|
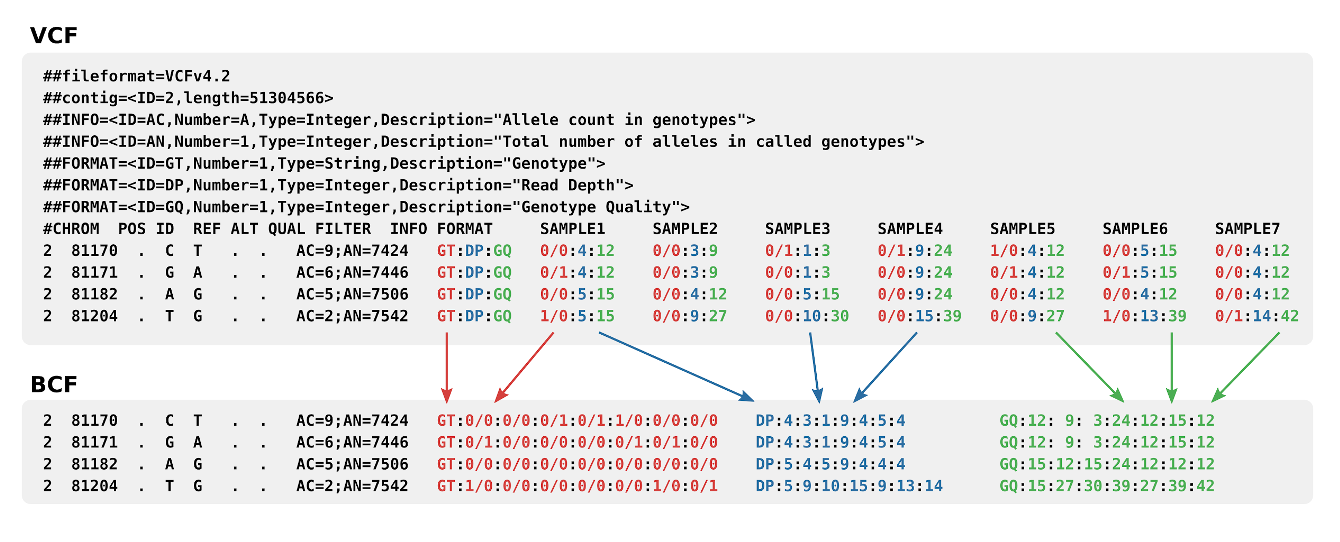
Variant Call Format
The Variant Call Format (VCF) specifies the format of a text file used in bioinformatics for storing gene sequence variations. The format has been developed with the advent of large-scale genotyping and DNA sequencing projects, such as the 1000 Genomes Project. Existing formats for genetic data such as General feature format, General feature format (GFF) stored all of the genetic data, much of which is redundant because it will be shared across the genomes. By using the variant call format only the variations need to be stored along with a reference genome. The standard is currently in version 4.3, although the 1000 Genomes Project has developed its own specification for structural variations such as duplications, which are not easily accommodated into the existing schema. There is also a genomic VCF (gVCF) extended format, which includes additional information about "blocks" that match the reference and their qualities. A set of tools is also available for editing and manipulati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tab-separated Values
A tab-separated values (TSV) file is a simple text format for storing data in a tabular structure, e.g., a database table or spreadsheet data, and a way of exchanging information between databases. Each record in the table is one line of the text file. Each field value of a record is separated from the next by a tab character. The TSV format is thus a variation of the comma-separated values format. TSV is a simple file format that is widely supported, so it is often used in data exchange to move tabular data between different computer programs that support the format. For example, a TSV file might be used to transfer information from a database program to a spreadsheet. The IANA standard for TSV achieves simplicity by simply disallowing tabs within fields. Example The head of the Iris flower data set can be stored as a TSV using the following plain text (note that the HTML rendering may convert tabs to spaces): Sepal length Sepal width Petal length Petal width&Tab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alleles
An allele (, ; ; modern formation from Greek ἄλλος ''állos'', "other") is a variation of the same sequence of nucleotides at the same place on a long DNA molecule, as described in leading textbooks on genetics and evolution. ::"The chromosomal or genomic location of a gene or any other genetic element is called a locus (plural: loci) and alternative DNA sequences at a locus are called alleles." The simplest alleles are single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP). but they can also be insertions and deletions of up to several thousand base pairs. Popular definitions of 'allele' typically refer only to different alleles within genes. For example, the ABO blood grouping is controlled by the ABO gene, which has six common alleles (variants). In population genetics, nearly every living human's phenotype for the ABO gene is some combination of just these six alleles. Most alleles observed result in little or no change in the function of the gene product it codes for. However, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Single-nucleotide Polymorphism
In genetics, a single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP ; plural SNPs ) is a germline substitution of a single nucleotide at a specific position in the genome. Although certain definitions require the substitution to be present in a sufficiently large fraction of the population (e.g. 1% or more), many publications do not apply such a frequency threshold. For example, at a specific base position in the human genome, the G nucleotide may appear in most individuals, but in a minority of individuals, the position is occupied by an A. This means that there is a SNP at this specific position, and the two possible nucleotide variations – G or A – are said to be the alleles for this specific position. SNPs pinpoint differences in our susceptibility to a wide range of diseases, for example age-related macular degeneration (a common SNP in the CFH gene is associated with increased risk of the disease) or nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (a SNP in the PNPLA3 gene is associated with inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Genetic Variation
Human genetic variation is the genetic differences in and among populations. There may be multiple variants of any given gene in the human population (alleles), a situation called polymorphism. No two humans are genetically identical. Even monozygotic twins (who develop from one zygote) have infrequent genetic differences due to mutations occurring during development and gene copy-number variation. Differences between individuals, even closely related individuals, are the key to techniques such as genetic fingerprinting. As of 2017, there are a total of 324 million known variants from sequenced human genomes. As of 2015, the typical difference between an individual's genome and the reference genome was estimated at 20 million base pairs (or 0.6% of the total of 3.2 billion base pairs). Comparatively speaking, humans are a genetically homogenous species. Although a small number of genetic variants are found more frequently in certain geographic regions or in people with ance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Genome
The human genome is a complete set of nucleic acid sequences for humans, encoded as DNA within the 23 chromosome pairs in cell nuclei and in a small DNA molecule found within individual mitochondria. These are usually treated separately as the nuclear genome and the mitochondrial genome. Human genomes include both protein-coding DNA sequences and various types of DNA that does not encode proteins. The latter is a diverse category that includes DNA coding for non-translated RNA, such as that for ribosomal RNA, transfer RNA, ribozymes, small nuclear RNAs, and several types of regulatory RNAs. It also includes promoters and their associated gene-regulatory elements, DNA playing structural and replicatory roles, such as scaffolding regions, telomeres, centromeres, and origins of replication, plus large numbers of transposable elements, inserted viral DNA, non-functional pseudogenes and simple, highly-repetitive sequences. Introns make up a large percentage of non-coding DNA. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Global Alliance For Genomics And Health (GA4GH)
The Global Alliance for Genomics and Health (GA4GH) is an international consortium that is developing standards for responsibly collecting, storing, analyzing, and sharing genomic data in order to enable an "internet of genomics". GA4GH was founded in 2013. GA4GH is founded on the '' Framework for the Responsible Sharing of Genomic and Health-related Data,'' which is based on the human right to benefit from scientific advances. Organization GA4GH maintained by four Host Institutions (Wellcome Sanger Institute, Broad Institute, Ontario Institute for Cancer Research and the European Bioinformatics Institute). Ewan Birney is the current GA4GH chair and Peter Goodhand is the Chief Executive Officer. Heidi Rehm and Kathryn North are the current Vice Chairs. Organizational members of the alliance include: Funding GA4GH is supported by a "Funder's Forum" composed of organizations whose funding commitments exceed USD $200,000 annually, for at least three years. Forum members incl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GFF3
In bioinformatics, the general feature format (gene-finding format, generic feature format, GFF) is a file format used for describing genes and other features of DNA, RNA and protein sequences. GFF Versions The following versions of GFF exist: General Feature Format Version 2 generally deprecated * a derivative used by Ensembl Generic Feature Format Version 3*Genome Variation Format with additional pragmas and attributes for sequence_alteration features GFF2/GTF had a number of deficiencies, notably that it can only represent two-level feature hierarchies and thus cannot handle the three-level hierarchy of gene → transcript → exon. GFF3 addresses this and other deficiencies. For example, it supports arbitrarily many hierarchical levels, and gives specific meanings to certain tags in the attributes field. The GTF is identical to GFF, version 2. GFF general structure All GFF formats (GFF2, GFF3 and GTF) are tab delimited with 9 fields per line. They all share the same stru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GVF Format
GVF may refer to: * Greta Van Fleet, an American rock band * Global Village Foundation, an American charity * Golin language Golin (also Gollum, Gumine) is a Papuan language of Papua New Guinea. Phonology Vowels Diphthongs that occur are . The consonants can also be syllabic. Consonant are treated as single consonants by Bunn & Bunn (1970),* but as combinatio ..., native to Papua New Guinea * Grapevine virus F, a plant virus species in the genus Vitivirus * Gradient vector flow, a computer vision method {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SAM (file Format)
Sequence Alignment Map (SAM) is a text-based format originally for storing biological sequences aligned to a reference sequence developed by Heng Li and Bob Handsaker ''et al''. It was developed when the 1000 Genomes Project wanted to move away from the MAQ mapper format and decided to design a new format. The overall TAB-delimited flavour of the format came from an earlier format inspired by BLAT’s PSL. The name of SAM came from Gabor Marth from University of Utah, who originally had a format under the same name but with a different syntax more similar to a BLAST output. It is widely used for storing data, such as nucleotide sequences, generated by next generation sequencing technologies, and the standard has been broadened to include unmapped sequences. The format supports short and long reads (up to 128 Mbp) produced by different sequencing platforms and is used to hold mapped data within the Genome Analysis Toolkit (GATK) and across the Broad Institute, the Wellcome S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FASTQ Format
FASTQ format is a text-based format for storing both a biological sequence (usually nucleotide sequence) and its corresponding quality scores. Both the sequence letter and quality score are each encoded with a single ASCII character for brevity. It was originally developed at the Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute to bundle a FASTA formatted sequence and its quality data, but has recently become the ''de facto'' standard for storing the output of high-throughput sequencing instruments such as the Illumina Genome Analyzer. Format A FASTQ file has four line-separated fields per sequence: * Field 1 begins with a '@' character and is followed by a sequence identifier and an ''optional'' description (like a FASTA title line). * Field 2 is the raw sequence letters. * Field 3 begins with a '+' character and is ''optionally'' followed by the same sequence identifier (and any description) again. * Field 4 encodes the quality values for the sequence in Field 2, and must contain the same num ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FASTA Format
In bioinformatics and biochemistry, the FASTA format is a text-based format for representing either nucleotide sequences or amino acid (protein) sequences, in which nucleotides or amino acids are represented using single-letter codes. The format also allows for sequence names and comments to precede the sequences. The format originates from the FASTA software package, but has now become a near universal standard in the field of bioinformatics. The simplicity of FASTA format makes it easy to manipulate and parse sequences using text-processing tools and scripting languages like the R programming language, Python, Ruby, Haskell, and Perl. Original format & overview The original FASTA/Pearson format is described in the documentation for the FASTA suite of programs. It can be downloaded with any free distribution of FASTA (see fasta20.doc, fastaVN.doc or fastaVN.me—where VN is the Version Number). In the original format, a sequence was represented as a series of lines, each of whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indel
Indel is a molecular biology term for an insertion or deletion of bases in the genome of an organism. It is classified among small genetic variations, measuring from 1 to 10 000 base pairs in length, including insertion and deletion events that may be separated by many years, and may not be related to each other in any way. A microindel is defined as an indel that results in a net change of 1 to 50 nucleotides. In coding regions of the genome, unless the length of an indel is a multiple of 3, it will produce a frameshift mutation. For example, a common microindel which results in a frameshift causes Bloom syndrome in the Jewish or Japanese population. Indels can be contrasted with a point mutation. An indel inserts or deletes nucleotides from a sequence, while a point mutation is a form of substitution that ''replaces'' one of the nucleotides without changing the overall number in the DNA. Indels can also be contrasted with Tandem Base Mutations (TBM), which may result from fun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |