|
Virodhamine
Virodhamine (''O''-arachidonoyl ethanolamine; O-AEA) is an endocannabinoid and a nonclassic eicosanoid, derived from arachidonic acid. ''O''-Arachidonoyl ethanolamine is arachidonic acid and ethanolamine joined by an ester linkage, the opposite of the amide linkage found in anandamide. Based on this opposite orientation, the molecule was named virodhamine from the Sanskrit word ''virodha'', which means opposition. It acts as an antagonist of the CB1 receptor and agonist of the CB2 receptor. Concentrations of virodhamine in the human hippocampus are similar to those of anandamide, but they are 2- to 9-fold higher in peripheral tissues that express CB2. Virodhamine lowers body temperature in mice, demonstrating cannabinoid activity ''in vivo''. See also * Anandamide * Oleamide Oleamide is an organic compound with the formula CH3(CH2)7CH=CH(CH2)7CONH2(. It is the amide derived from the fatty acid oleic acid. It is a colorless waxy solid and occurs in nature. Sometimes lab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cannabinoids
Cannabinoids () are several structural classes of compounds found in the cannabis plant primarily and most animal organisms (although insects lack such receptors) or as synthetic compounds. The most notable cannabinoid is the phytocannabinoid tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) (delta-9-THC), the primary intoxicating compound in cannabis. Cannabidiol (CBD) is a major constituent of temperate Cannabis plants and a minor constituent in tropical varieties. At least 113 distinct phytocannabinoids have been isolated from cannabis, although only four (i.e., THCA, CBDA, CBCA and their common precursor CBGA) have been demonstrated to have a biogenetic origin. It was reported in 2020 that phytocannabinoids can be found in other plants such as rhododendron, licorice and liverwort, and earlier in Echinacea. Phytocannabinoids are multi-ring phenolic compounds structurally related to THC, but endocannabinoids are fatty acid derivatives. Nonclassical synthetic cannabinoids (cannabimimetics) include ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endocannabinoids
Cannabinoids () are several structural classes of compounds found in the cannabis plant primarily and most animal organisms (although insects lack such receptors) or as synthetic compounds. The most notable cannabinoid is the phytocannabinoid tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) (delta-9-THC), the primary intoxicating compound in cannabis. Cannabidiol (CBD) is a major constituent of temperate Cannabis plants and a minor constituent in tropical varieties. At least 113 distinct phytocannabinoids have been isolated from cannabis, although only four (i.e., THCA, CBDA, CBCA and their common precursor CBGA) have been demonstrated to have a biogenetic origin. It was reported in 2020 that phytocannabinoids can be found in other plants such as rhododendron, licorice and liverwort, and earlier in Echinacea. Phytocannabinoids are multi-ring phenolic compounds structurally related to THC, but endocannabinoids are fatty acid derivatives. Nonclassical synthetic cannabinoids (cannabimimetics) include ami ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oleamide
Oleamide is an organic compound with the formula CH3(CH2)7CH=CH(CH2)7CONH2(. It is the amide derived from the fatty acid oleic acid. It is a colorless waxy solid and occurs in nature. Sometimes labeled as a fatty acid primary amide (FAPA), it is biosynthesized from N-oleoylglycine. Biochemical and medical aspects In terms of natural occurrence, oleamide was first detected in human plasma. It was later shown to accumulate in the cerebrospinal fluid during sleep deprivation and induces sleep in animals. It has been considered as a potential treatment for mood and sleep disorders, as well as cannabinoid-regulated depression. In terms of its sleep inducing effects, it is speculated that oleamide interacts with multiple neurotransmitter systems. Some in-vitro studies show that the cis enantomer of oleamide is an agnoist for the cannabinoid receptor CB-1 with an affinity around 8 micromolar. However, given oleamide's relatively low affinity for CB-1 and uncertainty about the concen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anandamide
Anandamide (ANA), also known as ''N''-arachidonoylethanolamine (AEA), is a fatty acid neurotransmitter. Anandamide was the first endocannabinoid to be discovered: it participates in the body's endocannabinoid system by binding to cannabinoid receptors, the same receptors that the psychoactive compound THC in cannabis acts on. Anandamide is found in nearly all tissues in a wide range of animals. Anandamide has also been found in plants, including small amounts in chocolate. The name 'anandamide' is taken from the Sanskrit word '' ananda'', which means "joy, bliss, delight", plus amide. Anandamide is derived from the non-oxidative metabolism of arachidonic acid, an essential omega-6 fatty acid. It is synthesized from ''N''-arachidonoyl phosphatidylethanolamine by multiple pathways. It is degraded primarily by the fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) enzyme, which converts anandamide into ethanolamine and arachidonic acid. As such, inhibitors of FAAH lead to elevated anandamid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anandamide
Anandamide (ANA), also known as ''N''-arachidonoylethanolamine (AEA), is a fatty acid neurotransmitter. Anandamide was the first endocannabinoid to be discovered: it participates in the body's endocannabinoid system by binding to cannabinoid receptors, the same receptors that the psychoactive compound THC in cannabis acts on. Anandamide is found in nearly all tissues in a wide range of animals. Anandamide has also been found in plants, including small amounts in chocolate. The name 'anandamide' is taken from the Sanskrit word '' ananda'', which means "joy, bliss, delight", plus amide. Anandamide is derived from the non-oxidative metabolism of arachidonic acid, an essential omega-6 fatty acid. It is synthesized from ''N''-arachidonoyl phosphatidylethanolamine by multiple pathways. It is degraded primarily by the fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) enzyme, which converts anandamide into ethanolamine and arachidonic acid. As such, inhibitors of FAAH lead to elevated anandamid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agonist
An agonist is a chemical that activates a receptor to produce a biological response. Receptors are cellular proteins whose activation causes the cell to modify what it is currently doing. In contrast, an antagonist blocks the action of the agonist, while an inverse agonist causes an action opposite to that of the agonist. Etymology From the Greek αγωνιστής (agōnistēs), contestant; champion; rival < αγων (agōn), contest, combat; exertion, struggle < αγω (agō), I lead, lead towards, conduct; drive Types of agonists can be activated by either endogenous agonists (such as[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fatty Acid Esters
Fatty is a derogatory term for someone who is obese. It may refer also to: People * Mai Fatty, Gambian politician * Roscoe Arbuckle (1887–1933), American actor and comedian * Fatty Briody (1858–1903), American Major League Baseball player * Fatty D (April Fores), American pornographic actress * Bob Fothergill (1897–1938), American Major League Baseball outfielder * William Foulke (footballer) (1874–1916), English cricketer and footballer * Fatty George (1927–1982), Austrian jazz musician * Richard Lamb (1907–1974), Australian racing cyclist * Fatty Lawrence (1903–1976), college gridiron football player * W. T. McLain (1885–1938), college gridiron football player, lawyer, and politician * Charles H. Smith (American football), University of Michigan football player in 1893–1894 * Roland Taylor (1946–2017), retired American Basketball Association and National Basketball Association player * Paul Vautin (born 1959), Australian former rugby league footballer a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eicosanoids
Eicosanoids are signaling molecules made by the enzymatic or non-enzymatic oxidation of arachidonic acid or other polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) that are, similar to arachidonic acid, around 20 carbon units in length. Eicosanoids are a sub-category of oxylipins, i.e. oxidized fatty acids of diverse carbon units in length, and are distinguished from other oxylipins by their overwhelming importance as cell signaling molecules. Eicosanoids function in diverse physiological systems and pathological processes such as: mounting or inhibiting inflammation, allergy, fever and other immune responses; regulating the abortion of pregnancy and normal childbirth; contributing to the perception of pain; regulating cell growth; controlling blood pressure; and modulating the regional flow of blood to tissues. In performing these roles, eicosanoids most often act as autocrine signaling agents to impact their cells of origin or as paracrine signaling agents to impact cells in the proximity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
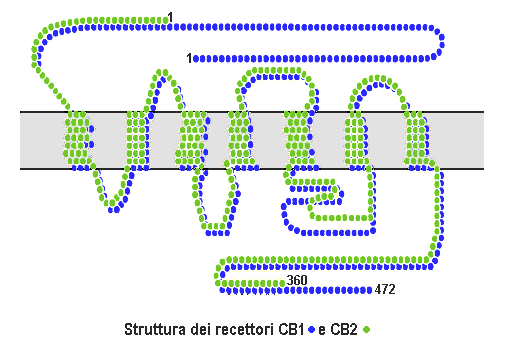
Cannabinoid Receptor
Cannabinoid receptors, located throughout the body, are part of the endocannabinoid system a class of cell membrane receptors in the G protein-coupled receptor superfamily. As is typical of G protein-coupled receptors, the cannabinoid receptors contain seven transmembrane spanning domains. Cannabinoid receptors are activated by three major groups of ligands: endocannabinoids; plant cannabinoids (such as Tetrahydrocannabinol, produced by the cannabis plant); and synthetic cannabinoids (such as HU-210). All of the endocannabinoids and phytocannabinoids (plant based cannabinoids) are lipophilic. There are two known subtypes of cannabinoid receptors, termed CB1 and CB2. The CB1 receptor is expressed mainly in the brain (central nervous system or "CNS"), but also in the lungs, liver and kidneys. The CB2 receptor is expressed mainly in the immune system, in hematopoietic cells, and in parts of the brain. The protein sequences of CB1 and CB2 receptors are about 44% simi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cannabinoid Receptor
Cannabinoid receptors, located throughout the body, are part of the endocannabinoid system a class of cell membrane receptors in the G protein-coupled receptor superfamily. As is typical of G protein-coupled receptors, the cannabinoid receptors contain seven transmembrane spanning domains. Cannabinoid receptors are activated by three major groups of ligands: endocannabinoids; plant cannabinoids (such as Tetrahydrocannabinol, produced by the cannabis plant); and synthetic cannabinoids (such as HU-210). All of the endocannabinoids and phytocannabinoids (plant based cannabinoids) are lipophilic. There are two known subtypes of cannabinoid receptors, termed CB1 and CB2. The CB1 receptor is expressed mainly in the brain (central nervous system or "CNS"), but also in the lungs, liver and kidneys. The CB2 receptor is expressed mainly in the immune system, in hematopoietic cells, and in parts of the brain. The protein sequences of CB1 and CB2 receptors are about 44% simi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eicosanoid
Eicosanoids are signaling molecules made by the enzymatic or non-enzymatic oxidation of arachidonic acid or other polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) that are, similar to arachidonic acid, around 20 carbon units in length. Eicosanoids are a sub-category of oxylipins, i.e. oxidized fatty acids of diverse carbon units in length, and are distinguished from other oxylipins by their overwhelming importance as cell signaling molecules. Eicosanoids function in diverse physiological systems and pathological processes such as: mounting or inhibiting inflammation, allergy, fever and other immune responses; regulating the abortion of pregnancy and normal childbirth; contributing to the perception of pain; regulating cell growth; controlling blood pressure; and modulating the regional flow of blood to tissues. In performing these roles, eicosanoids most often act as autocrine signaling agents to impact their cells of origin or as paracrine signaling agents to impact cells in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Receptor Antagonist
A receptor antagonist is a type of receptor ligand or drug that blocks or dampens a biological response by binding to and blocking a receptor rather than activating it like an agonist. Antagonist drugs interfere in the natural operation of receptor proteins.Pharmacology Guide: In vitro pharmacology: concentration-response curves " '' GlaxoWellcome.'' Retrieved on December 6, 2007. They are sometimes called blockers; examples include alpha blockers, beta blocker [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |