|
Voltage Multiplier
image:Voltage Multiplier diagram.PNG, 280px, Villard cascade voltage multiplier. A voltage multiplier is an electrical circuit that converts Alternating current, AC electrical power from a lower voltage to a higher Direct current, DC voltage, typically using a network of capacitors and diodes. Voltage multipliers can be used to generate a few volts for electronic appliances, to millions of volts for purposes such as high-energy physics experiments and lightning safety testing. The most common type of voltage multiplier is the half-wave series multiplier, also called the Villard cascade (but actually invented by Heinrich Greinacher). Operation Assuming that the peak voltage of the AC source is +Us, and that the C values are sufficiently high to allow, when charged, that a current flows with no significant change in voltage, then the (simplified) working of the cascade is as follows: # going from positive peak (+Us) to negative peak (−Us): The C1 capacitor is charged through dio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voltage Multiplier Diagram
Voltage, also known as (electrical) potential difference, electric pressure, or electric tension, is the difference in electric potential between two points. In a Electrostatics, static electric field, it corresponds to the Work (electrical), work needed per unit of Electric charge, charge to move a positive Test particle#Electrostatics, test charge from the first point to the second point. In the SI unit, International System of Units (SI), the SI derived unit, derived unit for voltage is the ''volt'' (''V''). The voltage between points can be caused by the build-up of electric charge (e.g., a capacitor), and from an electromotive force (e.g., electromagnetic induction in a Electric generator, generator). On a macroscopic scale, a potential difference can be caused by electrochemical processes (e.g., cells and batteries), the pressure-induced piezoelectric effect, and the thermoelectric effect. Since it is the difference in electric potential, it is a physical Scalar (physics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
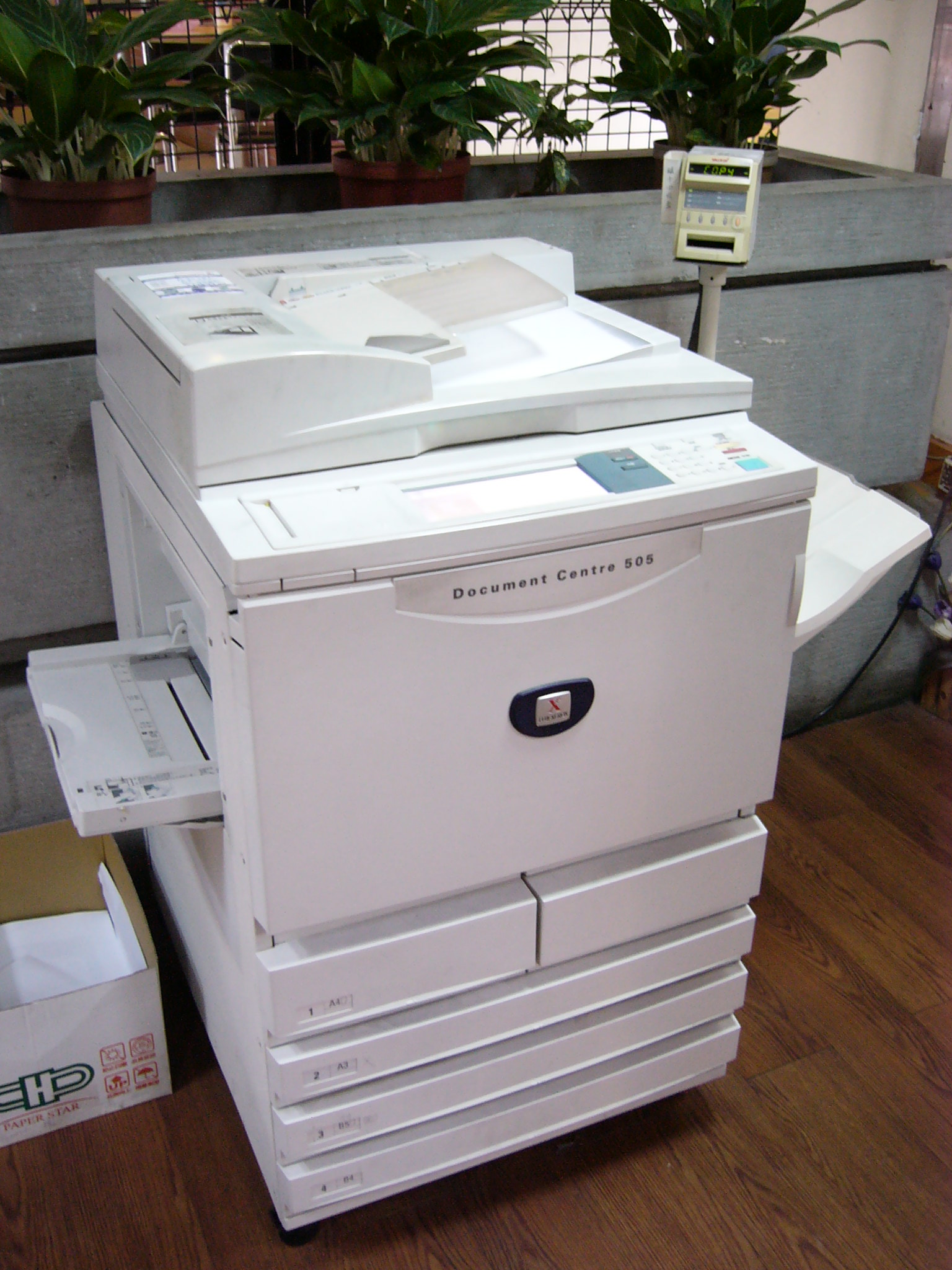
Copier
A photocopier (also called copier or copy machine, and formerly Xerox machine, the generic trademark) is a machine that makes copies of documents and other visual images onto paper or plastic film quickly and cheaply. Most modern photocopiers use a technology called ''xerography'', a dry process that uses electrostatic charges on a light-sensitive photoreceptor to first attract and then transfer toner particles (a powder) onto paper in the form of an image. The toner is then fused onto the paper using heat, pressure, or a combination of both. Copiers can also use other technologies, such as inkjet, but xerography is standard for office copying. Commercial xerographic office photocopying gradually replaced copies made by verifax, photostat, carbon paper, mimeograph machines, and other duplicating machines. Photocopying is widely used in the business, education, and government sectors. While there have been predictions that photocopiers will eventually become obsolete as in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Envelope Detector
An envelope detector (sometimes called a peak detector) is an electronic circuit that takes a (relatively) high-frequency signal as input and outputs the '' envelope'' of the original signal. Diode detector A simple form of envelope detector used in detectors for early radios is the diode detector. Its output approximates a voltage-shifted version of the input's upper envelope. Between the circuit's input and output is a diode that performs half-wave rectification, allowing substantial current flow only when the input voltage is around a diode drop higher than the output terminal. The output is connected to a capacitor of value C and resistor of value R in parallel to ground. The capacitor is charged as the input voltage approaches its positive peaks. At other times, the capacitor is gradually discharged through the resistor. The resistor and capacitor form a 1st-order low pass filter, which attenuates higher frequencies at a rate of -6 dB per octave above its cu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charge Pump
A charge pump is a kind of DC-to-DC converter that uses capacitors for energetic charge storage to raise or lower voltage. Charge-pump circuits are capable of high efficiencies, sometimes as high as 90–95%, while being electrically simple circuits. Description Charge pumps use some form of switching device to control the connection of a supply voltage across a load through a capacitor in a two stage cycle. In the first stage a capacitor is connected across the supply, charging it to that same voltage. In the second stage the circuit is reconfigured so that the capacitor is in series with the supply and the load. This doubles the voltage across the load - the sum of the original supply and the capacitor voltages. The pulsing nature of the higher voltage switched output is often smoothed by the use of an output capacitor. An external or secondary circuit drives the switching, typically at tens of kilohertz up to several megahertz. The high frequency minimizes the amount of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
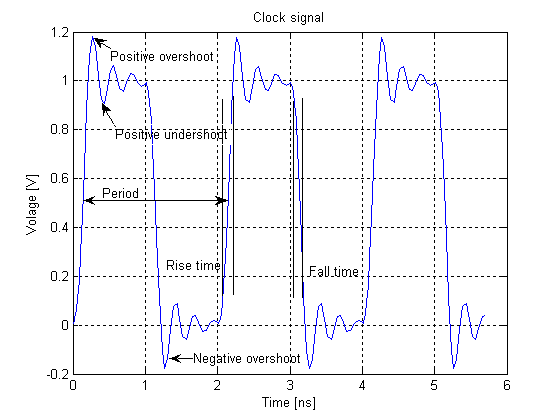
Clock Pulse
In electronics and especially synchronous digital circuits, a clock signal (historically also known as ''logic beat'') is an electronic logic signal (voltage or current) which oscillates between a high and a low state at a constant frequency and is used like a metronome to synchronize actions of digital circuits. In a synchronous logic circuit, the most common type of digital circuit, the clock signal is applied to all storage devices, flip-flops and latches, and causes them all to change state simultaneously, preventing race conditions. A clock signal is produced by an electronic oscillator called a clock generator. The most common clock signal is in the form of a square wave with a 50% duty cycle. Circuits using the clock signal for synchronization may become active at either the rising edge, falling edge, or, in the case of double data rate, both in the rising and in the falling edges of the clock cycle. Digital circuits Most integrated circuits (ICs) of sufficien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DC-to-DC Converter
A DC-to-DC converter is an electronic circuit or electromechanical device that converts a source of direct current (DC) from one voltage level to another. It is a type of Electric power conversion, electric power converter. Power levels range from very low (small batteries) to very high (high-voltage power transmission). History Before the development of power semiconductors, one way to convert the voltage of a DC supply to a higher voltage, for low-power applications, was to convert it to AC by using a vibrator (electronic), vibrator, then by a step-up transformer, and finally a rectifier. Where higher power was needed, a motor–generator unit was often used, in which an electric motor drove a generator that produced the desired voltage. (The motor and generator could be separate devices, or they could be combined into a single "dynamotor" unit with no external power shaft.) These relatively inefficient and expensive designs were used only when there was no alternative, as to po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cockcroft–Walton Generator
The Cockcroft–Walton (CW) generator, or multiplier, is an electric circuit that generates a high DC voltage from a low-voltage AC. It was named after the British and Irish physicists John Douglas Cockcroft and Ernest Thomas Sinton Walton, who in 1932 used this circuit design to power their particle accelerator, performing the first accelerator-induced nuclear disintegration in history. They used this voltage multiplier cascade for most of their research, which in 1951 won them the Nobel Prize in Physics for " Transmutation of atomic nuclei by artificially accelerated atomic particles". The circuit was developed in 1919, by Heinrich Greinacher, a Swiss physicist. For this reason, this doubler cascade is sometimes also referred to as the Greinacher multiplier. Cockcroft–Walton circuits are still used in particle accelerators. They also are used in everyday electronic devices that require high voltages, such as X-ray machines and photocopiers. Operation The CW gener ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dickson Voltage Multiplier
Dickson may refer to: People * Dickson (given name) * Dickson (surname) Places In Australia: * Dickson, Australian Capital Territory in Canberra * Dickson College in Canberra *Dickson Centre, Australian Capital Territory in Canberra * Division of Dickson, Electoral Division, Queensland In Canada: * Dickson, Alberta * Dickson Hill, Ontario In Greenland: * Dickson Fjord In Malaysia: * Port Dickson, Negeri Sembilan In Russia: * Dikson (urban-type settlement), Krasnoyarsk Krai (named for Oscar Dickson) In the United States: * Dickson, Alaska * Dickson, Oklahoma *Dickson, Tennessee * Dickson City, Pennsylvania *Dickson County, Tennessee * Dickson Township, Michigan * Dickson Tavern Erie, PA Historical Building * Dickson, West Virginia Lakes * Dickson Lake in Argentina and Chile Literature *'' Dickson!'', a collection of short stories by Gordon R. Dickson Ships * , a cargo ship leased to the Soviet Union during the Second World War Other * a 6-row barley variety *Father D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ripple (electrical)
Ripple (specifically ripple voltage) in electronics is the residual periodic variation of the DC voltage within a power supply which has been derived from an alternating current (AC) source. This ripple is due to incomplete suppression of the alternating waveform after rectification. Ripple voltage originates as the output of a rectifier or from generation and commutation of DC power. Ripple (specifically ripple current or surge current) may also refer to the pulsed current consumption of non-linear devices like capacitor-input rectifiers. As well as these time-varying phenomena, there is a frequency domain ripple that arises in some classes of filter and other signal processing networks. In this case the periodic variation is a variation in the insertion loss of the network against increasing frequency. The variation may not be strictly linearly periodic. In this meaning also, ripple is usually to be considered an incidental effect, its existence being a compromise between t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stacked Villard Cascade
''Stacked'' is an American television sitcom that aired on Fox from April 13, 2005, to January 11, 2006. Premise ''Stacked'' was described as the opposite of ''Cheers'', instead of a smart person in a "dumb" place, it is based on the concept of a dumb person in a "smart" place. A workplace, ensemble comedy, ''Stacked'' revolves around Skyler Dayton (Pamela Anderson), who is tired of her non-stop partying lifestyle and bad choices in boyfriends. Wanting a major life change, she wanders into Stacked Books - a small, family-run bookstore in the San Francisco area - owned by Gavin Miller ( Elon Gold) and his brother, Stuart ( Brian Scolaro). Divorced and unlucky in love himself, Gavin's inclined to regard Skyler as an embodiment of the vacuous, image-obsessed culture he has come to abhor. Stuart, however, is dazzled by Skyler's beauty and - much to Gavin's horror - offers her a job at their store, which she happily accepts as the first step in her quest for a steadier lifestyle. Un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |