|
Vosevi
Sofosbuvir/velpatasvir/voxilaprevir, sold under the brand name Vosevi, is a fixed-dose combination medication for the treatment of hepatitis C. It combines three drugs that each act by a different mechanism of action against the hepatitis C virus: sofosbuvir, velpatasvir, and voxilaprevir.Vosevi was approved for medical use in the United States and in the European Union in July 2017. Vosevi is sold by Gilead Sciences Gilead Sciences, Inc. () is an American biopharmaceutical company headquartered in Foster City, California, that focuses on researching and developing antiviral drugs used in the treatment of HIV/AIDS, hepatitis B, hepatitis C, influenza, and CO .... References External links * Combination drugs NS3/4A protease inhibitors NS5B (polymerase) inhibitors NS5A inhibitors {{antiinfective-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voxilaprevir
Voxilaprevir is a hepatitis C virus (HCV) nonstructural (NS) protein 3/ 4A protease inhibitor (by Gilead) that is used in combination with sofosbuvir and velpatasvir. The combination has the trade name Vosevi and received a positive opinion from the European Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use in June 2017. On 18 July 2017, Vosevi was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a List of United States federal agencies, federal agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is respon .... References NS3/4A protease inhibitors Tert-butyl compounds {{antiinfective-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gilead Sciences
Gilead Sciences, Inc. () is an American biopharmaceutical company headquartered in Foster City, California, that focuses on researching and developing antiviral drugs used in the treatment of HIV/AIDS, hepatitis B, hepatitis C, influenza, and COVID-19, including ledipasvir/sofosbuvir and sofosbuvir. Gilead is a member of the NASDAQ Biotechnology Index and the S&P 500. Gilead was founded in 1987 under the name Oligogen by Michael L. Riordan. The original name was a reference to oligomers, small strands of DNA used to target genetic sequences. Gilead held its IPO in 1992, and successfully developed drugs like Tamiflu and Vistide that decade. In the 2000s, Gilead received approval for drugs including Viread and Hepsera, among others. It began evolving from a biotechnology company into a pharmaceutical company, acquiring several subsidiaries, though it still relied heavily on contracting to manufacture its drugs. The company continued its growth in the 2010s, but came under heavy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is an infectious disease caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV) that primarily affects the liver; it is a type of viral hepatitis. During the initial infection people often have mild or no symptoms. Occasionally a fever, dark urine, abdominal pain, and yellow tinged skin occurs. The virus persists in the liver in about 75% to 85% of those initially infected. Early on, chronic infection typically has no symptoms. Over many years however, it often leads to liver disease and occasionally cirrhosis. In some cases, those with cirrhosis will develop serious complications such as liver failure, liver cancer, or dilated blood vessels in the esophagus and stomach. HCV is spread primarily by blood-to-blood contact associated with injection drug use, poorly sterilized medical equipment, needlestick injuries in healthcare, and transfusions. Using blood screening, the risk from a transfusion is less than one per two million. It may also be spread from an infected mother to her ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oral Administration
Oral administration is a route of administration where a substance is taken through the mouth. Per os abbreviated to P.O. is sometimes used as a direction for medication to be taken orally. Many medications are taken orally because they are intended to have a systemic effect, reaching different parts of the body via the bloodstream, for example. Oral administration can be easier and less painful than other routes, such as injection. However, the onset of action is relatively low, and the effectiveness is reduced if it is not absorbed properly in the digestive system, or if it is broken down by digestive enzymes before it can reach the bloodstream. Some medications may cause gastrointestinal side effects, such as nausea or vomiting, when taken orally. Oral administration can also only be applied to conscious patients, and patients willing and able to swallow. Terminology ''Per os'' (; ''P.O.'') is an adverbial phrase meaning literally from Latin "through the mouth" or "by mouth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fixed-dose Combination
A combination drug or a fixed-dose combination (FDC) is a medicine that includes two or more active ingredients combined in a single dosage form. Terms like "combination drug" or "combination drug product" can be common shorthand for a FDC product (since most combination drug products are currently FDCs), although the latter is more precise if in fact referring to a mass-produced product having a predetermined combination of drugs and respective dosages (as opposed to ''customized'' polypharmacy via compounding). And it should also be distinguished from the term "combination product" in medical contexts, which without further specification can refer to products that combine different ''types'' of medical products—such as device/drug combinations as opposed to drug/drug combinations. Note that when a combination drug product (whether fixed-dose or not) is a "pill" (i.e., a tablet or capsule), then it may also be a kind of "polypill" or combopill. Initially, fixed-dose combinati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mechanism Of Action
In pharmacology, the term mechanism of action (MOA) refers to the specific biochemical interaction through which a drug substance produces its pharmacological effect. A mechanism of action usually includes mention of the specific molecular targets to which the drug binds, such as an enzyme or receptor. Receptor sites have specific affinities for drugs based on the chemical structure of the drug, as well as the specific action that occurs there. Drugs that do not bind to receptors produce their corresponding therapeutic effect by simply interacting with chemical or physical properties in the body. Common examples of drugs that work in this way are antacids and laxatives. In contrast, a mode of action (MoA) describes functional or anatomical changes, at the cellular level, resulting from the exposure of a living organism to a substance. Importance Elucidating the mechanism of action of novel drugs and medications is important for several reasons: * In the case of anti-infectiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
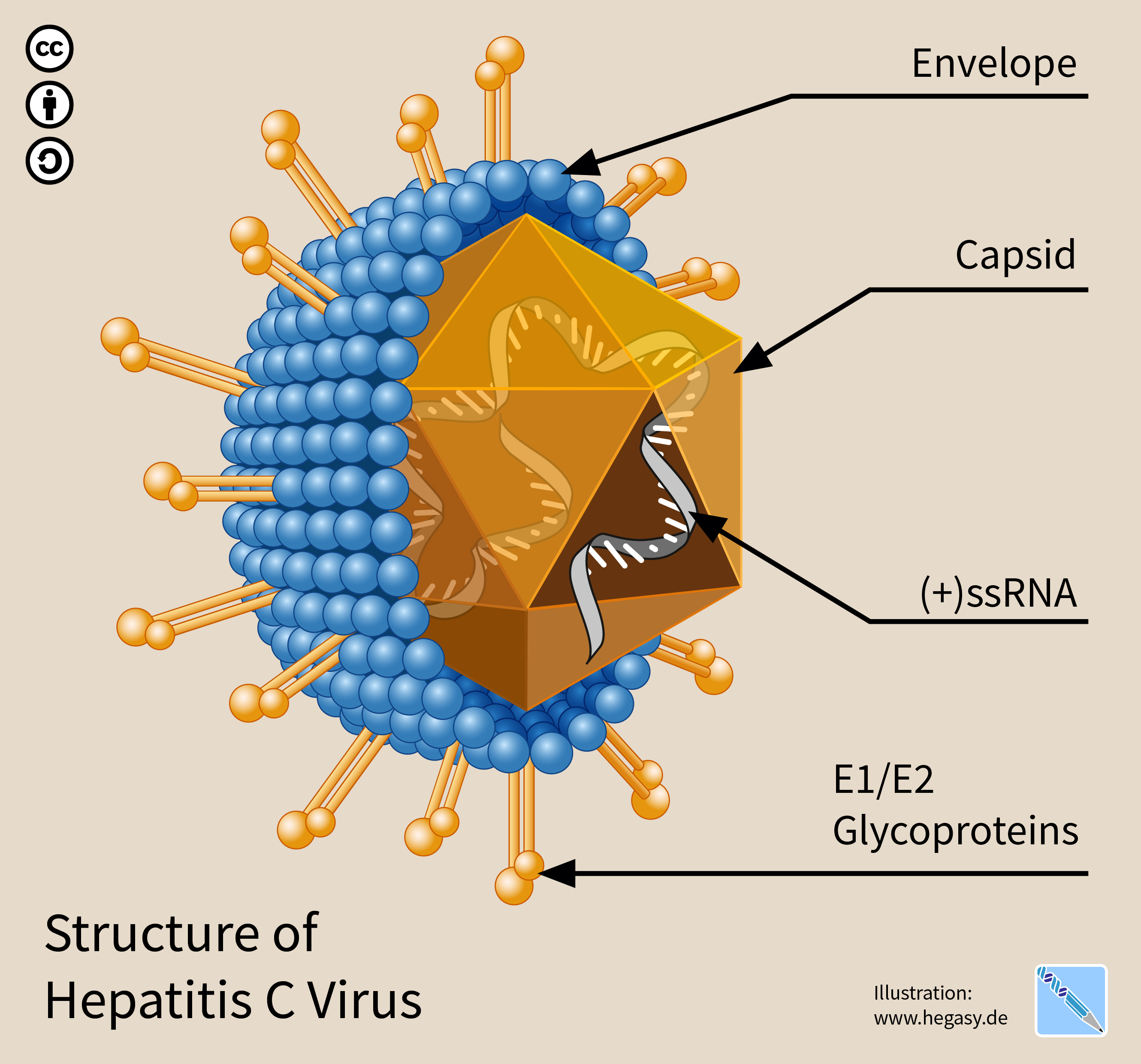
Hepatitis C Virus
The hepatitis C virus (HCV) is a small (55–65 nm in size), enveloped, positive-sense single-stranded RNA virus of the family ''Flaviviridae''. The hepatitis C virus is the cause of hepatitis C and some cancers such as liver cancer ( hepatocellular carcinoma, abbreviated HCC) and lymphomas in humans. Taxonomy The hepatitis C virus belongs to the genus ''Hepacivirus'', a member of the family ''Flaviviridae''. Before 2011, it was considered to be the only member of this genus. However a member of this genus has been discovered in dogs: canine hepacivirus. There is also at least one virus in this genus that infects horses. Several additional viruses in the genus have been described in bats and rodents. Structure The hepatitis C virus particle consists of a lipid membrane envelope that is 55 to 65 nm in diameter. Two viral envelope glycoproteins, E1 and E2, are embedded in the lipid envelope. They take part in viral attachment and entry into the cell. Within the envel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sofosbuvir
Sofosbuvir, sold under the brand name Sovaldi among others, is a medication used to treat hepatitis C. It is taken Oral administration, by mouth. Common side effects include fatigue, headache, nausea, and trouble sleeping. Side effects are generally more common in interferon-containing regimens. Sofosbuvir may reactivate hepatitis B in those who have been previously infected. In combination with ledipasvir, daclatasvir or simeprevir, it is not recommended with amiodarone due to the risk of an bradycardia, abnormally slow heartbeat. Sofosbuvir is in the nucleotide analog family of medications and works by blocking the hepatitis C NS5B protein. Sofosbuvir was discovered in 2007 and approved for medical use in the United States in 2013. It is on the WHO Model List of Essential Medicines, World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Medical uses Initial HCV treatment In 2016, the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases and the Infectious Diseases ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Velpatasvir
Velpatasvir is an NS5A inhibitor (by Gilead) which is used together with sofosbuvir in the treatment of hepatitis C infection of all six major genotypes. Side effects Side effects in studies occurred with similar frequencies as in people treated with placebo. Interactions Velpatasvir is both an inhibitor and a substrate of the transporter proteins P-glycoprotein (Pgp), ABCG2, OATP1B1 and OATP1B3. It is partly degraded by the liver enzymes CYP2B6, CYP2C8 and CYP3A4. Substances that are transported or inactivated by these proteins, or interfere with them, can interact with velpatasvir. In studies, this has been found for the HIV combination efavirenz/emtricitabine/tenofovir, which reduces the area under the curve (AUC) of velpatasvir by about 50%, and the CYP3A4 and Pgp inducer rifampicin, which reduces its AUC by about 80%, rendering it likely ineffective. Digoxin is eliminated by Pgp; its AUC is increased by about 30% in combination with velpatasvir and sofosbuvir (although ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Food And Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a List of United States federal agencies, federal agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is responsible for protecting and promoting public health through the control and supervision of food safety, tobacco products, caffeine products, dietary supplements, Prescription drug, prescription and Over-the-counter drug, over-the-counter pharmaceutical drugs (medications), vaccines, biopharmaceuticals, blood transfusions, medical devices, electromagnetic radiation emitting devices (ERED), cosmetics, Animal feed, animal foods & feed and Veterinary medicine, veterinary products. The FDA's primary focus is enforcement of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FD&C), but the agency also enforces other laws, notably Section 361 of the Public Health Service Act, as well as associated regulations. Much of this regulatory-enforcement work is not d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Medicines Agency
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) is an agency of the European Union (EU) in charge of the evaluation and supervision of medicinal products. Prior to 2004, it was known as the European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products or European Medicines Evaluation Agency (EMEA).Set up by EC Regulation No. 2309/93 as the European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products, and renamed by EC Regulation No. 726/2004 to the European Medicines Agency, it had the acronym EMEA until December 2009. The European Medicines Agency does not call itself EMA either – it has no official acronym but may reconsider if EMA becomes commonly accepted (secommunication on new visual identity an). The EMA was set up in 1995, with funding from the European Union and the pharmaceutical industry, as well as indirect subsidy from member states, its stated intention to harmonise (but not replace) the work of existing national medicine regulatory bodies. The hope was that this plan would not onl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Combination Drugs
A combination drug or a fixed-dose combination (FDC) is a medicine that includes two or more active ingredients combined in a single dosage form. Terms like "combination drug" or "combination drug product" can be common shorthand for a FDC product (since most combination drug products are currently FDCs), although the latter is more precise if in fact referring to a mass-produced product having a predetermined combination of drugs and respective dosages (as opposed to ''customized'' polypharmacy via compounding). And it should also be distinguished from the term "combination product" in medical contexts, which without further specification can refer to products that combine different ''types'' of medical products—such as device/drug combinations as opposed to drug/drug combinations. Note that when a combination drug product (whether fixed-dose or not) is a "pill" (i.e., a tablet or capsule), then it may also be a kind of "polypill" or combopill. Initially, fixed-dose combinati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)