|
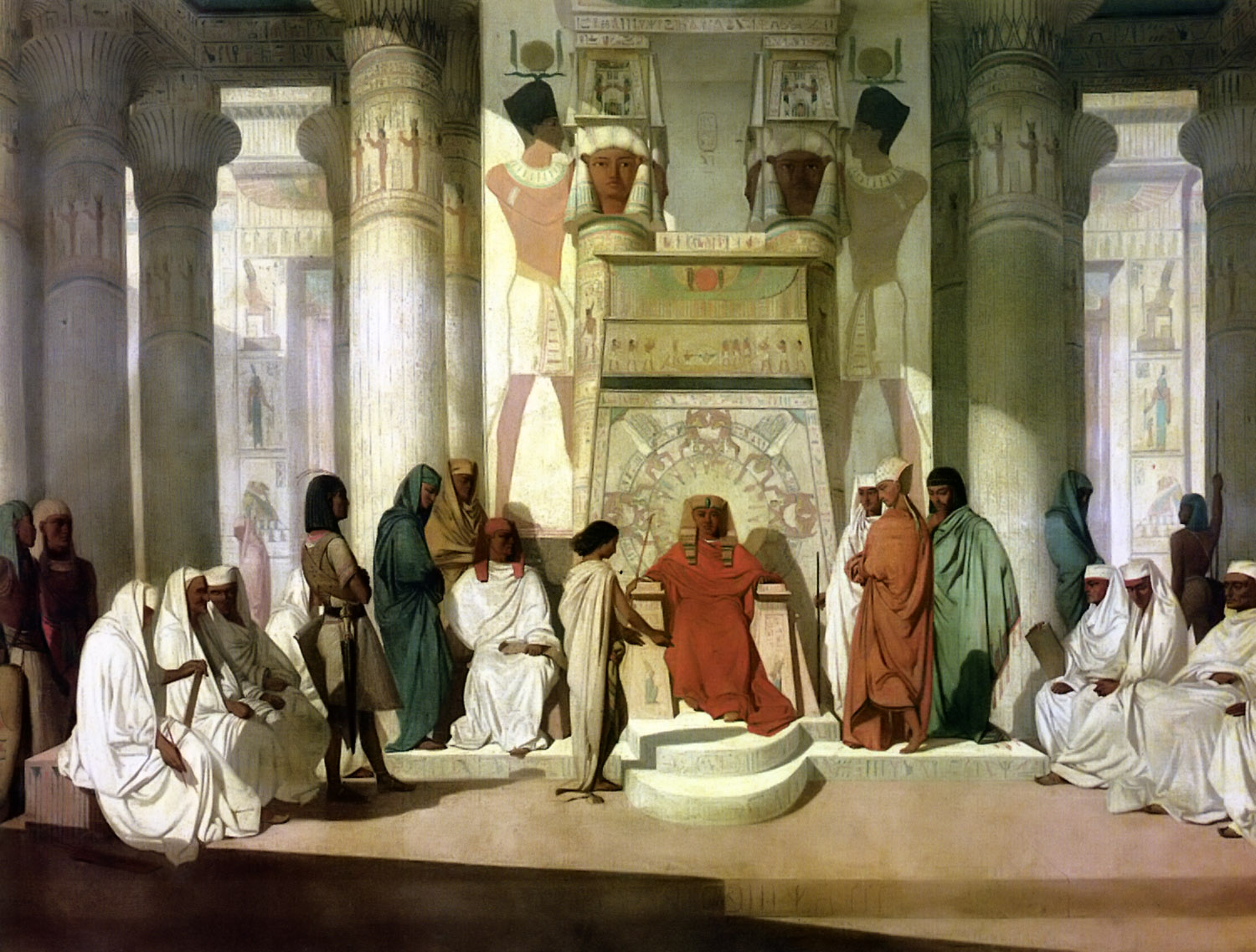
Vayishlach
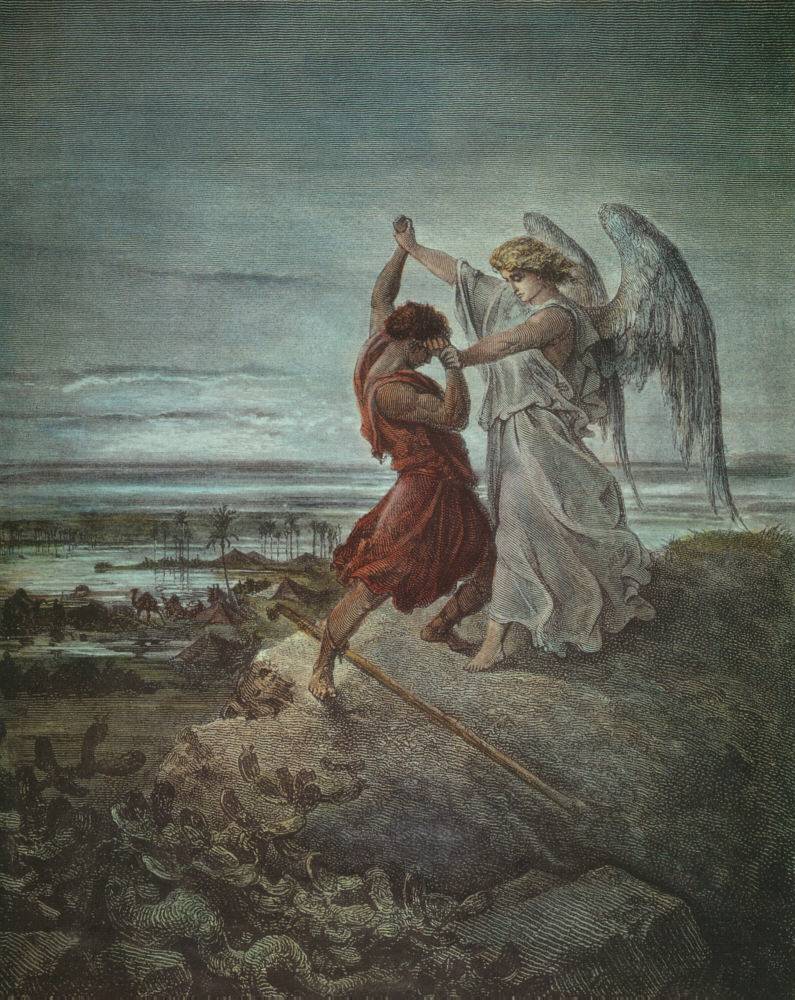
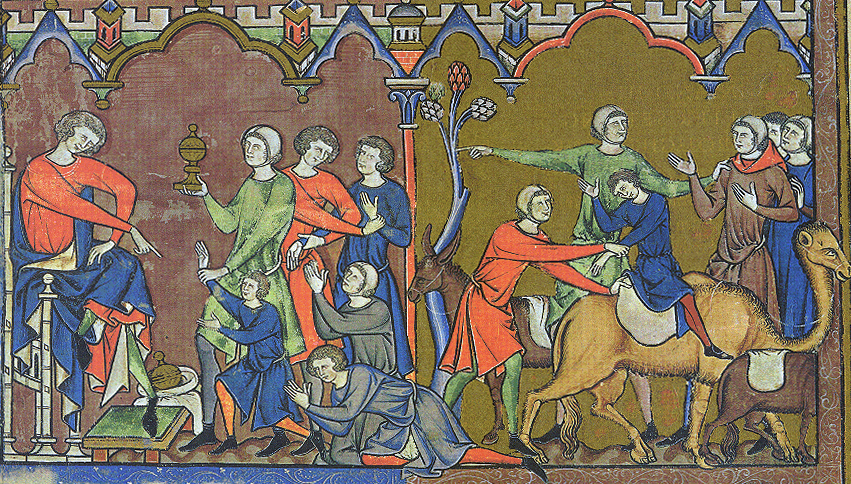
Vayishlach or Vayishlah ( — Hebrew for "and he sent," the first word of the parashah) is the eighth weekly Torah portion (, ) in the annual Jewish cycle of Torah reading. In the parashah, Jacob reconciles with Esau after wrestling with a "man." The prince Shechem rapes Dinah, whose brothers sack the city of Shechem in revenge. In the family's subsequent flight, Rachel gives birth to Benjamin and dies in childbirth. The parashah constitutes . The parashah has the most verses of any weekly Torah portion in the Book of Genesis (Parashat Miketz has the most letters, Parashat Vayeira has the most words, and Parashat Noach has an equal number of verses as Parashat Vayishlach). It is made up of 7,458 Hebrew letters, 1,976 Hebrew words, 153 verses, and 237 lines in a Torah Scroll (''Sefer Torah''). Jews read it the eighth Sabbath after Simchat Torah, in November or December. Readings In traditional Sabbath Torah reading, the parashah is divided into seven readings, or , '' aliyot' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weekly Torah Portion
It is a custom among religious Jewish communities for a weekly Torah portion to be read during Jewish prayer services on Monday, Thursday, and Saturday. The full name, ''Parashat HaShavua'' ( he, פָּרָשַׁת הַשָּׁבוּעַ), is popularly abbreviated to ''parashah'' (also ''parshah'' or parsha), and is also known as a Seder (Bible), Sidra or Sedra . The ''parashah'' is a section of the Torah (Five Books of Moses) used in Jewish liturgy during a particular week. There are 54 parshas, or ''parashiyot'' in Hebrew, and the full cycle is read over the course of one Jewish year. Content and number Each Torah portion consists of two to six chapters to be read during the week. There are 54 weekly portions or ''parashot''. Torah reading mostly follows an annual cycle beginning and ending on the Jewish holiday of Simchat Torah, with the divisions corresponding to the lunisolar calendar, lunisolar Hebrew calendar, which contains up to 55 weeks, the exact number varying betwe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noach (parsha)
Noach, Noiach, Nauach, Nauah, or Noah (, Hebrew for the name "Noah", the third word, and first distinctive word, of the parashah) is the second weekly Torah portion (, ''parashah'') in the annual Jewish cycle of Torah reading. It constitutes . The parashah tells the stories of the Flood and Noah's Ark, of Noah's subsequent drunkenness and cursing of Canaan, and of the Tower of Babel. The parashah has the most verses of any weekly Torah portion in the Book of Genesis (but not the most letters or words). It is made up of 6,907 Hebrew letters, 1,861 Hebrew words, 153 verses, and 230 lines in a Torah Scroll (, ''Sefer Torah''). In the Book of Genesis, Parashat Miketz has the most letters, Parashat Vayeira has the most words, and Parashat Vayishlach has an equal number of verses as Parashat Noach. Jews read it on the second Sabbath after Simchat Torah, generally in October or early November. Readings In traditional Sabbath Torah reading, the parashah is divided into seven readings, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vayeira
Vayeira, Vayera, or ( — Hebrew language, Hebrew for "and He appeared," the incipit, first word in the parashah) is the fourth weekly Torah portion (, ''parashah'') in the annual Judaism, Jewish cycle of Torah reading. It constitutes . The parashah tells the stories of Abraham's three visitors, Abraham's bargaining with God in Judaism, God over Sodom and Gomorrah, Lot (Bible), Lot's two visitors, Lot's bargaining with the Sodomites, Lot's flight, the destruction of Sodom and Gomorrah, how Lot's daughters became pregnant by their father, how Abraham once again Wife–sister narratives in the Book of Genesis, passed off his wife Sarah as his sister, the birth of Isaac, the expulsion of Hagar (Bible), Hagar, disputes over wells, and the binding of Isaac (, the ''Akedah''). The parashah has the most words (but not the most letters or Chapters and verses of the Bible, verses) of any of the weekly Torah portions in the Book of Genesis, and its word-count is second only to Parashat Nas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miketz
Miketz or Mikeitz (—Hebrew for "at the end", the second word, and first distinctive word of the ''parashah'') is the tenth weekly Torah portion (, ''parashah'') in the annual Jewish cycle of Torah reading. It constitutes . The parashah tells of Joseph's interpretation of Pharaoh's dreams, Joseph's rise to power in Egypt, and Joseph's testing of his brothers. The parashah has the most letters (although not the most words or verses) of any of the weekly Torah portions in the Book of Genesis. It is made up of 7,914 Hebrew letters, 2,022 Hebrew words, 146 verses, and 255 lines in a Torah Scroll (, '' Sefer Torah''). (In the Book of Genesis, Parashat Vayeira has the most words, and Parashiyot Noach and Vayishlach have the most verses.) Jews read Parashat Miketz on the tenth Sabbath after Simchat Torah, generally in December, or rarely in late November or early January, usually during Chanukah. Readings In traditional Sabbath Torah reading, the parashah is divided into seven read ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benjamin
Benjamin ( he, ''Bīnyāmīn''; "Son of (the) right") blue letter bible: https://www.blueletterbible.org/lexicon/h3225/kjv/wlc/0-1/ H3225 - yāmîn - Strong's Hebrew Lexicon (kjv) was the last of the two sons of Jacob and Rachel (Jacob's thirteenth child and twelfth and youngest son) in Jewish, Christian and Islamic tradition. He was also the progenitor of the Israelite Tribe of Benjamin. Unlike Rachel's first son, Joseph, Benjamin was born in Canaan according to biblical narrative. In the Samaritan Pentateuch, Benjamin's name appears as "Binyamēm" ( Samaritan Hebrew: , "son of days"). In the Quran, Benjamin is referred to as a righteous young child, who remained with Jacob when the older brothers plotted against Joseph. Later rabbinic traditions name him as one of four ancient Israelites who died without sin, the other three being Chileab, Jesse and Amram. Name The name is first mentioned in letters from King Sîn-kāšid of Uruk (1801–1771 BC), who called himself “K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hebrew Language
Hebrew (; ; ) is a Northwest Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family. Historically, it is one of the spoken languages of the Israelites and their longest-surviving descendants, the Jews and Samaritans. It was largely preserved throughout history as the main liturgical language of Judaism (since the Second Temple period) and Samaritanism. Hebrew is the only Canaanite language still spoken today, and serves as the only truly successful example of a dead language that has been revived. It is also one of only two Northwest Semitic languages still in use, with the other being Aramaic. The earliest examples of written Paleo-Hebrew date back to the 10th century BCE. Nearly all of the Hebrew Bible is written in Biblical Hebrew, with much of its present form in the dialect that scholars believe flourished around the 6th century BCE, during the time of the Babylonian captivity. For this reason, Hebrew has been referred to by Jews as '' Lashon Hakodesh'' (, ) since an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hebrew Bible
The Hebrew Bible or Tanakh (;"Tanach" ''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary''. Hebrew: ''Tānāḵh''), also known in Hebrew as Miqra (; Hebrew: ''Mīqrā''), is the Biblical canon, canonical collection of Hebrew language, Hebrew scriptures, including the Torah, the Nevi'im, and the Ketuvim. Different branches of Judaism and Samaritanism have maintained different versions of the canon, including the 3rd-century Septuagint text used by Second-Temple Judaism, the Syriac language Peshitta, the Samaritan Torah, the Dead Sea Scrolls, and most recently the 10th century medieval Masoretic Text, Masoretic text created by the Masoretes currently used in modern Rabbinic Judaism. The terms "Hebrew Bible" or "Hebrew Canon" are frequently confused with the Masoretic text, however, this is a medieval version and one of several ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Masoretic Text
The Masoretic Text (MT or 𝕸; he, נֻסָּח הַמָּסוֹרָה, Nūssāḥ Hammāsōrā, lit. 'Text of the Tradition') is the authoritative Hebrew and Aramaic text of the 24 books of the Hebrew Bible (Tanakh) in Rabbinic Judaism. The Masoretic Text defines the Jewish canon and its precise letter-text, with its vocalization and accentuation known as the ''mas'sora''. Referring to the Masoretic Text, ''mesorah'' specifically means the diacritic markings of the text of the Hebrew scriptures and the concise marginal notes in manuscripts (and later printings) of the Tanakh which note textual details, usually about the precise spelling of words. It was primarily copied, edited and distributed by a group of Jews known as the Masoretes between the 7th and 10th centuries of the Common Era (CE). The oldest known complete copy, the Leningrad Codex, dates from the early 11th century CE. The differences attested to in the Dead Sea Scrolls indicate that multiple versions of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tanakh
The Hebrew Bible or Tanakh (;"Tanach" ''''. : ''Tānāḵh''), also known in Hebrew as Miqra (; : ''Mīqrā''), is the canonical collection of script ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pe (Semitic Letter)
Pe is the seventeenth letter of the Semitic abjads, including Phoenician Pē , Hebrew Pē , Aramaic Pē , Syriac Pē ܦ, and Arabic (in abjadi order). The original sound value is a voiceless bilabial plosive: ; it retains this value in most Semitic languages, except for Arabic, where the sound changed into the voiceless labiodental fricative , carrying with it the pronunciation of the letter. Not to be confused with the Turned g. The Phoenician letter gave rise to the Greek Pi (Π), Latin P, and Cyrillic П. Origins Pe is usually assumed to come from a pictogram of a “mouth” (in Hebrew ''pe''; in Arabic, فا ''fah''). Hebrew Pe The Hebrew spelling is . It is also romanized pei or pey, especially when used in Yiddish. Variations on written form/pronunciation The letter Pe is one of the six letters which can receive a Dagesh Kal. The six are Bet, Gimel, Daleth, Kaph, Pe, and Tav. Variant forms of Pe/Fe A notable variation on the letter Pe is the Pe Kefulah ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samekh
Samekh (Phoenician ''sāmek'' ; Hebrew ''samekh'' , Syriac ''semkaṯ'') is the fifteenth letter of the Semitic abjads, including the Hebrew alphabet. Samekh represents a voiceless alveolar fricative . Unlike most Semitic consonants, the pronunciation of remains constant between vowels and before voiced consonants. In the Hebrew language, the samekh generally shares a similar pronunciation as the left-dotted shin. The numerical value of samekh is 60. History The Phoenician letter may continue a glyph from the Middle Bronze Age alphabets, either based on a hieroglyph for a tent peg or support, possibly the ''djed'' "pillar" hieroglyph (c.f. Hebrew root סמך s-m-kh 'support', סֶמֶךְ semekh 'support, rest', סוֹמֵךְ somekh 'support peg, post', סוֹמְכָה somkha 'armrest', סָמוֹכָה smokha 'stake, support', indirectly '' s'mikhah'' ; Aramaic סַמְכָא samkha 'socket, base', סְמַךְ smakh 'support, help'; Syriac ܣܡܟܐ semkha 'support') ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |