|
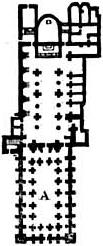
Narthex
The narthex is an architectural element typical of early Christian and Byzantine basilicas and churches consisting of the entrance or lobby area, located at the west end of the nave, opposite the church's main altar. Traditionally the narthex was a part of the church building, but was not considered part of the church proper. In early Christian churches the narthex was often divided into two distinct parts: an esonarthex (inner narthex) between the west wall and the body of the church proper, separated from the nave and aisles by a wall, arcade, colonnade, screen, or rail, and an external closed space, the exonarthex (outer narthex), a court in front of the church facade delimited on all sides by a colonnade as in the first St. Peter's Basilica in Rome or in the Basilica of Sant'Ambrogio in Milan. The exonarthex may have been either open or enclosed with a door leading to the outside, as in the Byzantine Chora Church. By extension, the narthex can also denote a covered porch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Narthex
The narthex is an architectural element typical of early Christian and Byzantine basilicas and churches consisting of the entrance or lobby area, located at the west end of the nave, opposite the church's main altar. Traditionally the narthex was a part of the church building, but was not considered part of the church proper. In early Christian churches the narthex was often divided into two distinct parts: an esonarthex (inner narthex) between the west wall and the body of the church proper, separated from the nave and aisles by a wall, arcade, colonnade, screen, or rail, and an external closed space, the exonarthex (outer narthex), a court in front of the church facade delimited on all sides by a colonnade as in the first St. Peter's Basilica in Rome or in the Basilica of Sant'Ambrogio in Milan. The exonarthex may have been either open or enclosed with a door leading to the outside, as in the Byzantine Chora Church. By extension, the narthex can also denote a covered porch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine Architecture
Byzantine architecture is the architecture of the Byzantine Empire, or Eastern Roman Empire. The Byzantine era is usually dated from 330 AD, when Constantine the Great moved the Roman capital to Byzantium, which became Constantinople, until the fall of the Byzantine Empire in 1453. However, there was initially no hard line between the Byzantine and Roman empires, and early Byzantine architecture is stylistically and structurally indistinguishable from earlier Roman architecture. This terminology was introduced by modern historians to designate the medieval Roman Empire as it evolved as a distinct artistic and cultural entity centered on the new capital of Constantinople (modern-day Istanbul) rather than the city of Rome and its environs. Its architecture dramatically influenced the later medieval architecture throughout Europe and the Near East, and became the primary progenitor of the Renaissance and Ottoman architectural traditions that followed its collapse. Characteristic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chora Church
'' '' tr, Kariye Mosque'' , image = Chora Church Constantinople 2007 panorama 002.jpg , caption = Exterior rear view , map_type = Istanbul Fatih , map_size = 220px , map_caption = Location within the Fatih district of Istanbul , location = Istanbul, Turkey , coordinates = , latitude = , longitude = , religious_affiliation = Greek Orthodox Church (before 1500), Sunni Islam (1500–1945, 2020–present), Directorate of Religious Affairs of Turkey (1924–1945, 2020–present) , status = , functional_status = Mosque , heritage_designation = , leadership = , website = , architecture = yes , architect = , architecture_type = Church , architecture_style = Byzantine architecture, Greek architecture, Ottoman architecture, Islamic , capacity = , length ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basilica Of Sant'Ambrogio
The Basilica of Sant'Ambrogio (official name: ''Basilica romana minore collegiata abbaziale prepositurale di Sant'Ambrogio'') is a church in the center of Milan, northern Italy. History One of the most ancient churches in Milan, it was built by St. Ambrose in 379–386, in an area where numerous martyrs of the Roman persecutions had been buried. The first name of the church was in fact ''Basilica Martyrum''. When St. Ambrose arrived in Milan, the local churches were in conflict with each other over the conflict between Arianism and the Nicene Creed as well as numerous local issues. He was firmly in support of the Nicene side of the conflict and wanted to make northern Italy into a pro-Rome stronghold. He did this through both preaching and construction. He built three or four churches surrounding the city; Basilica Apostolorum (now San Nazaro in Brolo), Basilica Virginum (now San Simpliciano), and Basilica Martyrum (which was later renamed in his honour). A fourth church, Ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penitent
Penance is any act or a set of actions done out of repentance for sins committed, as well as an alternate name for the Catholic, Lutheran, Eastern Orthodox, and Oriental Orthodox sacrament of Reconciliation or Confession. It also plays a part in confession among Anglicans and Methodists, in which it is a rite, as well as among other Protestants. The word ''penance'' derives from Old French and Latin ''paenitentia'', both of which derive from the same root meaning repentance, the desire to be forgiven (in English see contrition). Penance and repentance, similar in their derivation and original sense, have come to symbolize conflicting views of the essence of repentance, arising from the controversy as to the respective merits of "faith" and "good works". Word derivations occur in many languages. According to dictionary definitions, the primary meaning of ''penance'' is the deeds done out of ''penitence'', which also focuses more on the external actions than does ''repentance'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William George Clark
William George Clark (March 18216 November 1878) was an English classical and Shakespearean scholar. Life He was born at Barford Hall, Darlington. He was educated at Sedbergh School, Shrewsbury School, and Trinity College, Cambridge, where he graduated in classics and won a Browne medal and was subsequently elected Fellow. In 1857 he was appointed Public Orator. He travelled much during the long vacations, visiting Spain, Greece, Italy and Poland. In 1853 Clark had taken orders, but left the Church after the passing of the Clerical Disabilities Act 1870, of which he was one of the promoters. He also resigned the public oratorship in the same year, and in consequence of illness left Cambridge in 1873. He died at York on 6 November 1878. He bequeathed a sum of money to his old college for the foundation of a lectureship in English literature. Works Clark established the ''Cambridge Journal of Philology'', and cooperated with Benjamin Hall Kennedy and James Riddell in the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liturgical East And West
Liturgical east and west is a concept in the orientation of churches. It refers to the fact that the end of a church which has the altar, for symbolic religious reasons, is traditionally on the east side of the church (to the right in a diagram). Traditionally churches are constructed so that during the celebration of the morning liturgy the priest and congregation face towards the rising sun, a symbol of Christ and the Second Coming. However, frequently the building cannot be built to match liturgical direction. In parish churches, liturgical directions often do not coincide with geography; even in cathedrals, liturgical and geographic directions can be in almost precise opposition (for example, at St. Mark's Episcopal Cathedral, Seattle, liturgical east is nearly due west). For convenience, churches are always described as though the end with the main altar is at the east, whatever the reality, with the other ends and sides described accordingly. Therefore common terms suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modern Greek
Modern Greek (, , or , ''Kiní Neoellinikí Glóssa''), generally referred to by speakers simply as Greek (, ), refers collectively to the dialects of the Greek language spoken in the modern era, including the official standardized form of the languages sometimes referred to as Standard Modern Greek. The end of the Medieval Greek period and the beginning of Modern Greek is often symbolically assigned to the fall of the Byzantine Empire in 1453, even though that date marks no clear linguistic boundary and many characteristic features of the modern language arose centuries earlier, beginning around the fourth century AD. During most of the Modern Greek period, the language existed in a situation of diglossia, with regional spoken dialects existing side by side with learned, more archaic written forms, as with the vernacular and learned varieties (''Dimotiki'' and ''Katharevousa'') that co-existed in Greece throughout much of the 19th and 20th centuries. Varieties Varieties of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Etymologicum Magnum
''Etymologicum Magnum'' ( grc, Ἐτυμολογικὸν Μέγα, ) (standard abbreviation ''EM'', or ''Etym. M.'' in older literature) is the traditional title of a Greek lexical encyclopedia compiled at Constantinople by an unknown lexicographer around 1150 AD. It is the largest Byzantine lexicon and draws on many earlier grammatical, lexical and rhetorical works. Its main sources were two previous ''etymologica'', the so-called '' Etymologicum Genuinum'' and the '' Etymologicum Gudianum''. Other sources include Stephanus of Byzantium, the ''Epitome'' of Diogenianus, the so-called ''Lexicon'' Αἱμωδεῖν (''Haimōdeῖn''), Eulogius’ Ἀπορίαι καὶ λύσεις (''Ἀporίai kaὶ lύseis''), George Choeroboscus’ ''Epimerismi ad Psalmos'', the ''Etymologicon'' of Orion of Thebes, and collections of ''scholia''. The compiler of the ''Etymologicum Magnum'' was not a mere copyist; rather he amalgamated, reorganised, augmented and freely modified his source ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine Greek
Medieval Greek (also known as Middle Greek, Byzantine Greek, or Romaic) is the stage of the Greek language between the end of classical antiquity in the 5th–6th centuries and the end of the Middle Ages, conventionally dated to the Ottoman conquest of Constantinople in 1453. From the 7th century onwards, Greek was the only language of administration and government in the Byzantine Empire. This stage of language is thus described as Byzantine Greek. The study of the Medieval Greek language and literature is a branch of Byzantine studies, the study of the history and culture of the Byzantine Empire. The beginning of Medieval Greek is occasionally dated back to as early as the 4th century, either to 330 AD, when the political centre of the Roman Empire was moved to Constantinople, or to 395 AD, the division of the empire. However, this approach is rather arbitrary as it is more an assumption of political, as opposed to cultural and linguistic, developments. Indeed, by this time ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thyrsus
A thyrsus /ˈθɜːrsəs/ or thyrsos /ˈθɜːrˌsɒs/ (Ancient Greek: θύρσος) was a wand or staff of giant fennel (''Ferula communis'') covered with ivy vines and leaves, sometimes wound with taeniae and topped with a pine cone, artichoke, or by a bunch of vine-leaves and grapes or ivy-leaves and berries, carried during Hellenic festivals and religious ceremonies. The thyrsus is typically associated with the Greek god Dionysus, and represents a symbol of prosperity, fertility, and hedonism similarly to Dionysus. Religious/Ceremonial use In Greek religion, the staff was carried by the votaries of Dionysus. Euripides wrote that honey dripped from the thyrsos staves that the Bacchic maenads carried. The thyrsus was a sacred instrument at religious rituals and fêtes. The fabulous history of Bacchus relates that he converted the thyrsi carried by himself and his followers into dangerous weapons, by concealing an iron point in the head of leaves. Hence his thyrsus is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)