|
Vranić
Vranić ( Serbian Cyrillic: Вранић) is a suburban settlement of Belgrade, Serbia. It is located in the municipality of Barajevo. Vranić is the westernmost settlement in the municipality, located east of the '' Ibarska magistrala'', but as the settlement grew, it reached the highway. Vranić was part of the municipality of Umka which was abolished in 1960 and divided between the municipalities of Čukarica and Barajevo (Vranić and Meljak). History Wooden church was built in Vranić in the 1823. Under its foundation, an archeological find was discovered, estimated to be 5,000 years old. It was built on the foundations of the older church from the 18th century, which had a role in preparations and organization of the rebellions of Koča's frontier rebellion (1788) and First Serbian Uprising (1804). The church has rectangular base, it was built from oak logs and roofed with wood shingles. With iconostasis and wall in narthex, the interior is divided in three rooms. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IB-22 Highway (Serbia)
State Road 22, commonly known as Ibar Highway ( sr, Ибарска магистрала, Ibarska magistrala), is an IB-class road, connecting Belgrade with Šumadija and Western Serbia and finally with Montenegro at Špiljani border crossing. It starts with Orlovača interchange in Belgrade's municipality of Čukarica and is going through several major municipalities such as Ljig, Gornji Milanovac, Preljina (town in the municipality of Čačak), Kraljevo and Novi Pazar. In the southern section, highway goes in parallel to the upper course of the river Ibar, hence the name. Before the new road categorization regulation given in 2013, the route wore the following names: M 22 and M 2 (before 2012) / A2, A4, 15 and 32 (after 2012). The road is a part of the following European routes: E65 and E80 (Bregovi – Mehov Krš), E761 (Preljina – Kraljevo) and E763 (Belgrade – Preljina). Motorway alternative In order to provide the safer and faster traffic link of Belgrade with We ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barajevo
Barajevo ( sr-cyr, Барајево, ) is a municipality of the city of Belgrade. According to the 2011 census results, the municipality has a population of 27,110 inhabitants. The municipality is located in the lower northern part of Šumadija, southeast of the Belgrade, with an elevation spanning from 140 meters to 364 meters. Most of the municipal territory belongs to the drainage area of the Turija river, right tributary of the Peštan river, which in turn flows into the Kolubara, thus whole area geographically gravitates to the Kolubara region. The cultural festival, "Barlet" (Barajevo summer) is held annually in Barajevo. History Barajevo got the status of municipality in 1956 and immediately became administratively part of the wider Belgrade area. In 1957, a nearby municipality of Beljina was annexed to Barajevo, and in 1960 Umka municipality has been divided between Čukarica and Barajevo (villages of Meljak and Vranić). The settlement of Barajevo is still statistically ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Belgrade Neighborhoods
Belgrade, the capital city of Serbia, is divided into seventeen municipalities, of which ten are urban and seven suburban. In this list, each neighbourhood or suburb is categorised by the municipality in which it is situated. Six of these ten urban municipalities are completely within the bounds of Belgrade City Proper, while the remaining four have both urban and suburban parts. The seven suburban municipalities, on the other hand, are completely located within suburban bounds. Municipalities of the City of Belgrade are officially divided into local communities ( Serbian: месна заједница / ''mesna zajednica''). These are arbitrary administrative units which on occasion correspond to the neighbourhoods and suburbs located in a municipality, though usually they don't. Their boundaries often change as the communities merge with each other, split from one another, or change names, so the historical and traditional names of the neighbourhoods survive. In the majorit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Umka
Umka ( sr-cyrl, Умка) is a suburban settlement of Belgrade, Serbia. It is located in the municipality of Čukarica. Location Umka is located south-west of Belgrade, on the right bank of the Sava river, close to river's . It is a crossroads on the IB-26 highway, with roads connecting it with another important highway to the east, the '' Ibarska magistrala''. Administration Umka was a separate municipality, comprising surrounding villages of Rucka and Pećani which had a population 3,044 by the 1953 census. It was later enlarged with several surrounding villages, but the municipality was ultimately dissolved in 1960 and divided between Čukarica (Umka, Rucka and Pećani) and Barajevo (Meljak and Vranić). Geography One of the characteristics of the Belgrade city terrain is mass wasting. On the territory covered by the General Urban Plan there are 1,155 recorded mass wasting points, out of which 602 are active and 248 are labeled as the "high risk". They cover almost 3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meljak
Meljak ( sr-cyr, Мељак) is a suburban settlement of Belgrade, Serbia. It is located in the municipality of Barajevo. It is located northeast of the municipal seat of Barajevo. It is a rural settlement and thanks to its location on the Ibarska magistrala (Highway of Ibar), one of the fastest growing in the municipality. It grew from a population of 1,307 (Census 1991) to 1,772 (Census 2002), with an average annual growth of 2.8%. Meljak was part of the municipality of Umka which was abolished in 1960 and divided between the municipalities of Čukarica and Barajevo (Meljak and Vranić Vranić ( Serbian Cyrillic: Вранић) is a suburban settlement of Belgrade, Serbia. It is located in the municipality of Barajevo. Vranić is the westernmost settlement in the municipality, located east of the '' Ibarska magistrala'', ...). Demographics References Suburbs of Belgrade Barajevo {{BelgradeRS-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Districts Of Serbia
An ''okrug'' is one of the first-level administrative divisions of Serbia, corresponding to a "district" in many other countries (Serbia also has two autonomous provinces at a higher level than districts). The term ''okrug'' (pl. ''okruzi)'' literally means "encircling" and corresponds to in German language. It can be translated as "county", though it is generally rendered by the Serbian government as "district". The Serbian local government reforms of 1992, going into effect the following year, created 29 districts, with the City of Belgrade holding similar authority. Following the 2008 Kosovo declaration of independence, the districts created by the UNMIK-Administration were adopted by Kosovo. The Serbian government does not recognize these districts. The districts of Serbia are generally named after historical and geographical regions, though some, such as the Pčinja District and the Nišava District, are named after local rivers. Their areas and populations vary, rang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
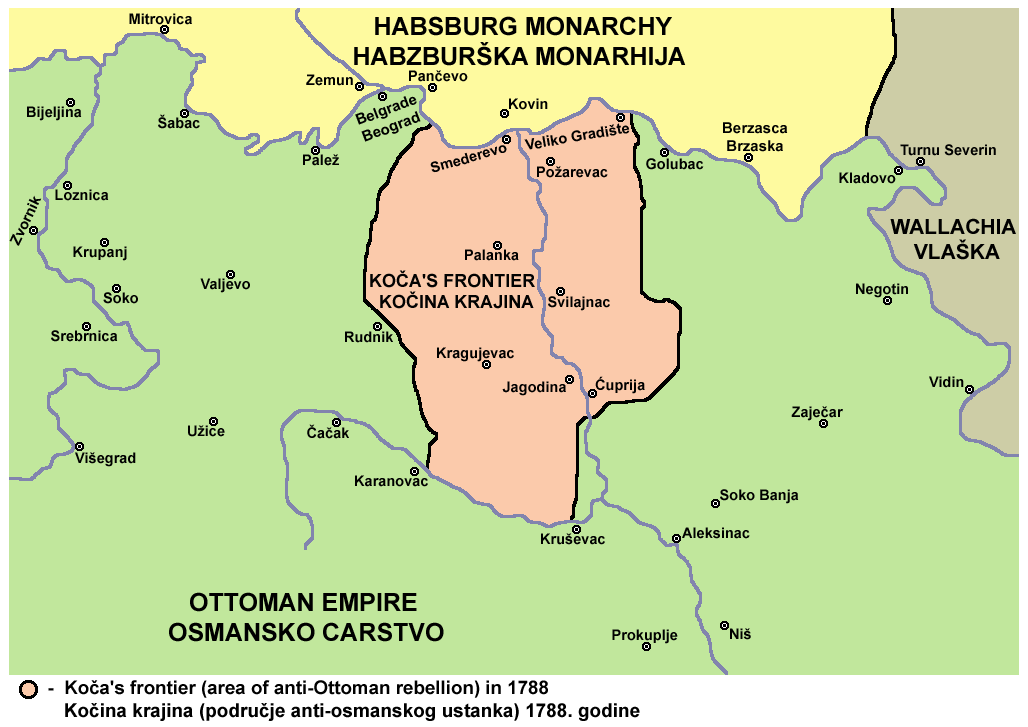
Habsburg-occupied Serbia (1788%E2%80%931792)
Koča's frontier ( sr, Кочина крајина / ''Kočina krajina'') refers to the Serbian territory established in the Sanjak of Smederevo, Ottoman Empire, during the Austro-Turkish War (1787–1791). The Habsburg-organized Serbian Free Corps, among whom Koča Anđelković was a prominent captain (hence the historiographical name), initially held the central part of the sanjak, between February and September 7, 1788; after the Austrians entered the conflict the territory was expanded and became a Habsburg protectorate under military administration, called Serbia (german: Serbien). After the Austrian withdrawal and Treaty of Sistova (1792), the territory was regained by the Ottomans. Background Serbs The Serbs had taken an active part in the wars fought in the Balkans against the Ottoman Empire, and also organized uprisings. Because of this, they suffered persecution and their territories were devastated. Major migrations from Serbia into Habsburg territory ensued. Habsbur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hamlet (place)
A hamlet is a human settlement that is smaller than a town or village. Its size relative to a Parish (administrative division), parish can depend on the administration and region. A hamlet may be considered to be a smaller settlement or subdivision or satellite entity to a larger settlement. The word and concept of a hamlet has roots in the Anglo-Norman settlement of England, where the old French ' came to apply to small human settlements. Etymology The word comes from Anglo-Norman language, Anglo-Norman ', corresponding to Old French ', the diminutive of Old French ' meaning a little village. This, in turn, is a diminutive of Old French ', possibly borrowed from (West Germanic languages, West Germanic) Franconian languages. Compare with modern French ', Dutch language, Dutch ', Frisian languages, Frisian ', German ', Old English ' and Modern English ''home''. By country Afghanistan In Afghanistan, the counterpart of the hamlet is the Qila, qala (Dari language, Dari: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cultural Monument
A national heritage site is a heritage site having a value that has been registered by a governmental agency as being of national importance to the cultural heritage or history of that country. Usually such sites are listed in a heritage register that is open to the public, and many are advertised by national visitor bureaus as tourist attractions. Usually such a heritage register list is split by type of feature (natural wonder, ruin, engineering marvel, etc.). In many cases a country may maintain more than one register; there are also registers for entities that span more than one country. History of national heritage listing Each country has its own national heritage list and naming conventions. Sites can be added to a list, and are occasionally removed and even destroyed for economic or other reasons. The concept of protecting and taking pride in cultural heritage is something that goes back to the Seven Wonders of the World, but usually it is only after destruction, espec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hadži-Ruvim
Hadži-Ruvim ( sr-cyr, Хаџи-Рувим; 19 April 1752 – 29 January 1804), born Rafailo Nenadović ( sr-Cyrl, Рафаило Ненадовић), was a Serbian Orthodox ''archimandrite'' (superior abbot) of the Bogovađa Monastery, near Lajkovac, an artist and engraver, who was part of a plot to overthrow the Dahije, renegade Janissaries that had taken control of the Sanjak of Smederevo. He was jailed and later killed in the event known as the Slaughter of the Knezes. Hadži-Ruvim was an artist, wood carver, engraver and book collector. His most beautiful engraved cross was the one for Čokešina Monastery dating from 1799. He left notes and drawings on empty pages at the monasteries he visited. In Mionica, 92 kilometers from Belgrade, there's a church famous for the icons belonging to the Hadzi-Ruvim Art School. Early life Rafailo Nenadović was born on in the village of Babina Luka, in the Valjevo ''nahija'' of the Sanjak of Smederevo (also known in historiography as the B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Narthex
The narthex is an architectural element typical of early Christian and Byzantine basilicas and churches consisting of the entrance or lobby area, located at the west end of the nave, opposite the church's main altar. Traditionally the narthex was a part of the church building, but was not considered part of the church proper. In early Christian churches the narthex was often divided into two distinct parts: an esonarthex (inner narthex) between the west wall and the body of the church proper, separated from the nave and aisles by a wall, arcade, colonnade, screen, or rail, and an external closed space, the exonarthex (outer narthex), a court in front of the church facade delimited on all sides by a colonnade as in the first St. Peter's Basilica in Rome or in the Basilica of Sant'Ambrogio in Milan. The exonarthex may have been either open or enclosed with a door leading to the outside, as in the Byzantine Chora Church. By extension, the narthex can also denote a covered porch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iconostasis
In Eastern Christianity, an iconostasis ( gr, εἰκονοστάσιον) is a wall of icons and religious paintings, separating the nave from the sanctuary in a Church (building), church. ''Iconostasis'' also refers to a portable icon stand that can be placed anywhere within a church. The iconostasis evolved from the Byzantine architecture, Byzantine templon, a process complete by the 15th century. A direct comparison for the function of the main iconostasis can be made to the layout of the great Temple in Jerusalem. That Temple was designed with three parts. The holiest and inner-most portion was that where the Ark of the Covenant was kept. This portion, the Holy of Holies, was separated from the second larger part of the building's interior by a curtain, the "parochet, veil of the temple". Only the High Priest (Judaism), High Priest was allowed to enter the Holy of Holies. The third part was the entrance court. This architectural tradition for the two main parts can be seen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |