|
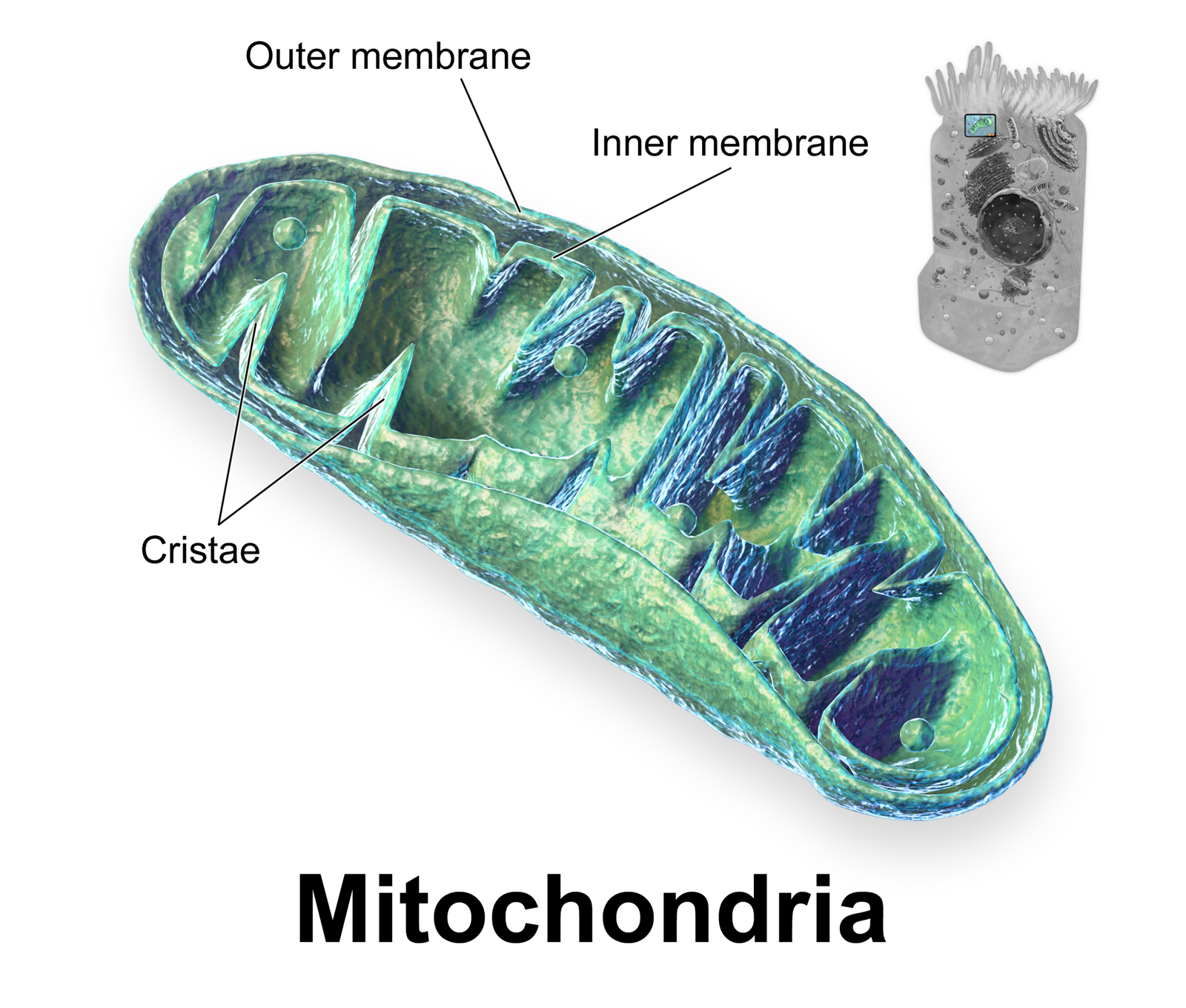
Crista
A crista (; plural cristae) is a fold in the inner membrane of a mitochondrion. The name is from the Latin for ''crest'' or ''plume'', and it gives the inner membrane its characteristic wrinkled shape, providing a large amount of surface area for chemical reactions to occur on. This aids aerobic cellular respiration, because the mitochondrion requires oxygen. Cristae are studded with proteins, including ATP synthase and a variety of cytochromes. Background With the discovery of the dual-membrane nature of mitochondria, the pioneers of mitochondrial ultrastructural research proposed different models for the organization of the mitochondrial inner membrane. Three models proposed were: *Baffle model – According to Palade (1953), the mitochondrial inner membrane is convoluted in a baffle-like manner with broad openings towards the intra-cristal space. This model entered most textbooks and was widely believed for a long time. *Septa model – Sjöstrand (1953) suggested that sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inner Mitochondrial Membrane
The inner mitochondrial membrane (IMM) is the mitochondrial membrane which separates the mitochondrial matrix from the intermembrane space. Structure The structure of the inner mitochondrial membrane is extensively folded and compartmentalized. The numerous invaginations of the membrane are called cristae, separated by crista junctions from the inner boundary membrane juxtaposed to the outer membrane. Cristae significantly increase the total membrane surface area compared to a smooth inner membrane and thereby the available working space for oxidative phosphorylation. The inner membrane creates two compartments. The region between the inner and outer membrane, called the intermembrane space, is largely continuous with the cytosol, while the more sequestered space inside the inner membrane is called the matrix. Cristae For typical liver mitochondria, the area of the inner membrane is about 5 times as large as the outer membrane due to cristae. This ratio is variable and mitoch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dynamin-like 120 KDa Protein
Dynamin-like 120 kDa protein, mitochondrial is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''OPA1'' gene. This protein regulates mitochondrial fusion and cristae structure in the inner mitochondrial membrane (IMM) and contributes to ATP synthesis and apoptosis, and small, round mitochondria. Mutations in this gene have been implicated in dominant optic atrophy (DOA), leading to loss in vision, hearing, muscle contraction, and related dysfunctions. Structure Eight transcript variants encoding different isoforms, resulting from alternative splicing of exon 4 and two novel exons named 4b and 5b, have been reported for this gene. They fall under two types of isoforms: long isoforms (L-OPA1), which attach to the IMM, and short isoforms (S-OPA1), which localize to the intermembrane space (IMS) near the outer mitochondrial membrane (OMM). S-OPA1 is formed by proteolysis of L-OPA1 at the cleavage sites S1 and S2, removing the transmembrane domain. Function This gene product is a nuc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitochondrion
A mitochondrion (; ) is an organelle found in the cells of most Eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and fungi. Mitochondria have a double membrane structure and use aerobic respiration to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is used throughout the cell as a source of chemical energy. They were discovered by Albert von Kölliker in 1857 in the voluntary muscles of insects. The term ''mitochondrion'' was coined by Carl Benda in 1898. The mitochondrion is popularly nicknamed the "powerhouse of the cell", a phrase coined by Philip Siekevitz in a 1957 article of the same name. Some cells in some multicellular organisms lack mitochondria (for example, mature mammalian red blood cells). A large number of unicellular organisms, such as microsporidia, parabasalids and diplomonads, have reduced or transformed their mitochondria into other structures. One eukaryote, ''Monocercomonoides'', is known to have completely lost its mitochondria, and one multicellular organism, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ATP Synthase
ATP synthase is a protein that catalyzes the formation of the energy storage molecule adenosine triphosphate (ATP) using adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and inorganic phosphate (Pi). It is classified under ligases as it changes ADP by the formation of P-O bond (phosphodiester bond). ATP synthase is a molecular machine. The overall reaction catalyzed by ATP synthase is: * ADP + Pi + 2H+out ATP + H2O + 2H+in The formation of ATP from ADP and Pi is energetically unfavorable and would normally proceed in the reverse direction. In order to drive this reaction forward, ATP synthase couples ATP synthesis during cellular respiration to an electrochemical gradient created by the difference in proton (H+) concentration across the inner mitochondrial membrane in eukaryotes or the plasma membrane in bacteria. During photosynthesis in plants, ATP is synthesized by ATP synthase using a proton gradient created in the thylakoid lumen through the thylakoid membrane and into the chloroplast st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cellular Respiration
Cellular respiration is the process by which biological fuels are oxidised in the presence of an inorganic electron acceptor such as oxygen to produce large amounts of energy, to drive the bulk production of ATP. Cellular respiration may be described as a set of metabolic reactions and processes that take place in the cells of organisms to convert chemical energy from nutrients into adenosine triphosphate (ATP), and then release waste products. The reactions involved in respiration are catabolic reactions, which break large molecules into smaller ones, releasing energy. Respiration is one of the key ways a cell releases chemical energy to fuel cellular activity. The overall reaction occurs in a series of biochemical steps, some of which are redox reactions. Although cellular respiration is technically a combustion reaction, it is an unusual one because of the slow, controlled release of energy from the series of reactions. Nutrients that are commonly used by animal and pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphate Group
In chemistry, a phosphate is an anion, salt, functional group or ester derived from a phosphoric acid. It most commonly means orthophosphate, a derivative of orthophosphoric acid . The phosphate or orthophosphate ion is derived from phosphoric acid by the removal of three protons . Removal of one or two protons gives the dihydrogen phosphate ion and the hydrogen phosphate ion ion, respectively. These names are also used for salts of those anions, such as ammonium dihydrogen phosphate and trisodium phosphate. File:3-phosphoric-acid-3D-balls.png, Phosphoricacid File:2-dihydrogenphosphate-3D-balls.png, Dihydrogenphosphate File:1-hydrogenphosphate-3D-balls.png, Hydrogenphosphate File:0-phosphate-3D-balls.png, Phosphate In organic chemistry, phosphate or orthophosphate is an organophosphate, an ester of orthophosphoric acid of the form where one or more hydrogen atoms are replaced by organic groups. An example is trimethyl phosphate, . The term also refers to the tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adenosine Diphosphate
Adenosine diphosphate (ADP), also known as adenosine pyrophosphate (APP), is an important organic compound in metabolism and is essential to the flow of energy in living cells. ADP consists of three important structural components: a sugar backbone attached to adenine and two phosphate groups bonded to the 5 carbon atom of ribose. The diphosphate group of ADP is attached to the 5’ carbon of the sugar backbone, while the adenine attaches to the 1’ carbon. ADP can be interconverted to adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and adenosine monophosphate (AMP). ATP contains one more phosphate group than does ADP. AMP contains one fewer phosphate group. Energy transfer used by all living things is a result of dephosphorylation of ATP by enzymes known as ATPases. The cleavage of a phosphate group from ATP results in the coupling of energy to metabolic reactions and a by-product of ADP. ATP is continually reformed from lower-energy species ADP and AMP. The biosynthesis of ATP is achieved through ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adenosine Triphosphate
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is an organic compound that provides energy to drive many processes in living cells, such as muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, condensate dissolution, and chemical synthesis. Found in all known forms of life, ATP is often referred to as the "molecular unit of currency" of intracellular energy transfer. When consumed in metabolic processes, it converts either to adenosine diphosphate (ADP) or to adenosine monophosphate (AMP). Other processes regenerate ATP. The human body recycles its own body weight equivalent in ATP each day. It is also a precursor to DNA and RNA, and is used as a coenzyme. From the perspective of biochemistry, ATP is classified as a nucleoside triphosphate, which indicates that it consists of three components: a nitrogenous base ( adenine), the sugar ribose, and the triphosphate. Structure ATP consists of an adenine attached by the 9-nitrogen atom to the 1′ carbon atom of a sugar ( ribose), which i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts are catalytic RNA molecules, called ribozymes. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures. Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the reac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proton-motive Force
Chemiosmosis is the movement of ions across a semipermeable membrane bound structure, down their electrochemical gradient. An important example is the formation of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) by the movement of hydrogen ions (H+) across a membrane during cellular respiration or photosynthesis. Hydrogen ions, or protons, will diffuse from a region of high proton concentration to a region of lower proton concentration, and an electrochemical concentration gradient of protons across a membrane can be harnessed to make ATP. This process is related to osmosis, the movement of water across a selective membrane, which is why it is called "chemiosmosis". ATP synthase is the enzyme that makes ATP by chemiosmosis. It allows protons to pass through the membrane and uses the free energy difference to phosphorylate adenosine diphosphate (ADP), making ATP. The generation of ATP by chemiosmosis occurs in mitochondria and chloroplasts, as well as in most bacteria and archaea. For instance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrochemical Gradient
An electrochemical gradient is a gradient of electrochemical potential, usually for an ion that can move across a membrane. The gradient consists of two parts, the chemical gradient, or difference in solute concentration across a membrane, and the electrical gradient, or difference in charge across a membrane. When there are unequal concentrations of an ion across a permeable membrane, the ion will move across the membrane from the area of higher concentration to the area of lower concentration through simple diffusion. Ions also carry an electric charge that forms an electric potential across a membrane. If there is an unequal distribution of charges across the membrane, then the difference in electric potential generates a force that drives ion diffusion until the charges are balanced on both sides of the membrane. Electrochemical gradients are essential to the operation of batteries and other electrochemical cells, photosynthesis and cellular respiration, and certain other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |