|
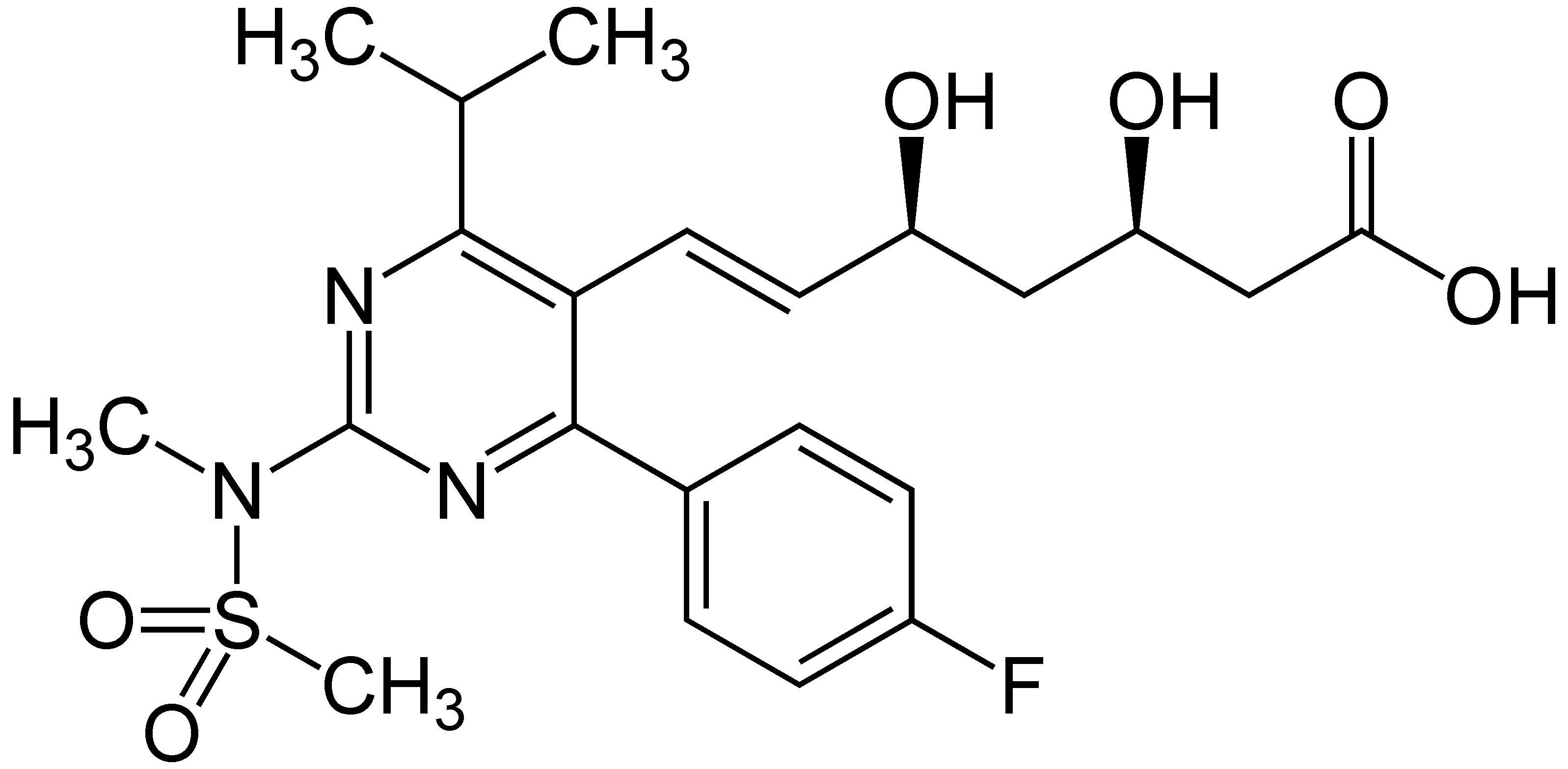
Vutrisiran
Vutrisiran, sold under the brand name Amvuttra, is a medication used for the treatment of the polyneuropathy of hereditary transthyretin-mediated (hATTR) amyloidosis in adults. It is a small interfering RNA (siRNA) that interferes with the expression of the transthyretin (TTR) gene. Vutrisiran was approved for medical use in the United States in June 2022, and in the European Union in September 2022. History The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) granted the application for vutrisiran orphan drug designation. Society and culture Legal status On 21 July 2022, the Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) of the European Medicines Agency The European Medicines Agency (EMA) is an agency of the European Union (EU) in charge of the evaluation and supervision of medicinal products. Prior to 2004, it was known as the European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products or Euro ... (EMA) adopted a positive opinion, recommending the granting of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subcutaneous Injection
Subcutaneous administration is the insertion of medications beneath the skin either by injection or infusion. A subcutaneous injection is administered as a bolus into the subcutis, the layer of skin directly below the dermis and epidermis, collectively referred to as the cutis. The instruments are usually a hypodermic needle and a syringe. Subcutaneous injections are highly effective in administering medications such as insulin, morphine, diacetylmorphine and goserelin. Subcutaneous administration may be abbreviated as SC, SQ, subcu, sub-Q, SubQ, or subcut. Subcut is the preferred abbreviation to reduce the risk of misunderstanding and potential errors. Subcutaneous tissue has few blood vessels and so drugs injected here are for slow, sustained rates of absorption, often with some amount of depot effect. Compared with other routes of administration, it is slower than intramuscular injections but still faster than intradermal injections. Subcutaneous infusion (as opposed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medication
A medication (also called medicament, medicine, pharmaceutical drug, medicinal drug or simply drug) is a drug used to diagnose, cure, treat, or prevent disease. Drug therapy (pharmacotherapy) is an important part of the medical field and relies on the science of pharmacology for continual advancement and on pharmacy for appropriate management. Drugs are classified in multiple ways. One of the key divisions is by level of control, which distinguishes prescription drugs (those that a pharmacist dispenses only on the order of a physician, physician assistant, or qualified nurse) from over-the-counter drugs (those that consumers can order for themselves). Another key distinction is between traditional small molecule drugs, usually derived from chemical synthesis, and biopharmaceuticals, which include recombinant proteins, vaccines, blood products used therapeutically (such as IVIG), gene therapy, monoclonal antibodies and cell therapy (for instance, stem cell therapies) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyneuropathy
Polyneuropathy ( poly- + neuro- + -pathy) is damage or disease affecting peripheral nerves (peripheral neuropathy) in roughly the same areas on both sides of the body, featuring weakness, numbness, and burning pain. It usually begins in the hands and feet and may progress to the arms and legs and sometimes to other parts of the body where it may affect the autonomic nervous system. It may be acute or chronic. A number of different disorders may cause polyneuropathy, including diabetes and some types of Guillain–Barré syndrome. Classification Polyneuropathies may be classified in different ways, such as by ''cause'', by ''presentation'', or by ''classes'' of polyneuropathy, in terms of which part of the nerve cell is affected mainly: the axon, the myelin sheath, or the cell body. * ''Distal axonopathy'', is the result of interrupted function of the peripheral nerves. It is the most common response of neurons to metabolic or toxic disturbances, and may be caused by metabolic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hereditary Transthyretin-mediated Amyloidosis
Familial amyloid polyneuropathy, also called transthyretin-related hereditary amyloidosis, transthyretin amyloidosis abbreviated also as ATTR (hereditary form), or Corino de Andrade's disease, is an autosomal dominant neurodegenerative disease. It is a form of amyloidosis, and was first identified and described by Portuguese neurologist Mário Corino da Costa Andrade, in 1952. FAP is distinct from senile systemic amyloidosis (SSA), which is not inherited, and which was determined to be the primary cause of death for 70% of supercentenarians who have been autopsied. FAP can be ameliorated by liver transplantation. Presentation Usually manifesting itself between 20 and 40 years of age, it is characterized by pain, paresthesia, muscular weakness and autonomic dysfunction. In its terminal state, the kidneys and the heart are affected. FAP is characterized by the systemic deposition of amyloidogenic variants of the transthyretin protein, especially in the peripheral nervous system, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Small Interfering RNA
Small interfering RNA (siRNA), sometimes known as short interfering RNA or silencing RNA, is a class of double-stranded RNA at first non-coding RNA molecules, typically 20-24 (normally 21) base pairs in length, similar to miRNA, and operating within the RNA interference (RNAi) pathway. It interferes with the expression of specific genes with complementary nucleotide sequences by degrading mRNA after transcription, preventing translation. Text was copied from this source, which is available under Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License Structure Naturally occurring siRNAs have a well-defined structure that is a short (usually 20 to 24- bp) double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) with phosphorylated 5' ends and hydroxylated 3' ends with two overhanging nucleotides. The Dicer enzyme catalyzes production of siRNAs from long dsRNAs and small hairpin RNAs. siRNAs can also be introduced into cells by transfection. Since in principle any gene can be knocked down by a syntheti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transthyretin
Transthyretin (TTR or TBPA) is a transport protein in the plasma and cerebrospinal fluid that transports the thyroid hormone thyroxine (T4) and retinol to the liver. This is how transthyretin gained its name: ''transports thyroxine and retinol''. The liver secretes TTR into the blood, and the choroid plexus secretes TTR into the cerebrospinal fluid. TTR was originally called prealbumin (or thyroxine-binding prealbumin) because it migrated faster than albumin on electrophoresis gels. Prealbumin was felt to be a misleading name, it is not a synthetic precursor of albumin. The alternative name TTR was proposed by DeWitt Goodman in 1981. Transthyretin protein is encoded by the ''TTR'' gene located on the 18th chromosome. Binding affinities It functions in concert with two other thyroid hormone-binding proteins in the serum: In cerebrospinal fluid TTR is the primary carrier of T4. TTR also acts as a carrier of retinol (vitamin A) through its association with retinol-binding pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Food And Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a List of United States federal agencies, federal agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is responsible for protecting and promoting public health through the control and supervision of food safety, tobacco products, caffeine products, dietary supplements, Prescription drug, prescription and Over-the-counter drug, over-the-counter pharmaceutical drugs (medications), vaccines, biopharmaceuticals, blood transfusions, medical devices, electromagnetic radiation emitting devices (ERED), cosmetics, Animal feed, animal foods & feed and Veterinary medicine, veterinary products. The FDA's primary focus is enforcement of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FD&C), but the agency also enforces other laws, notably Section 361 of the Public Health Service Act, as well as associated regulations. Much of this regulatory-enforcement work is not d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orphan Drug
An orphan drug is a pharmaceutical agent developed to treat medical conditions which, because they are so rare, would not be profitable to produce without government assistance. The conditions are referred to as orphan diseases. The assignment of orphan status to a disease and to drugs developed to treat it is a matter of public policy in many countries and has yielded medical breakthroughs that might not otherwise have been achieved, due to the economics of drug research and development. In the U.S. and the EU, it is easier to gain marketing approval for an orphan drug. There may be other financial incentives, such as an extended period of exclusivity, during which the producer has sole rights to market the drug. All are intended to encourage development of drugs which would otherwise lack sufficient profit motive to attract corporate research budgets and personnel. Definition According to the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), an orphan drug is defined as one "intended for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Committee For Medicinal Products For Human Use
The Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP), formerly known as Committee for Proprietary Medicinal Products (CPMP), is the European Medicines Agency's committee responsible for elaborating the agency's opinions on all issues regarding medicinal products for human use. See also * Committee for Medicinal Products for Veterinary Use The Committee for Medicinal Products for Veterinary Use (CVMP) is the European Medicines Agency's committee responsible for elaborating the agency's opinions on all issues regarding veterinary medicines. Text was copied from this source which is © ... References External links Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) Health and the European Union {{eu-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Medicines Agency
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) is an agency of the European Union (EU) in charge of the evaluation and supervision of medicinal products. Prior to 2004, it was known as the European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products or European Medicines Evaluation Agency (EMEA).Set up by EC Regulation No. 2309/93 as the European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products, and renamed by EC Regulation No. 726/2004 to the European Medicines Agency, it had the acronym EMEA until December 2009. The European Medicines Agency does not call itself EMA either – it has no official acronym but may reconsider if EMA becomes commonly accepted (secommunication on new visual identity an). The EMA was set up in 1995, with funding from the European Union and the pharmaceutical industry, as well as indirect subsidy from member states, its stated intention to harmonise (but not replace) the work of existing national medicine regulatory bodies. The hope was that this plan would not onl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orphan Drugs
An orphan drug is a pharmaceutical agent developed to treat medical conditions which, because they are so rare, would not be profitable to produce without government assistance. The conditions are referred to as orphan diseases. The assignment of orphan status to a disease and to drugs developed to treat it is a matter of public policy in many countries and has yielded medical breakthroughs that might not otherwise have been achieved, due to the economics of drug research and development. In the U.S. and the EU, it is easier to gain marketing approval for an orphan drug. There may be other financial incentives, such as an extended period of exclusivity, during which the producer has sole rights to market the drug. All are intended to encourage development of drugs which would otherwise lack sufficient profit motive to attract corporate research budgets and personnel. Definition According to the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), an orphan drug is defined as one "intended for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)