|
Vocology
Vocology is the science and practice of vocal habilitation, or vocal training and therapy.Titze IR. (1996). What is vocology? Logopedics Phoniatrics Vocology, 21:5-6. Its concerns include the nature of speech and language pathology, the defects of the vocal tract ( laryngology), the remediation of speech therapy, and the voice training ( voice therapy) and voice pedagogy of song and speech for actors and public speakers. In its broadest sense, vocology is the study of voice, but as a professional discipline it has a narrower focus: the science and practice of voice habilitation, which includes evaluation, diagnosis, and intervention. History Vocology was invented (simultaneously, but independently) by Ingo Titze, and an otolaryngologist at Washington University, Prof. George Gates. Titze defines vocology as "the science and practice of voice habilitation, with a strong emphasis on habilitation". To habilitate means to “enable”, to “equip for”, to “capacitate”; i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ingo Titze
Ingo R. Titze is a voice scientist and executive director of the National Center for Voice and Speech and Adjunct Professor in the Department of Otolaryngology/Head and Neck Surgery at the University of Utah in Salt Lake City. He also teaches at the Summer Vocology Institute, also housed at the University of Utah. He is a Distinguished Professor at the Department of Communication Sciences and Disorders at the University of Iowa and has written several books relating to the human voice. Education Titze received a B.S. in Electrical Engineering from the University of Utah, and then an M.S.E.E. in Electrical Engineering, with a minor in Physics from the University of Utah. He graduated with a Ph.D. in physics from Brigham Young University in 1972. In 1976 he went to Gallaudet University, where he received his first of many grants from the National Institutes of Health. Career Prior to his conjoint positions at the Universities of Utah and Iowa (for which he began in 2009 and 1990, r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Center For Voice And Speech
The National Center for Voice and Speech (NCVS), is a multi-site research and teaching organization dedicated to studying the characteristics, limitations and enhancement of human voice and speech. The NCVS is located in Salt Lake City, Utah with the Lead Institution located at the University of Utah. NCVS is also a Center at the University of Iowa where it has laboratories in the Department of Speech Pathology and Audiology. In addition, the NCVS has collaborators in Denver and at many institutions around the United States. Its focus is vocology, or the science and practice of voice habilitation. History Initially conceived as a "center without walls," the NCVS was formally organized in 1990 with the assistance of a grant from the National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders (NIDCD), an institute of the National Institutes of Health (NIH). The NCVS was organized on the premise that a consortium of institutions (including the Wilber James Gould Voice Center at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
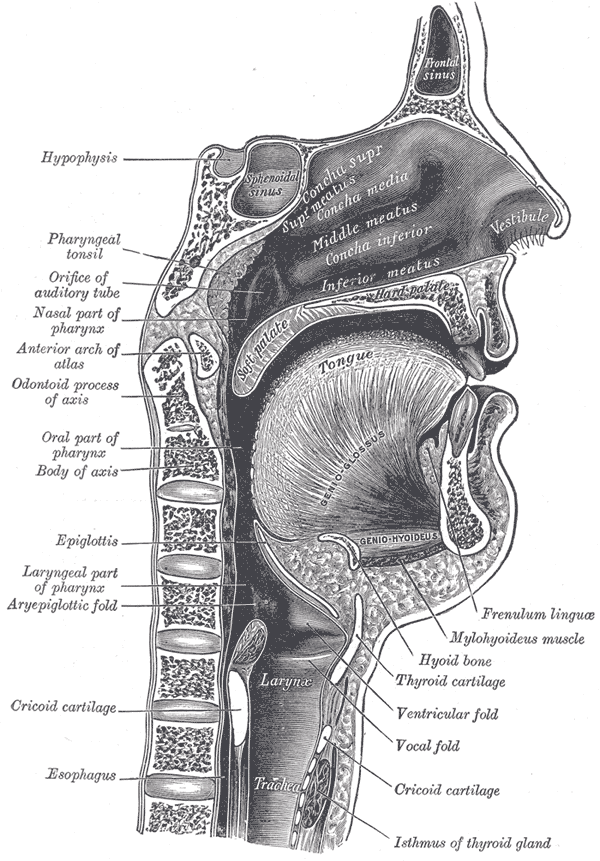
Voice Disorders
Voice disordersTitze, I.R. (1994). Principles of Voice Production, Prentice Hall, . are medical conditions involving abnormal pitch, loudness or quality of the sound produced by the larynx and thereby affecting speech production. These include: * * * Vocal fold nodules * Vocal fold cysts * Vocal cord paresis * Reinke's edema * Spasmodic dysphonia * Foreign accent syndrome * Bogart–Bacall syndrome * Laryngeal papillomatosis * Laryngitis See also * Aphasia * Dysphonia * Human voice * Laryngectomy * Parkinson's disease * Speech disorder * Vocology Vocology is the science and practice of vocal habilitation, or vocal training and therapy.Titze IR. (1996). What is vocology? Logopedics Phoniatrics Vocology, 21:5-6. Its concerns include the nature of speech and language pathology, the defects of ... * Voice changes during puberty References {{Reflist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vocal Warm Up
A vocal warm-up is a series of exercises meant to prepare the voice for singing, acting, or other use. There is very little scientific data about the benefits of vocal warm-ups. Relatively few studies have researched the effects of thesexerciseson muscle function and even fewer have studied their effect on singing-specific outcomes. Description Vocal warm-ups are intended to accomplish five things: a physical whole-body warm-up, preparing the breath, preparing the articulators and resonators, moving from the spoken register to the singing register (or an extended spoken register for acting), and preparing for the material that is going to be rehearsed or performed. Physical whole-body warm-ups help prepare a singer or actor's body in many ways. Muscles all over the body are used when singing/acting. Stretching helps to activate and prepare the large muscle groups that take care of balance and posture, and the smaller muscle groups that are directly involved with breathing a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vocal Fry
The human voice consists of sound made by a human being using the vocal tract, including talking, singing, laughing, crying, screaming, shouting, humming or yelling. The human voice frequency is specifically a part of human sound production in which the vocal folds (vocal cords) are the primary sound source. (Other sound production mechanisms produced from the same general area of the body involve the production of unvoiced consonants, clicks, whistling and whispering.) Generally speaking, the mechanism for generating the human voice can be subdivided into three parts; the lungs, the vocal folds within the larynx (voice box), and the articulators. The lungs, the "pump" must produce adequate airflow and air pressure to vibrate vocal folds. The vocal folds (vocal cords) then vibrate to use airflow from the lungs to create audible pulses that form the laryngeal sound source. The muscles of the larynx adjust the length and tension of the vocal folds to 'fine-tune' pitch and ton ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Speech
Speech is a human vocal communication using language. Each language uses Phonetics, phonetic combinations of vowel and consonant sounds that form the sound of its words (that is, all English words sound different from all French words, even if they are the same word, e.g., "role" or "hotel"), and using those words in their semantic character as words in the lexicon of a language according to the Syntax, syntactic constraints that Governance, govern lexical words' function in a sentence. In speaking, speakers perform many different intentional speech acts, e.g., informing, declaring, asking, persuading, directing, and can use Elocution, enunciation, Intonation (linguistics), intonation, degrees of loudness, tempo, and other non-representational or Paralanguage, paralinguistic aspects of vocalization to convey meaning. In their speech, speakers also unintentionally communicate many aspects of their social position such as sex, age, place of origin (through Accent (sociolinguistics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Voice
The human voice consists of sound made by a human being using the vocal tract, including talking, singing, laughing, crying, screaming, shouting, humming or yelling. The human voice frequency is specifically a part of human sound production in which the vocal folds (vocal cords) are the primary sound source. (Other sound production mechanisms produced from the same general area of the body involve the production of unvoiced consonants, clicks, whistling and whispering.) Generally speaking, the mechanism for generating the human voice can be subdivided into three parts; the lungs, the vocal folds within the larynx (voice box), and the articulators. The lungs, the "pump" must produce adequate airflow and air pressure to vibrate vocal folds. The vocal folds (vocal cords) then vibrate to use airflow from the lungs to create audible pulses that form the laryngeal sound source. The muscles of the larynx adjust the length and tension of the vocal folds to 'fine-tune' pitch and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otolaryngologist
Otorhinolaryngology ( , abbreviated ORL and also known as otolaryngology, otolaryngology–head and neck surgery (ORL–H&N or OHNS), or ear, nose, and throat (ENT)) is a surgical subspeciality within medicine that deals with the surgical and medical management of conditions of the head and neck. Doctors who specialize in this area are called otorhinolaryngologists, otolaryngologists, head and neck surgeons, or ENT surgeons or physicians. Patients seek treatment from an otorhinolaryngologist for diseases of the ear, nose, throat, base of the skull, head, and neck. These commonly include functional diseases that affect the senses and activities of eating, drinking, speaking, breathing, swallowing, and hearing. In addition, ENT surgery encompasses the surgical management of cancers and benign tumors and reconstruction of the head and neck as well as plastic surgery of the face and neck. Etymology The term is a combination of New Latin combining forms ('' oto-'' + ''rhino-'' + ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Speech And Language Pathology
Speech is a human vocal communication using language. Each language uses phonetic combinations of vowel and consonant sounds that form the sound of its words (that is, all English words sound different from all French words, even if they are the same word, e.g., "role" or "hotel"), and using those words in their semantic character as words in the lexicon of a language according to the syntactic constraints that govern lexical words' function in a sentence. In speaking, speakers perform many different intentional speech acts, e.g., informing, declaring, asking, persuading, directing, and can use enunciation, intonation, degrees of loudness, tempo, and other non-representational or paralinguistic aspects of vocalization to convey meaning. In their speech, speakers also unintentionally communicate many aspects of their social position such as sex, age, place of origin (through accent), physical states (alertness and sleepiness, vigor or weakness, health or illness), psychological ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Speech
Speech is a human vocal communication using language. Each language uses Phonetics, phonetic combinations of vowel and consonant sounds that form the sound of its words (that is, all English words sound different from all French words, even if they are the same word, e.g., "role" or "hotel"), and using those words in their semantic character as words in the lexicon of a language according to the Syntax, syntactic constraints that Governance, govern lexical words' function in a sentence. In speaking, speakers perform many different intentional speech acts, e.g., informing, declaring, asking, persuading, directing, and can use Elocution, enunciation, Intonation (linguistics), intonation, degrees of loudness, tempo, and other non-representational or Paralanguage, paralinguistic aspects of vocalization to convey meaning. In their speech, speakers also unintentionally communicate many aspects of their social position such as sex, age, place of origin (through Accent (sociolinguistics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Speech Therapy
Speech is a human vocal communication using language. Each language uses phonetic combinations of vowel and consonant sounds that form the sound of its words (that is, all English words sound different from all French words, even if they are the same word, e.g., "role" or "hotel"), and using those words in their semantic character as words in the lexicon of a language according to the syntactic constraints that govern lexical words' function in a sentence. In speaking, speakers perform many different intentional speech acts, e.g., informing, declaring, asking, persuading, directing, and can use enunciation, intonation, degrees of loudness, tempo, and other non-representational or paralinguistic aspects of vocalization to convey meaning. In their speech, speakers also unintentionally communicate many aspects of their social position such as sex, age, place of origin (through accent), physical states (alertness and sleepiness, vigor or weakness, health or illness), psychological ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voice Therapy
Voice therapy consists of techniques and procedures that target vocal parameters, such as vocal fold closure, pitch, volume, and quality. This therapy is provided by speech-language pathologists and is primarily used to aid in the management of voice disorders, or for altering the overall quality of voice, as in the case of transgender voice therapy. Vocal pedagogy is a related field to alter voice for the purpose of singing. Voice therapy may also serve to teach preventive measures such as vocal hygiene and other safe speaking or singing practices. Orientations There are several orientations towards management in voice therapy. The approach taken to voice therapy varies between individuals, as no set treatment method applies for all individuals. The specific method of treatment should consider the type and severity of the disorder, as well as individual qualities such as personal and cultural characteristics. Some common orientations are described below. Symptomatic Symptomat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |