|
Vampyrellidium
The family Vampyrellidae is a subgroup of the order Aconchulinida (formerly Vampyrellida) within the phylum Cercozoa. Based on molecular sequence data, the family currently comprises the genus ''Vampyrella'', and maybe several other vampyrellid amoebae (e.g. ''Gobiella''). The cells are naked and characterised by radiating, filose pseudopodia (also referred to as filopodia) and an orange colouration of the main cell body. In former times the family Vampyrellidae contained several genera (e.g. ''Vampyrella'', ''Gobiella'', ''Leptophrys'', ''Platyreta'', ''Theratromyxa'') and was identical with the order Vampyrellida West, 1901, also known under the name "Aconchulinida". However, based on molecular sequence data it seemed reasonable to restrict the family Vampyrellidae to a subgroup (containing the genus ''Vampyrella'') and to establish another family for the genera ''Leptophrys'', ''Platyreta'' and ''Theratromyxa'', namely the Leptophryidae Hess et al., 2012. Characteristics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Platyreta
The family Vampyrellidae is a subgroup of the order Aconchulinida (formerly Vampyrellida) within the phylum Cercozoa. Based on molecular sequence data, the family currently comprises the genus '' Vampyrella'', and maybe several other vampyrellid amoebae (e.g. ''Gobiella''). The cells are naked and characterised by radiating, filose pseudopodia (also referred to as filopodia) and an orange colouration of the main cell body. In former times the family Vampyrellidae contained several genera (e.g. ''Vampyrella'', ''Gobiella'', ''Leptophrys'', ''Platyreta'', ''Theratromyxa'') and was identical with the order Vampyrellida West, 1901, also known under the name "Aconchulinida". However, based on molecular sequence data it seemed reasonable to restrict the family Vampyrellidae to a subgroup (containing the genus ''Vampyrella'') and to establish another family for the genera ''Leptophrys'', ''Platyreta'' and ''Theratromyxa'', namely the Leptophryidae Hess et al., 2012. Characteristics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vampyrellium
The family Vampyrellidae is a subgroup of the order Aconchulinida (formerly Vampyrellida) within the phylum Cercozoa. Based on molecular sequence data, the family currently comprises the genus '' Vampyrella'', and maybe several other vampyrellid amoebae (e.g. ''Gobiella''). The cells are naked and characterised by radiating, filose pseudopodia (also referred to as filopodia) and an orange colouration of the main cell body. In former times the family Vampyrellidae contained several genera (e.g. ''Vampyrella'', ''Gobiella'', ''Leptophrys'', ''Platyreta'', ''Theratromyxa'') and was identical with the order Vampyrellida West, 1901, also known under the name "Aconchulinida". However, based on molecular sequence data it seemed reasonable to restrict the family Vampyrellidae to a subgroup (containing the genus ''Vampyrella'') and to establish another family for the genera ''Leptophrys'', ''Platyreta'' and ''Theratromyxa'', namely the Leptophryidae Hess et al., 2012. Characteristics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Physiology; An Outline Of The Science Of Life (1899) (14596233838)
A general officer is an officer of high rank in the armies, and in some nations' air forces, space forces, and marines or naval infantry. In some usages the term "general officer" refers to a rank above colonel."general, adj. and n.". OED Online. March 2021. Oxford University Press. https://www.oed.com/view/Entry/77489?rskey=dCKrg4&result=1 (accessed May 11, 2021) The term ''general'' is used in two ways: as the generic title for all grades of general officer and as a specific rank. It originates in the 16th century, as a shortening of ''captain general'', which rank was taken from Middle French ''capitaine général''. The adjective ''general'' had been affixed to officer designations since the late medieval period to indicate relative superiority or an extended jurisdiction. Today, the title of ''general'' is known in some countries as a four-star rank. However, different countries use different systems of stars or other insignia for senior ranks. It has a NATO rank sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleariid
Nucleariida is a group of amoebae with filose pseudopods, known mostly from soils and freshwater. They are distinguished from the superficially similar vampyrellids mainly by having mitochondria with discoid cristae, in the absence of superficial granules, and in the way they consume food. Classification Molecular studies indicate that nucleariids are closely related to fungi. and more distantly to the lineage that gave rise to choanoflagellates and metazoa opisthokonts, the group which includes animals, fungi. Some use a broad definition of Opisthokonta to include all of these organisms with flattened mitochondrial cristae. The genera '' Rabdiophrys'', '' Pinaciophora'', and '' Pompholyxophrys'', freshwater forms with hollow siliceous scales or spines, were included in Nucleariida by some. This was disputed by Smith and Chao who placed them in the Rhizaria. Their affinity with the nucleariids has been confirmed. Historically, nucleariids were included among the heliozoa as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
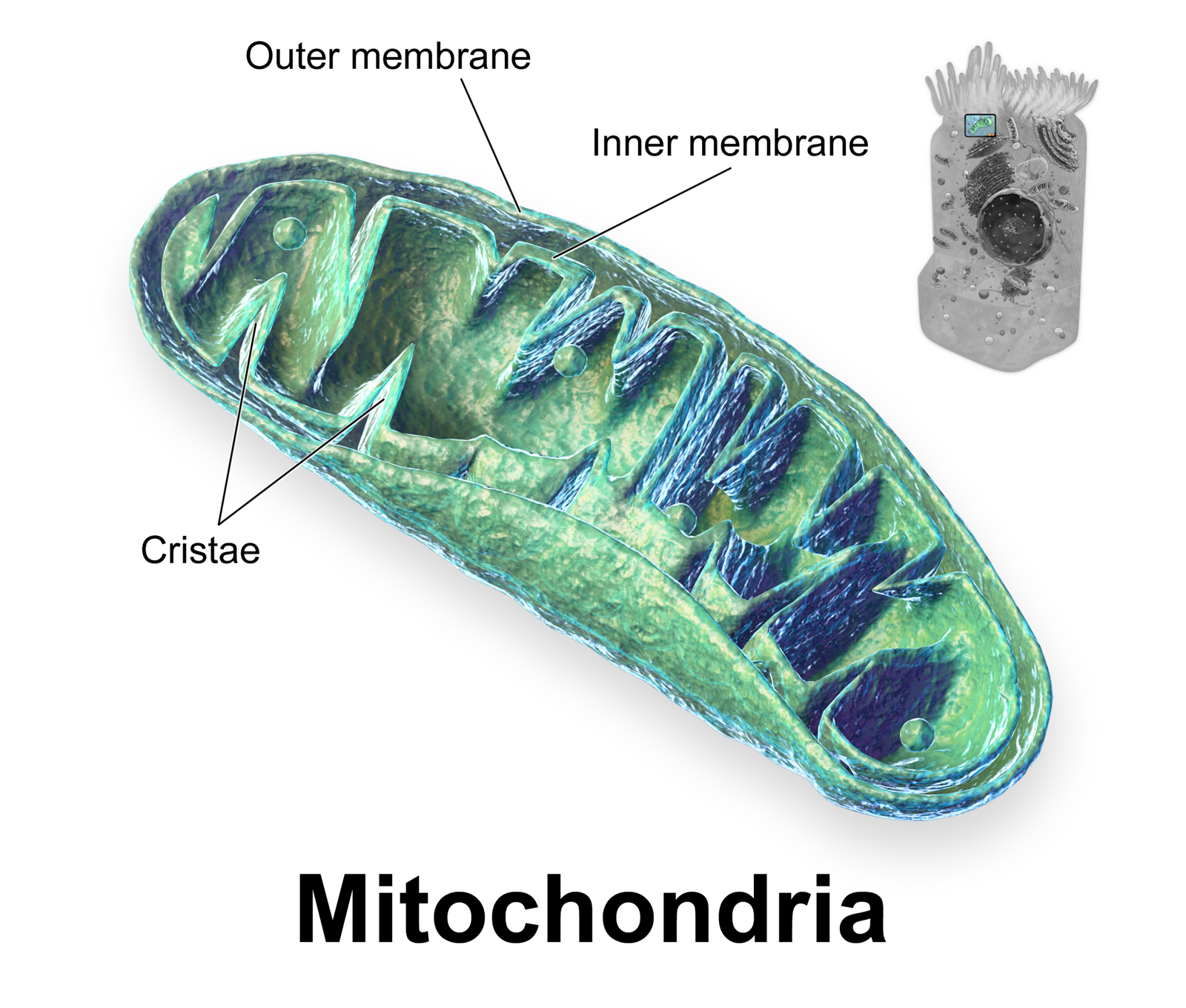
Crista
A crista (; plural cristae) is a fold in the inner membrane of a mitochondrion. The name is from the Latin for ''crest'' or ''plume'', and it gives the inner membrane its characteristic wrinkled shape, providing a large amount of surface area for chemical reactions to occur on. This aids aerobic cellular respiration, because the mitochondrion requires oxygen. Cristae are studded with proteins, including ATP synthase and a variety of cytochromes. Background With the discovery of the dual-membrane nature of mitochondria, the pioneers of mitochondrial ultrastructural research proposed different models for the organization of the mitochondrial inner membrane. Three models proposed were: *Baffle model – According to Palade (1953), the mitochondrial inner membrane is convoluted in a baffle-like manner with broad openings towards the intra-cristal space. This model entered most textbooks and was widely believed for a long time. *Septa model – Sjöstrand (1953) suggested that sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitochondrion
A mitochondrion (; ) is an organelle found in the cells of most Eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and fungi. Mitochondria have a double membrane structure and use aerobic respiration to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is used throughout the cell as a source of chemical energy. They were discovered by Albert von Kölliker in 1857 in the voluntary muscles of insects. The term ''mitochondrion'' was coined by Carl Benda in 1898. The mitochondrion is popularly nicknamed the "powerhouse of the cell", a phrase coined by Philip Siekevitz in a 1957 article of the same name. Some cells in some multicellular organisms lack mitochondria (for example, mature mammalian red blood cells). A large number of unicellular organisms, such as microsporidia, parabasalids and diplomonads, have reduced or transformed their mitochondria into other structures. One eukaryote, ''Monocercomonoides'', is known to have completely lost its mitochondria, and one multicellular organism, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
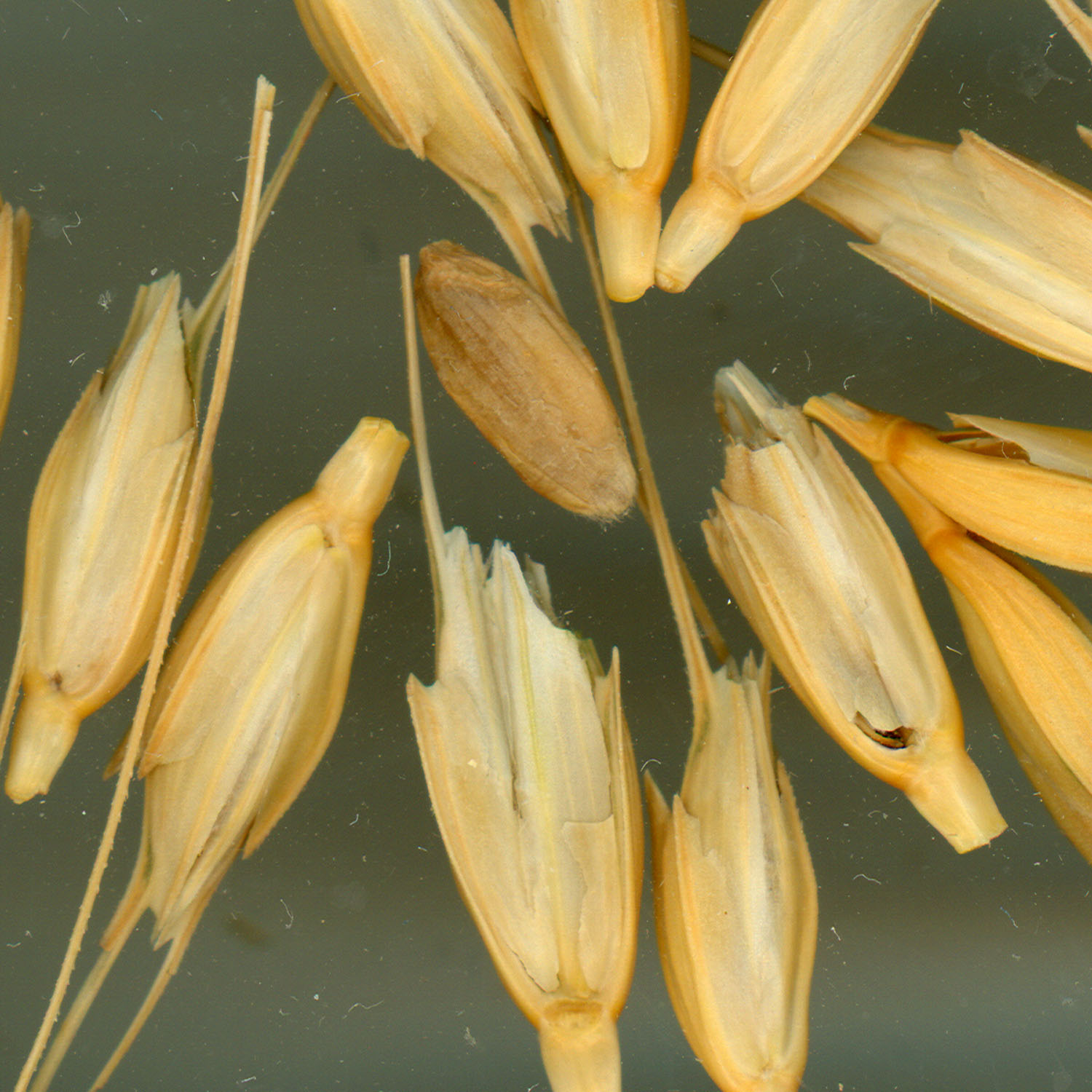
Wheat
Wheat is a grass widely cultivated for its seed, a cereal grain that is a worldwide staple food. The many species of wheat together make up the genus ''Triticum'' ; the most widely grown is common wheat (''T. aestivum''). The archaeological record suggests that wheat was first cultivated in the regions of the Fertile Crescent around 9600 BCE. Botanically, the wheat kernel is a type of fruit called a caryopsis. Wheat is grown on more land area than any other food crop (, 2014). World trade in wheat is greater than for all other crops combined. In 2020, world production of wheat was , making it the second most-produced cereal after maize. Since 1960, world production of wheat and other grain crops has tripled and is expected to grow further through the middle of the 21st century. Global demand for wheat is increasing due to the unique viscoelastic and adhesive properties of gluten proteins, which facilitate the production of processed foods, whose consumption is inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rust (fungus)
Rusts are plant diseases caused by pathogenic fungi of the order Pucciniales (previously known as Uredinales). An estimated 168 rust genera and approximately 7,000 species, more than half of which belong to the genus '' Puccinia'', are currently accepted. Rust fungi are highly specialized plant pathogens with several unique features. Taken as a group, rust fungi are diverse and affect many kinds of plants. However, each species has a very narrow range of hosts and cannot be transmitted to non-host plants. In addition, most rust fungi cannot be grown easily in pure culture. A single species of rust fungi may be able to infect two different plant hosts in different stages of its life cycle, and may produce up to five morphologically and cytologically distinct spore-producing structures viz., spermogonia, aecia, uredinia, telia, and basidia in successive stages of reproduction. Each spore type is very host specific, and can typically infect only one kind of plant. Rust fungi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungi
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related organisms, named the ''Eumycota'' (''t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |