|
Vaginal Cytology
Vaginal cytology is a microscopic examination of cells from the vaginal epithelium. In veterinary medicine, it helps differentiate the stages of the mammalian estrous cycle because the vaginal epithelium changes in response to sex hormone levels; practically, it is used to distinguish when a female canine is at a particular point in the estrous cycle. In a normal vaginal smear, lactational cells, navicular cells, endocervical cells, endometrial cells, trophoblastic cells, and leucocytes may be present. Vaginal cytology allows a clinician to: * Determine whether a canine is actually in heat. * Aid in determining the correct time to begin performing more expensive serum progesterone and luteinizing hormone (LH) assays for precise ovulation timing. * Determine if it is too late in the estrous cycle to perform artificial insemination in dogs unable or unwilling to breed naturally. * Determine if a bitch is under the influence of estrogen. * Predict the correct day to perform an e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vagina
In mammals, the vagina is the elastic, muscular part of the female genital tract. In humans, it extends from the vestibule to the cervix. The outer vaginal opening is normally partly covered by a thin layer of mucosal tissue called the hymen. At the deep end, the cervix (neck of the uterus) bulges into the vagina. The vagina allows for sexual intercourse and birth. It also channels menstrual flow, which occurs in humans and closely related primates as part of the menstrual cycle. Although research on the vagina is especially lacking for different animals, its location, structure and size are documented as varying among species. Female mammals usually have two external openings in the vulva; these are the urethral opening for the urinary tract and the vaginal opening for the genital tract. This is different from male mammals, who usually have a single urethral opening for both urination and reproduction. The vaginal opening is much larger than the nearby urethral opening, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Microscope
The optical microscope, also referred to as a light microscope, is a type of microscope that commonly uses visible light and a system of lenses to generate magnified images of small objects. Optical microscopes are the oldest design of microscope and were possibly invented in their present compound form in the 17th century. Basic optical microscopes can be very simple, although many complex designs aim to improve resolution and sample contrast. The object is placed on a stage and may be directly viewed through one or two eyepieces on the microscope. In high-power microscopes, both eyepieces typically show the same image, but with a stereo microscope, slightly different images are used to create a 3-D effect. A camera is typically used to capture the image (micrograph). The sample can be lit in a variety of ways. Transparent objects can be lit from below and solid objects can be lit with light coming through ( bright field) or around (dark field) the objective lens. Polarised ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keratin
Keratin () is one of a family of structural fibrous proteins also known as ''scleroproteins''. Alpha-keratin (α-keratin) is a type of keratin found in vertebrates. It is the key structural material making up scales, hair, nails, feathers, horns, claws, hooves, and the outer layer of skin among vertebrates. Keratin also protects epithelial cells from damage or stress. Keratin is extremely insoluble in water and organic solvents. Keratin monomers assemble into bundles to form intermediate filaments, which are tough and form strong unmineralized epidermal appendages found in reptiles, birds, amphibians, and mammals. Excessive keratinization participate in fortification of certain tissues such as in horns of cattle and rhinos, and armadillos' osteoderm. The only other biological matter known to approximate the toughness of keratinized tissue is chitin. Keratin comes in two types, the primitive, softer forms found in all vertebrates and harder, derived forms found only amon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vacuole
A vacuole () is a membrane-bound organelle which is present in plant and fungal cells and some protist, animal, and bacterial cells. Vacuoles are essentially enclosed compartments which are filled with water containing inorganic and organic molecules including enzymes in solution, though in certain cases they may contain solids which have been engulfed. Vacuoles are formed by the fusion of multiple membrane vesicles and are effectively just larger forms of these. The organelle has no basic shape or size; its structure varies according to the requirements of the cell. Discovery Contractile vacuoles ("stars") were first observed by Spallanzani (1776) in protozoa, although mistaken for respiratory organs. Dujardin (1841) named these "stars" as ''vacuoles''. In 1842, Schleiden applied the term for plant cells, to distinguish the structure with cell sap from the rest of the protoplasm. In 1885, de Vries named the vacuole membrane as tonoplast. Function The function and signifi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyknosis
Pyknosis, or karyopyknosis, is the irreversible condensation of chromatin in the nucleus of a cell undergoing necrosis or apoptosis. It is followed by karyorrhexis, or fragmentation of the nucleus. Pyknosis (from Ancient Greek meaning "thick, closed or condensed") is also observed in the maturation of erythrocytes (a red blood cell) and the neutrophil (a type of white blood cell). The maturing metarubricyte (a stage in RBC maturation) will condense its nucleus before expelling it to become a reticulocyte. The maturing neutrophil will condense its nucleus into several connected lobes that stay in the cell until the end of its cell life. File:4_Bd_obs_4_680x512px.tif, Micrograph of an infarct in the biliary tract, with pyknotic nuclei (arrows) (400x). Pyknotic nuclei are often found in the zona reticularis of the adrenal gland. They are also found in the keratinocytes of the outermost layer in parakeratinised epithelium. Another use of the word pyknotic, introduced in mathemati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epithelium
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. It is a thin, continuous, protective layer of compactly packed cells with a little intercellular matrix. Epithelial tissues line the outer surfaces of organs and blood vessels throughout the body, as well as the inner surfaces of cavities in many internal organs. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. There are three principal shapes of epithelial cell: squamous (scaly), columnar, and cuboidal. These can be arranged in a singular layer of cells as simple epithelium, either squamous, columnar, or cuboidal, or in layers of two or more cells deep as stratified (layered), or ''compound'', either squamous, columnar or cuboidal. In some tissues, a layer of columnar cells may appear to be stratified due to the placement of the nuclei. This sort of tissue is called pseudostratified. All glands are made up of epithe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromatin
Chromatin is a complex of DNA and protein found in eukaryotic cells. The primary function is to package long DNA molecules into more compact, denser structures. This prevents the strands from becoming tangled and also plays important roles in reinforcing the DNA during cell division, preventing DNA damage, and regulating gene expression and DNA replication. During mitosis and meiosis, chromatin facilitates proper segregation of the chromosomes in anaphase; the characteristic shapes of chromosomes visible during this stage are the result of DNA being coiled into highly condensed chromatin. The primary protein components of chromatin are histones. An octamer of two sets of four histone cores (Histone H2A, Histone H2B, Histone H3, and Histone H4) bind to DNA and function as "anchors" around which the strands are wound.Maeshima, K., Ide, S., & Babokhov, M. (2019). Dynamic chromatin organization without the 30-nm fiber. ''Current opinion in cell biology, 58,'' 95–104. https://doi.o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
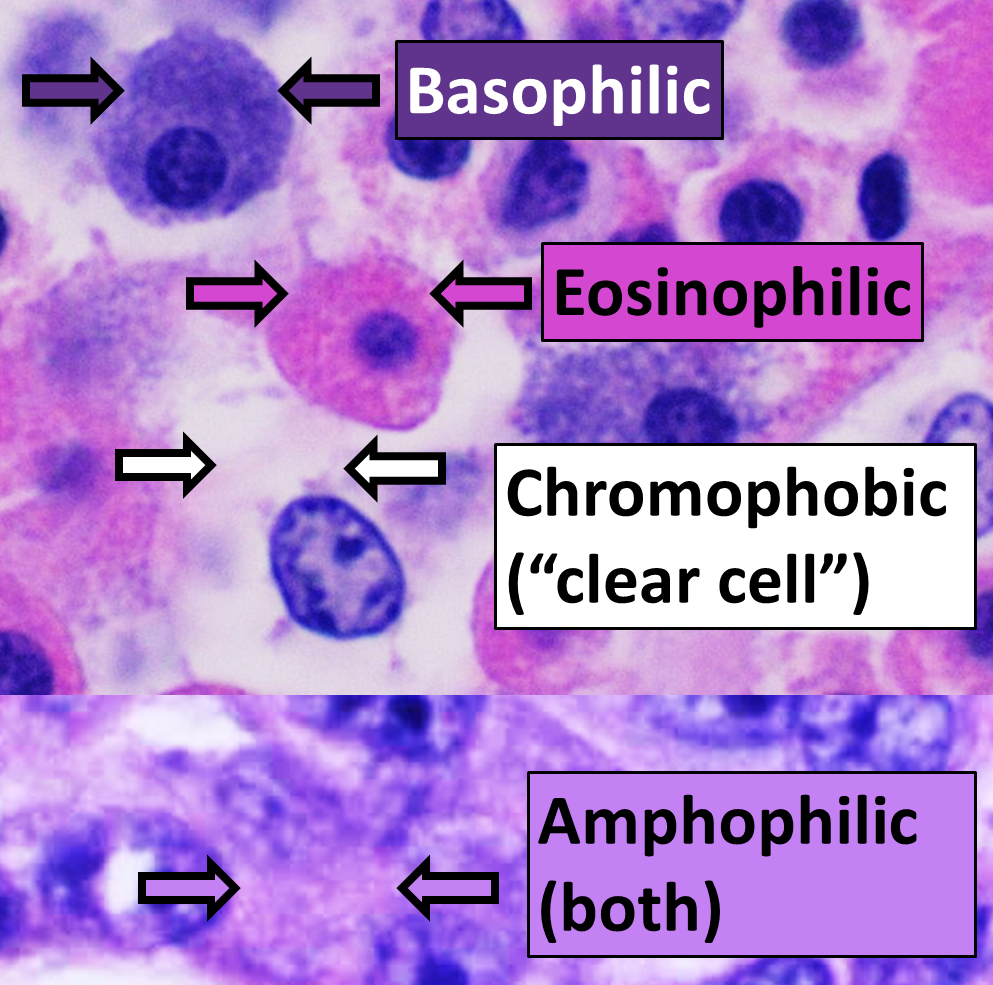
Basophilic
Basophilic is a technical term used by pathologists. It describes the appearance of cells, tissues and cellular structures as seen through the microscope after a histological section has been stained with a basic dye. The most common such dye is haematoxylin. The name basophilic refers to the characteristic of these structures to be stained very well by basic dyes. This can be explained by their charges. Basic dyes are cationic, i.e. contain positive charges, and thus they stain anionic structures (i.e. structures containing negative charges), such as the phosphate backbone of DNA in the cell nucleus and ribosomes. "Basophils" are cells that "love" (from greek "-phil") basic dyes, for example haematoxylin, azure and methylene blue. Specifically, this term refers to: * basophil granulocytes * anterior pituitary basophils An abnormal increase in basophil granulocytes is therefore also described as basophilia.https://www.collinsdictionary.com/de/worterbuch/englisch/basophilia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simple Squamous Epithelium
A simple squamous epithelium, also known as pavement epithelium, and tessellated epithelium is a single layer of flattened, polygonal cells in contact with the basal lamina (one of the two layers of the basement membrane) of the epithelium. This type of epithelium is often permeable and occurs where small molecules need to pass quickly through membranes via filtration or diffusion. Simple squamous epithelia are found in endothelium (lining of blood and lymph capillaries), mesothelium (coelomic epithelium/peritoneum), alveoli of lungs, glomeruli, and other tissues where rapid diffusion is required.AAMC - 2015 MCAT Question Pack Explanations Within the cardiovascular system such as lining capillaries or the inside of the heart, simple squamous epithelium is specifically called the endothelium The endothelium is a single layer of squamous endothelial cells that line the interior surface of blood vessels and lymphatic vessels. The endothelium forms an interface between circulatin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basal Layer
The ''stratum basale'' (basal layer, sometimes referred to as ''stratum germinativum'') is the deepest layer of the five layers of the epidermis, the external covering of skin in mammals. The ''stratum basale'' is a single layer of columnar or cuboidal basal cells. The cells are attached to each other and to the overlying stratum spinosum cells by desmosomes and hemidesmosomes. The nucleus is large, ovoid and occupies most of the cell. Some basal cells can act like stem cells with the ability to divide and produce new cells, and these are sometimes called basal keratinocyte stem cells. Others serve to anchor the epidermis glabrous skin (hairless), and hyper-proliferative epidermis (from a skin disease).McGrath, J.A.; Eady, R.A.; Pope, F.M. (2004). ''Rook's Textbook of Dermatology'' (Seventh Edition). Blackwell Publishing. Pages 3.7. . They divide to form the keratinocytes of the stratum spinosum, which migrate superficially. Other types of cells found within the ''stratum basa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vaginal Epithelium
The vaginal epithelium is the inner lining of the vagina consisting of multiple layers of (squamous) cells. The basal membrane provides the support for the first layer of the epithelium-the basal layer. The intermediate layers lie upon the basal layer, and the superficial layer is the outermost layer of the epithelium. Anatomists have described the epithelium as consisting of as many as 40 distinct layers. The mucus found on the epithelium is secreted by the cervix and uterus. The rugae of the epithelium create an involuted surface and result in a large surface area that covers 360 cm2. This large surface area allows the trans-epithelial absorption of some medications via the vaginal route. In the course of the reproductive cycle, the vaginal epithelium is subject to normal, cyclic changes, that are influenced by estrogen: with increasing circulating levels of the hormone, there is proliferation of epithelial cells along with an increase in the number of cell layers. As cell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |