|
Vera Buch
Vera Wilhelmine Buch Weisbord (Forestville, Connecticut 19 August 1895 – Chicago 6 September 1987) was an American political activist and union organizer. Early life Vera Buch was born on 19 August 1895 Forestville, Connecticut. Her parents were John Casper Buch and Nellie Amelia Louisa Crawford. At an early age, the family moved to the Bronx New York. Buch studied at the Hunter High School and graduated from Hunter College in 1916. Shortly after that, she got tuberculosis and spent a year in a sanatorium. During her stay, she met a woman who inspired her to stury socialist economic theory. Political activism and union organization In 1918, Buch moved to Caldwell, New Jersey, where she got involved with the Left Wing Section of the Socialist Party. She later joined the Industrial Workers of the World and the Communist Party USA. Under the Leona Smith pseudonym, she helped organizing workers during the 1926 Passaic textile strike, the first mass strike led by communists i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Connecticut
Connecticut () is the southernmost state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It is bordered by Rhode Island to the east, Massachusetts to the north, New York to the west, and Long Island Sound to the south. Its capital is Hartford and its most populous city is Bridgeport. Historically the state is part of New England as well as the tri-state area with New York and New Jersey. The state is named for the Connecticut River which approximately bisects the state. The word "Connecticut" is derived from various anglicized spellings of "Quinnetuket”, a Mohegan-Pequot word for "long tidal river". Connecticut's first European settlers were Dutchmen who established a small, short-lived settlement called House of Hope in Hartford at the confluence of the Park and Connecticut Rivers. Half of Connecticut was initially claimed by the Dutch colony New Netherland, which included much of the land between the Connecticut and Delaware Rivers, although the firs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Detroit
Detroit ( , ; , ) is the largest city in the U.S. state of Michigan. It is also the largest U.S. city on the United States–Canada border, and the seat of government of Wayne County. The City of Detroit had a population of 639,111 at the 2020 census, making it the 27th-most populous city in the United States. The metropolitan area, known as Metro Detroit, is home to 4.3 million people, making it the second-largest in the Midwest after the Chicago metropolitan area, and the 14th-largest in the United States. Regarded as a major cultural center, Detroit is known for its contributions to music, art, architecture and design, in addition to its historical automotive background. ''Time'' named Detroit as one of the fifty World's Greatest Places of 2022 to explore. Detroit is a major port on the Detroit River, one of the four major straits that connect the Great Lakes system to the Saint Lawrence Seaway. The City of Detroit anchors the second-largest regional economy in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Art Institute Of Chicago
The Art Institute of Chicago in Chicago's Grant Park, founded in 1879, is one of the oldest and largest art museums in the world. Recognized for its curatorial efforts and popularity among visitors, the museum hosts approximately 1.5 million people annually. Its collection, stewarded by 11 curatorial departments, is encyclopedic, and includes iconic works such as Georges Seurat's ''A Sunday on La Grande Jatte'', Pablo Picasso's ''The Old Guitarist'', Edward Hopper's '' Nighthawks'', and Grant Wood's '' American Gothic''. Its permanent collection of nearly 300,000 works of art is augmented by more than 30 special exhibitions mounted yearly that illuminate aspects of the collection and present cutting-edge curatorial and scientific research. As a research institution, the Art Institute also has a conservation and conservation science department, five conservation laboratories, and one of the largest art history and architecture libraries in the country—the Ryerson and B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Civil Rights Movement
The civil rights movement was a nonviolent social and political movement and campaign from 1954 to 1968 in the United States to abolish legalized institutional Racial segregation in the United States, racial segregation, Racial discrimination in the United States, discrimination, and disenfranchisement in the United States, disenfranchisement throughout the United States. The movement had its origins in the Reconstruction era during the late 19th century, although it made its largest legislative gains in the 1960s after years of direct actions and grassroots protests. The social movement's major nonviolent resistance and civil disobedience campaigns eventually secured new protections in federal law for the civil rights of all Americans. After the American Civil War and the subsequent Abolitionism in the United States, abolition of slavery in the 1860s, the Reconstruction Amendments to the United States Constitution granted emancipation and constitutional rights of citizenship ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congress Of Racial Equality
The Congress of Racial Equality (CORE) is an African Americans, African-American civil rights organization in the United States that played a pivotal role for African Americans in the civil rights movement. Founded in 1942, its stated mission is "to bring about equality for all people regardless of race, creed, sex, age, disability, sexual orientation, religion or ethnic background." History Founding CORE was founded in Chicago, Illinois, in March 1942. The organization's founding members included James Farmer, James Leonard Farmer Jr., Pauli Murray, Anna Pauline "Pauli" Murray, George Houser, George Mills Houser, Bernice Fisher, Elsie Bernice Fisher and Homer A. Jack. Of the 50 original founding members, 28 were men and 22 were women, roughly one-third of them were Black and the other two-thirds white. Bayard Rustin, while not a founding member of the organization, was (as Farmer and Houser later noted) "an uncle to CORE" and provided it with significant support. The group ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trotskyism
Trotskyism is the political ideology and branch of Marxism developed by Ukrainian-Russian revolutionary Leon Trotsky and some other members of the Left Opposition and Fourth International. Trotsky self-identified as an orthodox Marxist, a revolutionary Marxist, and Bolshevik–Leninist, a follower of Marx, Engels, and 3L: Vladimir Lenin, Karl Liebknecht, and Rosa Luxemburg. He supported founding a vanguard party of the proletariat, proletarian internationalism, and a dictatorship of the proletariat (as opposed to the " dictatorship of the bourgeoisie", which Marxists argue defines capitalism) based on working-class self-emancipation and mass democracy. Trotskyists are critical of Stalinism as they oppose Joseph Stalin's theory of socialism in one country in favour of Trotsky's theory of permanent revolution. Trotskyists criticize the bureaucracy and anti-democratic current developed in the Soviet Union under Stalin. Vladimir Lenin and Trotsky, despite their ideological disp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communist League Of Struggle
The Communist League of Struggle (CLS) was a small communist organization active in the United States during the 1930s. Founded by Albert Weisbord and his wife, Vera Buch, who were veterans of the Left Socialist movement and the Communist Party USA, the CLS briefly affiliated with Leon Trotsky independently of the Communist League of America. It was affiliated to the International Bureau of Revolutionary Youth Organizations until 1935. The small group dwindled and quietly was terminated in the spring of 1937. Organizational history Formation The Communist League of Struggle (CLS) was a factional offshoot of the Communist League of America (CLA), a Trotskyist political party headed by James P. Cannon. The organization was formed on March 15, 1931, owing to what it declared "the principled errors of the other Communist groups" and "organizational violence...within the Communist movement."Nathan Fine (ed.), ''The American Labor Year Book, 1932.'' New York: Rand School Press, 1932 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lovestoneites
The Lovestoneites, led by former General Secretary of the Communist Party USA (CPUSA) Jay Lovestone, were a small American oppositionist Communism, communist movement of the 1930s. The organization emerged from a factional fight in the CPUSA in 1929 and unsuccessfully sought to reintegrate with that organization for several years. Over the course of its existence the organization made use of four names: * Communist Party (Majority Group) (November 1929-September 1932) * Communist Party of the USA (Opposition) (September 1932-May 1937) * Independent Communist Labor League (May 1937-July 1938) * Independent Labor League of America (July 1938-January 1941) The members often referred to their organization as the Communist Party (Opposition) or "CPO." Activists in the Communist Party (Opposition) played a role in a number of trade union organizations of the 1930s, particularly in the automobile and garment industries. A growing disaffection with the Soviet Union in the years after the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Textile Workers Union
National may refer to: Common uses * Nation or country ** Nationality – a ''national'' is a person who is subject to a nation, regardless of whether the person has full rights as a citizen Places in the United States * National, Maryland, census-designated place * National, Nevada, ghost town * National, Utah, ghost town * National, West Virginia, unincorporated community Commerce * National (brand), a brand name of electronic goods from Panasonic * National Benzole (or simply known as National), former petrol station chain in the UK, merged with BP * National Car Rental, an American rental car company * National Energy Systems, a former name of Eco Marine Power * National Entertainment Commission, a former name of the Media Rating Council * National Motor Vehicle Company, Indianapolis, Indiana, USA 1900-1924 * National Supermarkets, a defunct American grocery store chain * National String Instrument Corporation, a guitar company formed to manufacture the first resonator gu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States National Guard
The National Guard is a state-based military force that becomes part of the reserve components of the United States Army and the United States Air Force when activated for federal missions.National Guard: FAQ . . Accessed February 2, 2022. It is a military reserve force composed of National Guard military members or units of each state and the territories of , the |
North Carolina
North Carolina () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States. The state is the 28th largest and 9th-most populous of the United States. It is bordered by Virginia to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, Georgia and South Carolina to the south, and Tennessee to the west. In the 2020 census, the state had a population of 10,439,388. Raleigh is the state's capital and Charlotte is its largest city. The Charlotte metropolitan area, with a population of 2,595,027 in 2020, is the most-populous metropolitan area in North Carolina, the 21st-most populous in the United States, and the largest banking center in the nation after New York City. The Raleigh-Durham-Cary combined statistical area is the second-largest metropolitan area in the state and 32nd-most populous in the United States, with a population of 2,043,867 in 2020, and is home to the largest research park in the United States, Research Triangle Park. The earliest evidence of human occupation i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastonia, North Carolina
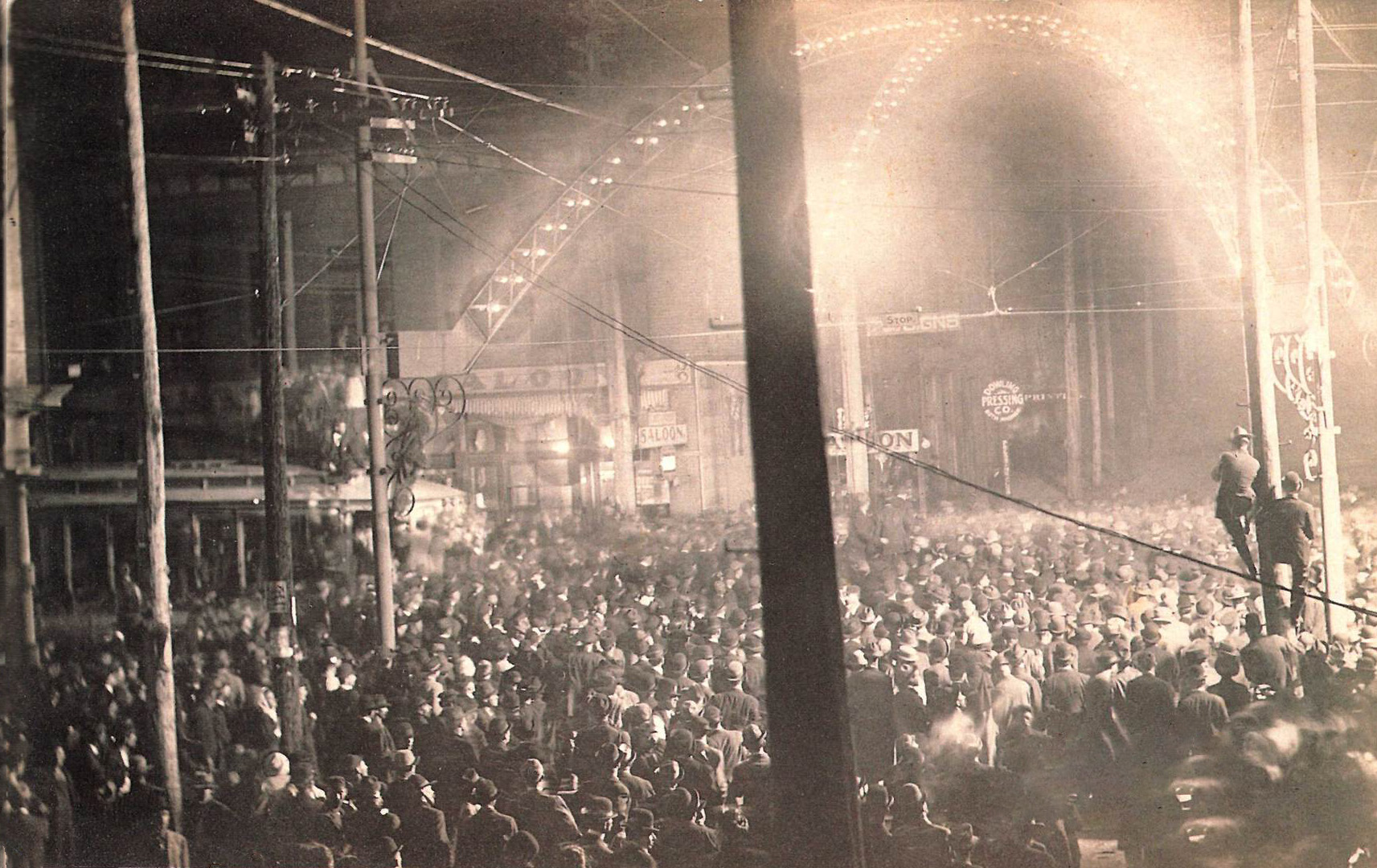
Gastonia is the largest city in and county seat of Gaston County, North Carolina, United States. It is the second-largest satellite city of the Charlotte area, behind Concord. The population was 80,411 at the 2020 census, up from 71,741 in 2010. Gastonia is the 13th most populous city in North Carolina. It is part of the Charlotte metropolitan area, officially designated the Charlotte Metropolitan Statistical Area (MSA). The city is a historic center for textile manufacturing and was the site of the Loray Mill Strike of 1929, which became a key event in the labor movement. While manufacturing remains important to the local economy, the city also has well-developed healthcare, education, and government sectors. History Gastonia is named for William Gaston, a jurist and United States Representative from North Carolina. The Loray Mill strike of 1929 in Gastonia was one of the most notable strikes in the labor history of the United States. The role of organizers for Communist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |