|
Valence Isomer
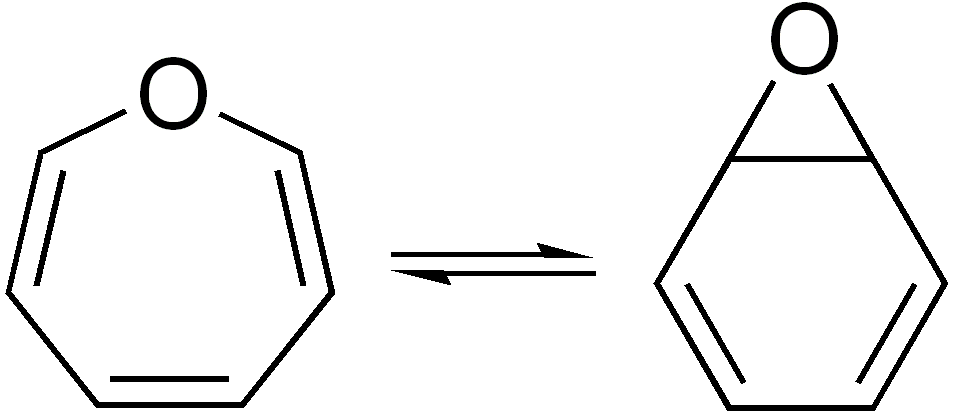
In organic chemistry, two molecules are valence isomers when they are constitutional isomers that can interconvert through pericyclic reactions. Benzene There are many valence isomers one can draw for the C6H6 formula benzene. Some were originally proposed for benzene itself before the actual structure of benzene was known. Others were later synthesized in lab. Some have been observed to isomerize to benzene, whereas others tend to undergo other reactions instead, or isomerize by ways other than pericyclic reactions. Image:Benzene-2D-flat.png, Benzene Image:Historic Benzene Formulae Dewar(1867) V.1.svg, Dewar benzene Image:Prisman2.svg, Prismane Image:Benzvalene.png, Benzvalene Image:Bicycloprop-2-enyl.svg, Bicyclopropenyl Cyclooctatetraene The valence isomers are not restricted to isomers of benzene. Valence isomers are also seen in the series (CH)8. Due to the larger number of units, the number of possible valence isomers is also greater and at least 21: Image:Cyclooct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constitutional Isomer
In chemistry, a structural isomer (or constitutional isomer in the IUPAC nomenclature) of a compound is another compound whose molecule has the same number of atoms of each element, but with logically distinct bonds between them. The term metamer was formerly used for the same concept. For example, butanol , methyl propyl ether , and diethyl ether have the same molecular formula but are three distinct structural isomers. The concept applies also to polyatomic ions with the same total charge. A classical example is the cyanate ion and the fulminate ion . It is also extended to ionic compounds, so that (for example) ammonium cyanate and urea are considered structural isomers,William F. Bynum, E. Janet Browne, Roy Porter (2014): ''Dictionary of the History of Science''. 530 pages. and so are methylammonium formate and ammonium acetate . Structural isomerism is the most radical type of isomerism. It is opposed to stereoisomerism, in which the atoms and bonding scheme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cuneane
Cuneane (C8H8, pentacyclo .3.0.02,4.03,7.06,8ctane) is a saturated hydrocarbon. Its name is derived from the Latin ''cuneus'', meaning a wedge. Cuneane may be produced from cubane by metal-ion-catalyzed σ-bond rearrangement. Similar reactions are known for homocubane (C9H10) and bishomocubane (C10H12). : Molecular geometry The carbon atoms in the cuneane molecule form a hexahedron with point group C2v. The cuneane molecule has three groups of equivalent carbon atoms (A, B, C), which have also been confirmed by NMR. The molecular graph of the carbon skeleton of cuneane is a regular graph with non-equivalent groups of vertices, and so it is a very important test object for different algorithms of mathematical chemistry. : Derivatives Some cuneane derivatives have liquid crystal Liquid crystal (LC) is a state of matter whose properties are between those of conventional liquids and those of solid crystals. For example, a liquid crystal may flow like a liquid, but it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azulene
Azulene is an organic compound and an isomer of naphthalene. Naphthalene is colourless, whereas azulene is dark blue. Two terpenoids, vetivazulene (4,8-dimethyl-2-isopropylazulene) and guaiazulene (1,4-dimethyl-7-isopropylazulene), that feature the azulene skeleton are found in nature as constituents of pigments in mushrooms, guaiac wood oil, and some marine invertebrates. Azulene has a long history, dating back to the 15th century as the azure-blue chromophore obtained by steam distillation of German chamomile. The chromophore was discovered in yarrow and wormwood and named in 1863 by Septimus Piesse. Its structure was first reported by Lavoslav Ružička, followed by its organic synthesis in 1937 by Placidus Plattner. Structure and bonding left, The blue color of the mushroom '' Lactarius indigo'' is due to the azulene derivative (7-isopropenyl-4-methylazulen-1-yl)methyl stearate. Azulene is usually viewed as resulting from fusion of cyclopentadiene and cyclohepta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naphthalene
Naphthalene is an organic compound with formula . It is the simplest polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon, and is a white crystalline solid with a characteristic odor that is detectable at concentrations as low as 0.08 ppm by mass. As an aromatic hydrocarbon, naphthalene's structure consists of a fused pair of benzene rings. It is best known as the main ingredient of traditional mothballs. History In the early 1820s, two separate reports described a white solid with a pungent odor derived from the distillation of coal tar. In 1821, John Kidd cited these two disclosures and then described many of this substance's properties and the means of its production. He proposed the name ''naphthaline'', as it had been derived from a kind of naphtha (a broad term encompassing any volatile, flammable liquid hydrocarbon mixture, including coal tar). Naphthalene's chemical formula was determined by Michael Faraday in 1826. The structure of two fused benzene rings was proposed by Emil Erlen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angewandte Chemie International Edition In English
''Angewandte Chemie'' (, meaning "Applied Chemistry") is a weekly peer-reviewed scientific journal that is published by Wiley-VCH on behalf of the German Chemical Society (Gesellschaft Deutscher Chemiker). Publishing formats include feature-length reviews, short highlights, research communications, minireviews, essays, book reviews, meeting reviews, correspondences, corrections, and obituaries. This journal contains review articles covering all aspects of chemistry. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal had a 2021 impact factor of 16.823. Editions The journal appears in two editions with separate volume and page numbering: a German edition, ''Angewandte Chemie'' ( (print), (online)), and a fully English-language edition, ''Angewandte Chemie International Edition'' ( (print), (online)). The editions are identical in content with the exception of occasional reviews of German-language books or German translations of IUPAC recommendations. Business model '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemische Berichte
''Chemische Berichte'' (usually abbreviated as ''Ber.'' or ''Chem. Ber.'') was a German-language scientific journal of all disciplines of chemistry founded in 1868. It was one of the oldest scientific journals in chemistry, until it merged with ''Recueil des Travaux Chimiques des Pays-Bas'' to form ''Chemische Berichte/Recueil'' in 1997. ''Chemische Berichte/Recueil'' was then merged with other European journals in 1998 to form ''European Journal of Inorganic Chemistry''. History Founded in 1868 as ''Berichte der Deutschen Chemischen Gesellschaft'' (, CODEN BDCGAS), it operated under this title until 1928 (Vol. 61). The journal was then split into: * ''Berichte der Deutschen Chemischen Gesellschaft, A: Vereins-Nachrichten'' (, CODEN BDCAAS), and * ''Berichte der Deutschen Chemischen Gesellschaft, B: Abhandlungen'' (, CODEN BDCBAD). Vol. 78 and 79 (1945–1946) were omitted and not published due to World War II. The journal was renamed ''Chemische Berichte'' (, CODEN CHBEAM) in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cis Isomer
Cis or cis- may refer to: Places * Cis, Trentino, in Italy * In Poland: ** Cis, Świętokrzyskie Voivodeship, south-central ** Cis, Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship, north Math, science and biology * cis (mathematics) (cis(''θ'')), a trigonometric mathematical function related to Euler's formula * ''Cis'' (beetle), genus * Cis–trans isomerism, in chemistry * cis-regulatory element, regions of non-coding DNA which regulate the transcription of nearby genes Other uses * Cisgender, in contrast with transgender * C♯ (musical note), known as cis See also * CIS (other) * * Ciss (other) Ciss (pronounced SIHS) is a Senegalese surname. Notable people with the surname include: * Amadou Ciss (born 1999), Senegalese footballer who plays for Fortuna Sittard * Elhadji Ciss (born 1994), Senegalese footballer who plays for Sion *Khadija ... * Csi (other) {{disambiguation, geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
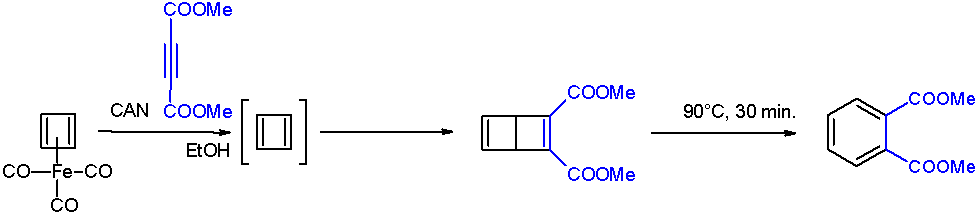
Cyclobutadiene
Cyclobutadiene is an organic compound with the formula . It is very reactive owing to its tendency to dimerize. Although the parent compound has not been isolated, some substituted derivatives are robust and a single molecule of cyclobutadiene is quite stable. Since the compound degrades by a bimolecular process, the species can be observed by matrix isolation techniques at temperatures below 35 K. It is thought to adopt a rectangular structure. Structure and reactivity The compound is the prototypical antiaromatic hydrocarbon with 4 π-electrons. It is the smallest 'n'' annulene ( annulene). Its rectangular structure is the result of the Jahn–Teller effect, which distorts the molecule and lowers its symmetry, converting the triplet to a singlet ground state. The electronic states of cyclobutadiene have been explored with a variety of computational methods. The rectangular structure is consistent with the existence of two different 1,2-dideutero-1,3-cyclobutadiene valence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tautomer
Tautomers () are structural isomers (constitutional isomers) of chemical compounds that readily interconvert. The chemical reaction interconverting the two is called tautomerization. This conversion commonly results from the relocation of a hydrogen atom within the compound. The phenomenon of tautomerization is called tautomerism, also called desmotropism. Tautomerism is for example relevant to the behavior of amino acids and nucleic acids, two of the fundamental building blocks of life. Care should be taken not to confuse tautomers with depictions of "contributing structures" in chemical resonance. Tautomers are distinct chemical species that can be distinguished by their differing atomic connectivities, molecular geometries, and physicochemical and spectroscopic properties, whereas resonance forms are merely alternative Lewis structure (valence bond theory) depictions of a single chemical species, whose true structure is best described as the "average" of the idealized, hypo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semibullvalene
Bullvalene is a hydrocarbon with the chemical formula . The molecule has a cage-like structure formed by the fusion of one cyclopropane and three cyclohepta-1,4-diene rings. Bullvalene is unusual as an organic molecule due to the and bonds forming and breaking rapidly on the Nuclear_magnetic_resonance, NMR timescale; this property makes it a fluxional molecule. Stereodynamics The bullvalene molecule is a cyclopropane platform with three vinylene group, vinylene arms conjoined at a methine group. This arrangement enables a degenerate Cope rearrangement with the result that all carbon atoms and hydrogen atoms appear equivalent on the NMR timescale. At room temperature the 1H NMR signals average to a rounded peak at 5.76 ppm. At lower temperatures the peak broadens into a mound-like appearance, and at very low temperatures the fluxional behavior of bullvalene is reduced, allowing for 4 total signals to be seen. This pattern is consistent with an exchange process whose rate ''k'' i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cubane
Cubane () is a synthetic hydrocarbon compound that consists of eight carbon atoms arranged at the corners of a Cube (geometry), cube, with one hydrogen atom attached to each carbon atom. A solid crystalline substance, cubane is one of the Platonic hydrocarbons and a member of the prismanes. It was first synthesized in 1964 by Philip Eaton and Thomas Cole. Before this work, Eaton believed that cubane would be impossible to synthesize due to the "required 90 degree molecular geometry, bond angles". The cubic shape requires the carbon atoms to adopt an unusually sharp 90° bonding angle, which would be highly strain (chemistry), strained as compared to the 109.45° angle of a tetrahedral geometry, tetrahedral carbon. Once formed, cubane is quite kinetic stability, kinetically stable, due to a lack of readily available decomposition paths. It is the simplest hydrocarbon with octahedral symmetry. Having high potential energy but kinetic stability makes cubane and its derivative compoun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pericyclic Reaction
In organic chemistry, a pericyclic reaction is the type of organic reaction wherein the transition state of the molecule has a cyclic geometry, the reaction progresses in a concerted fashion, and the bond orbitals involved in the reaction overlap in a continuous cycle at the transition state. Pericyclic reactions stand in contrast to ''linear reactions'', encompassing most organic transformations and proceeding through an acyclic transition state, on the one hand and '' coarctate reactions'', which proceed through a doubly cyclic, concerted transition state on the other hand. Pericyclic reactions are usually rearrangement or addition reactions. The major classes of pericyclic reactions are given in the table below (the three most important classes are shown in bold). Ene reactions and cheletropic reactions are often classed as group transfer reactions and cycloadditions/cycloeliminations, respectively, while dyotropic reactions and group transfer reactions (if ene reactions are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |