|
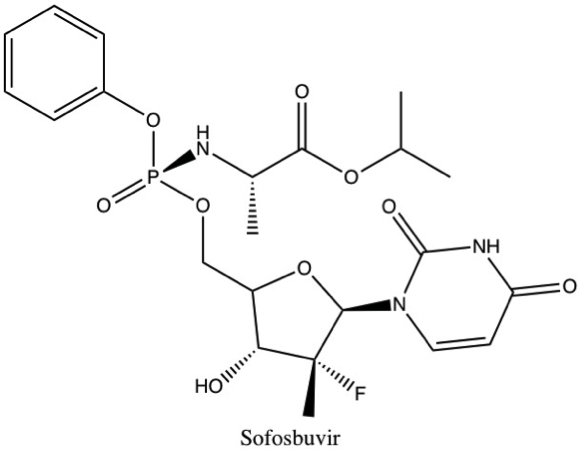
Sofosbuvir
Sofosbuvir, sold under the brand name Sovaldi among others, is a medication used to treat hepatitis C. It is taken by mouth. Common side effects include fatigue, headache, nausea, and trouble sleeping. Side effects are generally more common in interferon-containing regimens. Sofosbuvir may reactivate hepatitis B in those who have been previously infected. In combination with ledipasvir, daclatasvir or simeprevir, it is not recommended with amiodarone due to the risk of an abnormally slow heartbeat. Sofosbuvir is in the nucleotide analog family of medications and works by blocking the hepatitis C NS5B protein. Sofosbuvir was discovered in 2007 and approved for medical use in the United States in 2013. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Medical uses Initial HCV treatment In 2016, the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases and the Infectious Diseases Society of America jointly published a recommendation for the mana ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HCV Polymerase Inhibitor
Non-structural protein 5B ( NS5B) inhibitors are a class of direct-acting antivirals widely used in the treatment of chronic hepatitis C. Depending on site of action and chemical composition, NS5B inhibitors may be categorized into three classes—nucleoside active site inhibitors (NIs), non-nucleoside allosteric inhibitors, and pyrophosphate analogues. Subsequently, all three classes are then subclassified. All inhibit RNA synthesis by NS5B but at different stages/sites resulting in inability of viral RNA replication. Expression of direct-acting NS5B inhibitors does not take place in cells that are not infected by hepatitis C virus, which seems to be beneficial for this class of drugs. Low efficacy, serious side effects, development of resistance of previously available hepatitis C treatments were the greatest concerns prior to the development of direct-acting antivirals, and remained a problem at the beginning of their development ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oral Administration
Oral administration is a route of administration where a substance is taken through the mouth. Per os abbreviated to P.O. is sometimes used as a direction for medication to be taken orally. Many medications are taken orally because they are intended to have a systemic effect, reaching different parts of the body via the bloodstream, for example. Oral administration can be easier and less painful than other routes, such as injection. However, the onset of action is relatively low, and the effectiveness is reduced if it is not absorbed properly in the digestive system, or if it is broken down by digestive enzymes before it can reach the bloodstream. Some medications may cause gastrointestinal side effects, such as nausea or vomiting, when taken orally. Oral administration can also only be applied to conscious patients, and patients willing and able to swallow. Terminology ''Per os'' (; ''P.O.'') is an adverbial phrase meaning literally from Latin "through the mouth" or "by mouth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cathepsin A
Cathepsin A is an enzyme that is classified both as a cathepsin and a carboxypeptidase. In humans, it is encoded by the ''CTSA'' gene. Function This gene encodes a glycoprotein that associates with lysosomal enzymes beta-galactosidase and neuraminidase to form a complex of high-molecular-weight multimers. The formation of this complex provides a protective role for stability and activity. It is protective for β-galactosidase and neuraminidase. Clinical significance Deficiencies in this gene are linked to multiple forms of galactosialidosis. Interactions Cathepsin A has been shown to interact Advocates for Informed Choice, dba interACT or interACT Advocates for Intersex Youth, is a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization using innovative strategies to advocate for the legal and human rights of children with intersex traits. The organizat ... with NEU1. References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * External links * EC 3.4.16 Prot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carboxylesterase 1
Liver carboxylesterase 1 also known as carboxylesterase 1 (CES1, hCE-1 or CES1A1) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''CES1'' gene. The protein is also historically known as serine esterase 1 (SES1), monocyte esterase and cholesterol ester hydrolase (CEH). Three transcript variants encoding three different isoforms have been found for this gene. The various protein products from isoform a, b and c range in size from 568, 567 and 566 amino acids long, respectively. CES1 is present in most tissues with higher levels in the liver and low levels in the gastrointestinal tract. Function Carboxylesterase 1 is a serine esterase and member of a large multigene carboxylesterase family. It is also part of the alpha/beta fold hydrolase family. These enzymes are responsible for the hydrolysis of ester- and amide-bond-containing xenobiotics and drugs such as cocaine and heroin. They also hydrolyze long-chain fatty acid esters and thioesters. As part of phase II metab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histidine Triad Nucleotide-binding Protein 1
Histidine triad nucleotide-binding protein 1 also known as adenosine 5'-monophosphoramidase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''HINT1'' gene. HINT1 hydrolyzes purine nucleotide phosphoramidates with a single phosphate group. In addition, functions as scaffolding protein that modulates transcriptional activation. It is a haploinsufficient tumor suppressor gene that inhibits the Wnt/β-catenin pathway in colon cancer cells and microphthalmia-associated transcription factor (MITF) activity in human mast cells. In the LysRS-Ap4A-MITF signaling pathway, HINT1 inhibits the MITF transcriptional activity by direct association. Upon pathway activation, HINT1 is released from MITF by diadenosine tetraphosphate (Ap4A), produced by LysRS. See also * Histidine triad nucleotide-binding protein 2 Histidine triad nucleotide binding protein 2 (HINT2) is a mitochondrial protein that in humans is encoded by the ''HINT2'' gene on chromosome 9. This protein is an AMP-lysine hydr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphorylation
In chemistry, phosphorylation is the attachment of a phosphate group to a molecule or an ion. This process and its inverse, dephosphorylation, are common in biology and could be driven by natural selection. Text was copied from this source, which is available under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Protein phosphorylation often activates (or deactivates) many enzymes. Glucose Phosphorylation of sugars is often the first stage in their catabolism. Phosphorylation allows cells to accumulate sugars because the phosphate group prevents the molecules from diffusing back across their transporter. Phosphorylation of glucose is a key reaction in sugar metabolism. The chemical equation for the conversion of D-glucose to D-glucose-6-phosphate in the first step of glycolysis is given by :D-glucose + ATP → D-glucose-6-phosphate + ADP :ΔG° = −16.7 kJ/mol (° indicates measurement at standard condition) Hepatic cells are freely permeable to glucose, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |