Cuneane on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Cuneane (C8H8, pentacyclo .3.0.02,4.03,7.06,8ctane) is a 
saturated
Saturation, saturated, unsaturation or unsaturated may refer to:
Chemistry
* Saturation, a property of organic compounds referring to carbon-carbon bonds
** Saturated and unsaturated compounds
**Degree of unsaturation
** Saturated fat or fatty ac ...
hydrocarbon
In organic chemistry, a hydrocarbon is an organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon. Hydrocarbons are examples of group 14 hydrides. Hydrocarbons are generally colourless and hydrophobic, and their odors are usually weak or ex ...
. Its name is derived from the Latin ''cuneus
The cuneus (; plural cunei) is a smaller lobe in the occipital lobe of the brain. The cuneus is bounded anteriorly by the parieto-occipital sulcus and inferiorly by the calcarine sulcus.
Function
The cuneus (Brodmann area 17) receives visua ...
'', meaning a wedge. Cuneane may be produced from cubane
Cubane () is a synthetic hydrocarbon compound that consists of eight carbon atoms arranged at the corners of a cube, with one hydrogen atom attached to each carbon atom. A solid crystalline substance, cubane is one of the Platonic hydrocarbons an ...
by metal-ion-catalyzed σ-bond rearrangement. Similar reactions are known for homocubane (C9H10) and bishomocubane (C10H12).
:
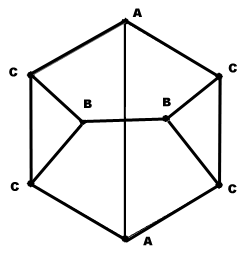
Molecular geometry
The carbon atoms in the cuneane molecule form ahexahedron
A hexahedron (plural: hexahedra or hexahedrons) or sexahedron (plural: sexahedra or sexahedrons) is any polyhedron with six faces. A cube, for example, is a regular hexahedron with all its faces square, and three squares around each vertex.
There ...
with point group C2v.
The cuneane molecule has three groups of equivalent carbon atoms (A, B, C), which have also been confirmed by NMR
Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) is a physical phenomenon in which nuclei in a strong constant magnetic field are perturbed by a weak oscillating magnetic field (in the near field) and respond by producing an electromagnetic signal with ...
. The molecular graph of the carbon skeleton of cuneane is a regular graph
In graph theory, a regular graph is a graph where each vertex has the same number of neighbors; i.e. every vertex has the same degree or valency. A regular directed graph must also satisfy the stronger condition that the indegree and outdegree o ...
with non-equivalent groups of vertices, and so it is a very important test object for different algorithms of mathematical chemistry
Mathematical chemistry is the area of research engaged in novel applications of mathematics to chemistry; it concerns itself principally with the mathematical modeling of chemical phenomena. Mathematical chemistry has also sometimes been called com ...
.
:
Derivatives
Some cuneane derivatives haveliquid crystal
Liquid crystal (LC) is a state of matter whose properties are between those of conventional liquids and those of solid crystals. For example, a liquid crystal may flow like a liquid, but its molecules may be oriented in a crystal-like way. T ...
properties.
References
{{Reflist Polycyclic nonaromatic hydrocarbons Cyclopropanes Cyclobutanes