|
VotingWorks
VotingWorks is a nonprofit organization that creates and sells open-source voting systems in the U.S. They currently have three products: one for casting and counting ballots, another, named Arlo, for risk-limiting audits (RLAs), and a third for accessible at-home voting. Organization VotingWorks is a 501(c)3 founded in 2018. At the time, the next youngest election systems provider in the United States was 13 years older, with the second youngest being 40 years older. Ben Adida, who helped found the organization, holds a PhD from Massachusetts Institute of Technology, MIT in cryptography with a focus on elections and had previously worked as the Director of Engineering at Mozilla and Block, Inc., Square. VotingWorks had a staff of 15 as of 2021. Adoption In 2019, VotingWorks piloted its election systems for vote counting in the primary and general elections in Choctaw County, Mississippi, thanks in part to a favorable regulatory environment. Since then, other counties in Miss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Open-source Voting System
An open-source voting system (OSVS), also known as open-source voting (or OSV), is a voting system that uses open-source software (and/or Open-source hardware, hardware) that is completely transparent in its design in order to be checked by anyone for bugs or issues. Free and open-source software, Free and open-source systems can be adapted and used by others without paying licensing fees, improving the odds they achieve the scale usually needed for long-term success. The development of open-source voting technology has shown a small but steady trend towards increased adoption since the first system was put into practice in Choctaw County, Mississippi in 2019. Significance Security and trust Systems where more people can understand more of the process and get insights into details serve a similar purpose to election observers who help to inspire trust with increased transparency and verification. Additionally, when 90% of the market of election systems in the United States, for ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Francisco Examiner
The ''San Francisco Examiner'' is a newspaper distributed in and around San Francisco, California, and published since 1863. Once self-dubbed the "Monarch of the Dailies" by then-owner William Randolph Hearst, and flagship of the Hearst Corporation chain, the ''Examiner'' converted to free distribution early in the 21st century and is owned by Clint Reilly Communications, which bought the newspaper at the end of 2020 along with the ''SF Weekly''. History Founding The ''Examiner'' was founded in 1863 as the ''Democratic Press'', a pro-Confederacy, pro-slavery, pro-Democratic Party paper opposed to Abraham Lincoln, but after his assassination in 1865, the paper's offices were destroyed by a mob, and starting on June 12, 1865, it was called ''The Daily Examiner''. Hearst acquisition In 1880, mining engineer and entrepreneur George Hearst bought the ''Examiner''. Seven years later, after being elected to the U.S. Senate, he gave it to his son, William Randolph Hearst, who wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voting In The United States
Elections in the United States are held for government officials at the federal, state, and local levels. At the federal level, the nation's head of state, the president, is elected indirectly by the people of each state, through an Electoral College. Today, these electors almost always vote with the popular vote of their state. All members of the federal legislature, the Congress, are directly elected by the people of each state. There are many elected offices at state level, each state having at least an elective governor and legislature. There are also elected offices at the local level, in counties, cities, towns, townships, boroughs, and villages; as well as for special districts and school districts which may transcend county and municipal boundaries. The country's election system is highly decentralized. While the United States Constitution does set parameters for the election of federal officials, state law, not federal, regulates most aspects of elections ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electoral Fraud
Electoral fraud, sometimes referred to as election manipulation, voter fraud or vote rigging, involves illegal interference with the process of an election, either by increasing the vote share of a favored candidate, depressing the vote share of rival candidates, or both. It differs from but often goes hand-in-hand with voter suppression. What exactly constitutes electoral fraud varies from country to country. Electoral legislation outlaws many kinds of election fraud, * also at but other practices violate general laws, such as those banning assault, harassment or libel. Although technically the term "electoral fraud" covers only those acts which are illegal, the term is sometimes used to describe acts which are legal, but considered morally unacceptable, outside the spirit of an election or in violation of the principles of democracy. Show elections, featuring only one candidate, are sometimes classified as electoral fraud, although they may comply with the law and are presen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Civic Technology
Civic technology, or civic tech, enhances the relationship between the people and government with software for communications, decision-making, service delivery, and political process. It includes information and communications technology supporting government with software built by community-led teams of volunteers, nonprofits, consultants, and private companies as well as embedded tech teams working within government. Definition There are four different types of e-government services and civic technology falls within the category of government-to-citizen (or G2C), the other categories include government-to-business (G2B), government-to-government (G2G), and government-to-employees (G2E). A 2013 report from the Knight Foundation, an American non-profit, attempts to map different focuses within the civic technology space. It broadly categorizes civic technology projects into two categories: open government and community action. Citizens are also now given access to their represe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Verified Voting Foundation
The Verified Voting Foundation is a non-governmental, nonpartisan organization founded in 2004 by David L. Dill, a computer scientist from Stanford University, focused on how technology impacts the administration of US elections. The organization’s mission is to “strengthen democracy for all voters by promoting the responsible use of technology in elections.” Verified Voting works with election officials, elected leaders, and other policymakers who are responsible for managing local and state election systems to mitigate the risks associated with novel voting technologies. History Foundation David L. Dill's research involves "circuit verification and synthesis and in verification methods for hard real-time systems". Part of this work has required him to testify on "electronic voting before the U.S. Senate and the Commission on Federal Election Reform". These interests ultimately led him to establishing the Verified Voting Foundation in 2003. Activities Partnerships a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
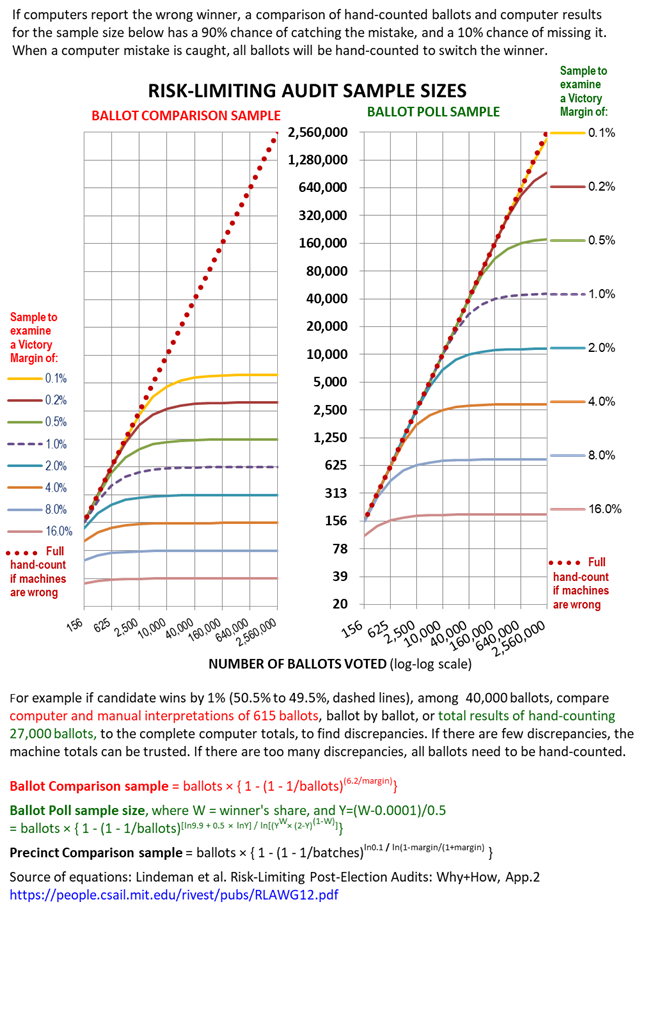
Risk-limiting Audit
A risk-limiting audit (RLA) is a post-election tabulation auditing procedure which can limit the risk that the reported outcome in an election contest is incorrect. It generally involves (1) storing voter-verified paper ballots securely until they can be checked, and (2) manually examining a statistical sample of the paper ballots until enough evidence is gathered to meet the risk limit. Advantages of an RLA include: samples can be small and inexpensive if the margin of victory is large; there are options for the public to watch and verify each step; and errors found in any step lead to corrective actions, including larger samples, up to a 100% hand count if needed. Disadvantages include: the sample needs to be a large fraction of all ballots to minimize the chance of missing mistakes, if any contest is close; and it is hard to check computer totals publicly, except by releasing computer records to the public. If examining sampled ballots shows flaws in ballot storage, the usual a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Concord Monitor
The ''Concord Monitor'' is the daily newspaper for Concord, the state capital of New Hampshire. It also covers surrounding towns in Merrimack County, most of Belknap County, as well as portions of Grafton, Rockingham and Hillsborough counties. The ''Monitor'' has several times been named as one of the best small papers in America and in April 2008, became a Pulitzer Prize winning paper, when photographer Preston Gannaway was honored for feature photography. History The ''Monitor'' has been published continuously since 1864, under a variety of names, including the ''Evening Monitor'', and owners. In the late 19th century it was owned by a publishing company called the Republican Press Association which also published a paper named the ''Independent Statesman''. Its masthead calls it the ''Concord Monitor and New Hampshire Patriot'', although the ''Monitor'' name is the only one in widespread use. James M. Langley, who had acquired both publications in the 1920s, was responsib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ProPublica
ProPublica (), legally Pro Publica, Inc., is a nonprofit organization based in New York City. In 2010, it became the first online news source to win a Pulitzer Prize, for a piece written by one of its journalists''The Guardian'', April 13, 2010Pulitzer progress for non-profit newsProPublicaPulitzer Prize in Investigative Reporting: Deadly Choices at Memorial and published in ''The New York Times Magazine'' Sheri Fink, ''New York Times Magazine'', August 25, 2009The Deadly Choices at Memorial as well as on ProPublica.org.ProPublica, August 27, 2009The Deadly Choices at Memorial ProPublica states that its investigations are conducted by its staff of full-time investigative reporters, and the resulting stories are distributed to news partners for publication or broadcast. In some cases, reporters from both ProPublica and its partners work together on a story. ProPublica has partnered with more than 90 different news organizations, and it has won six Pulitzer Prizes. History ProPu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WBUR
WBUR-FM (90.9 FM) is a public radio station located in Boston, Massachusetts, owned by Boston University. It is the largest of three NPR member stations in Boston, along with WGBH and WUMB-FM and produces several nationally distributed programs, including '' On Point'', ''Here and Now'' and ''Open Source.'' WBUR previously produced '' Car Talk'', '' Only a Game'', and '' The Connection'' (which was cancelled on August 5, 2005). ''RadioBoston'', launched in 2007, is its only purely local show. WBUR's positioning statement is "Boston's NPR News Station". WBUR also carries its programming on two other stations serving Cape Cod and the Islands: WBUH (89.1 FM) in Brewster, and WBUA (92.7 FM) in Tisbury. The latter station, located on Martha's Vineyard, uses the frequency formerly occupied by WMVY."WBUR Bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mozilla
Mozilla (stylized as moz://a) is a free software community founded in 1998 by members of Netscape. The Mozilla community uses, develops, spreads and supports Mozilla products, thereby promoting exclusively free software and open standards, with only minor exceptions. The community is supported institutionally by the non-profit Mozilla Foundation and its tax-paying subsidiary, the Mozilla Corporation. Mozilla's current products include the Firefox web browser, Thunderbird e-mail client (now through a subsidiary), Bugzilla bug tracking system, Gecko layout engine, Pocket "read-it-later-online" service, and others. History On January 23, 1998, Netscape made two announcements. First, that Netscape Communicator would be free; second, that the source code would also be free. One day later, Jamie Zawinski from Netscape registered . The project took its name "Mozilla", after the original code name of the Netscape Navigator browser—a portmanteau of "Mosaic and Godzill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |