley civilization, as well as fabric remnants dat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |