|
Vincent Rijmen
Vincent Rijmen (; born 16 October 1970) is a Belgian cryptographer and one of the two designers of the Rijndael, the Advanced Encryption Standard. Rijmen is also the co-designer of the WHIRLPOOL cryptographic hash function, and the block ciphers Anubis, KHAZAD, Square, NOEKEON and SHARK. In 1993, Rijmen obtained a degree in electronics engineering at the Katholieke Universiteit Leuven. Afterwards, he was a PhD student at the ESAT/COSIC lab of the K.U.Leuven. In 1997, Rijmen finished his doctoral dissertation titled ''Cryptanalysis and design of iterated block ciphers''. After his PhD he did postdoctoral work at the COSIC lab, on several occasions collaborating with Joan Daemen. One of their joint projects resulted in the algorithm Rijndael, which in October 2000 was selected by the National Institute for Standards and Technology (NIST) to become the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES). Since 1 August 2001, Rijmen has been working as chief cryptographer at Cryptomathic where ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
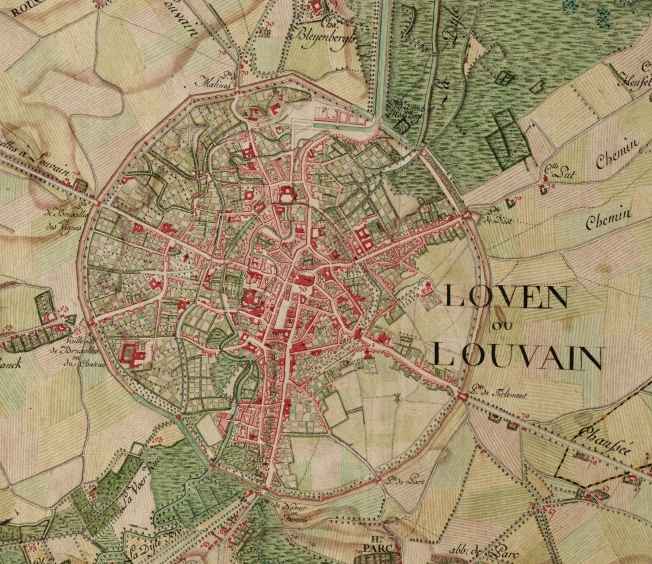
Leuven
Leuven (, ) or Louvain (, , ; german: link=no, Löwen ) is the capital and largest city of the province of Flemish Brabant in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is located about east of Brussels. The municipality itself comprises the historic city and the former neighbouring municipalities of Heverlee, Kessel-Lo, a part of Korbeek-Lo, Wilsele and Wijgmaal. It is the eighth largest city in Belgium, with more than 100,244 inhabitants. KU Leuven, Belgium's largest university, has its flagship campus in Leuven, which has been a university city since 1425. This makes it the oldest university city in the Low Countries. The city is home of the headquarters of Anheuser-Busch InBev, the world's largest beer brewer and sixth-largest fast-moving consumer goods company. History Middle Ages The earliest mention of Leuven (''Loven'') dates from 891, when a Viking army was defeated by the Frankish king Arnulf of Carinthia (see: Battle of Leuven). According to a legend, the city's red ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joan Daemen
Joan Daemen (; born 1965) is a Belgian cryptographer who co-designed with Vincent Rijmen the Rijndael cipher, which was selected as the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) in 2001. More recently, he co-designed the Keccak cryptographic hash, which was selected as the new SHA-3 hash by NIST in October 2012. He has also designed or co-designed the MMB, Square, SHARK, NOEKEON, 3-Way, and BaseKing block ciphers. In 2017 he won the Levchin Prize for Real World Cryptography "for the development of AES and SHA3". He describes his development of encryption algorithms as creating the bricks which are needed to build the secure foundations online. In 1988, Daemen graduated in electro-mechanical engineering at the Katholieke Universiteit Leuven. He subsequently joined the COSIC research group, and has worked on the design and cryptanalysis of block ciphers, stream ciphers and cryptographic hash functions. Daemen completed his PhD in 1995, at which point he worked for a year at Janssen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TR35
The Innovators Under 35 is a peer-reviewed annual award and listicle published by ''MIT Technology Review'' magazine, naming the world's top 35 innovators under the age of 35. at ''Technology Review'' with lists of winners at technologyreview.com Background The subcategories for the awards change from year to year, but generally focus on biomedicine, computing, communications, business, energy, materials, and the web. Nominations are sent from around the world and evaluated by a panel of expert judges. In some years, an Innovator of the Year or a Humanitarian of the Year is also named from among the winners. The purpose of the award is to honor "Exceptionally talented young innovators whose work has the greatest potential to transform the world." History The award was started in 1999 as the TR100, with 100 winners, but was changed to TR35 (35 winners) starting in 2005. The awards are presented to the winners at the annual Emtech conference on emerging technologies, held in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Technology Review
''MIT Technology Review'' is a bimonthly magazine wholly owned by the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, and editorially independent of the university. It was founded in 1899 as ''The Technology Review'', and was re-launched without "The" in its name on April 23, 1998 under then publisher R. Bruce Journey. In September 2005, it was changed, under its then editor-in-chief and publisher, Jason Pontin, to a form resembling the historical magazine. Before the 1998 re-launch, the editor stated that "nothing will be left of the old magazine except the name." It was therefore necessary to distinguish between the modern and the historical ''Technology Review''. The historical magazine had been published by the MIT Alumni Association, was more closely aligned with the interests of MIT alumni, and had a more intellectual tone and much smaller public circulation. The magazine, billed from 1998 to 2005 as "MIT's Magazine of Innovation," and from 2005 onwards as simply "published by MIT" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Massachusetts Institute Of Technology
The Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) is a private land-grant research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Established in 1861, MIT has played a key role in the development of modern technology and science, and is one of the most prestigious and highly ranked academic institutions in the world. Founded in response to the increasing industrialization of the United States, MIT adopted a European polytechnic university model and stressed laboratory instruction in applied science and engineering. MIT is one of three private land grant universities in the United States, the others being Cornell University and Tuskegee University. The institute has an urban campus that extends more than a mile (1.6 km) alongside the Charles River, and encompasses a number of major off-campus facilities such as the MIT Lincoln Laboratory, the Bates Center, and the Haystack Observatory, as well as affiliated laboratories such as the Broad and Whitehead Institutes. , 98 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe, the mainland territory of which comprises the western and northernmost portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and the archipelago of Svalbard also form part of Norway. Bouvet Island, located in the Subantarctic, is a dependency of Norway; it also lays claims to the Antarctic territories of Peter I Island and Queen Maud Land. The capital and largest city in Norway is Oslo. Norway has a total area of and had a population of 5,425,270 in January 2022. The country shares a long eastern border with Sweden at a length of . It is bordered by Finland and Russia to the northeast and the Skagerrak strait to the south, on the other side of which are Denmark and the United Kingdom. Norway has an extensive coastline, facing the North Atlantic Ocean and the Barents Sea. The maritime influence dominates Norway's climate, with mild lowland temperatures on the se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Bergen
The University of Bergen ( no, Universitetet i Bergen, ) is a research-intensive state university located in Bergen, Norway. As of 2019, the university has over 4,000 employees and 18,000 students. It was established by an act of parliament in 1946 based on several older scientific institutions dating back to 1825, and is Norway's second oldest university. It is considered one of Norway's four "established universities" and has faculties and programmes in all the fields of a classical university including fields that are traditionally reserved by law for established universities, including medicine and law. It is also one of Norway's leading universities in many natural sciences, including marine research and climate research. It is consistently ranked in the top one percentage among the world's universities, usually among the best 200 universities and among the best 10 or 50 universities worldwide in some fields such as earth and marine sciences. It is part of the Coimbra Group and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous city and state. A landlocked country, Austria is bordered by Germany to the northwest, the Czech Republic to the north, Slovakia to the northeast, Hungary to the east, Slovenia and Italy to the south, and Switzerland and Liechtenstein to the west. The country occupies an area of and has a population of 9 million. Austria emerged from the remnants of the Eastern and Hungarian March at the end of the first millennium. Originally a margraviate of Bavaria, it developed into a duchy of the Holy Roman Empire in 1156 and was later made an archduchy in 1453. In the 16th century, Vienna began serving as the empire's administrative capital and Austria thus became the heartland of the Habsburg monarchy. After the dissolution of the H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graz University Of Technology
Graz University of Technology (german: link=no, Technische Universität Graz, short ''TU Graz'') is one of five universities in Styria, Austria. It was founded in 1811 by Archduke John of Austria and is the oldest science and technology research and educational institute in Austria. It currently comprises seven faculties and is a public university. It offers 19 bachelors and 35 masters study programmes (of which 18 are in English) across all technology and natural science disciplines. Doctoral training is organised in 14 English-speaking doctoral schools. The university has more than 13,000 students, and approximately 2,000 students graduate every year. Science study programmes are offered in the framework of NAWI Graz together with the University of Graz. The university has a staff of 3,912. Research areas are combined in five fields of expertise. ''TU Graz'', the ''University of Leoben'' and ''TU Wien'' form the network ''Austrian Universities of Technology (TU Austria)'' wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IAIK
The Institute for Applied Information Processing and Communications (IAIK) is part of the Faculty of Computer Science and Biomedical Engineering at the Graz University of Technology (TU Graz). IAIK is concerned with aspects of computer security and information security. Current focal points are set on design of new cryptographic algorithms, implementation of cryptographic algorithms and protocols in hardware as well as in software, network security, e-Government, and trusted computing. IAIK conducts applied research into these areas, fostering a holistic view of the aspects of computer and information security. Teaching activities closely follow the latest developments in IAIK’s research fields. The activities of IAIK are led by Stefan Mangard after Reinhard Posch abdicated in 2019.IAIK Homepage"New head of IAIK" Retrieved on 26 December 2019 IAIK is specialized on following specific aspects of computer and information security: * VLSI Very large-scale integration (VLSI) is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter Landrock
Peter Landrock (born August 20, 1948 in Horsens) is a Danish cryptographer and mathematician. He is known for his contributions to data encryption methods and codes. Landrock has been active since the 1970s as research scientist and faculty member for Cambridge University and the University of Aarhus and others, and was active for Microsoft and Cryptomathic. He has been visiting professor at Oxford University, Leuven University and Princeton University. Background and career Landrock obtained a diploma in mathematics and physics in 1972 from the University of Aarhus. He received his Ph.D. in mathematics from the University of Chicago in 1974 for his research on elementary abelian and dihedral defect groups, under George Isaac Glauberman and Richard Dagobert Brauer. In 1975, Landrock became associate Professor in the Department of Mathematics at Aarhus University, then full Professor. From 1982 until 1983, Landrock was visiting professor at the Institute for Advanced Study in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryptomathic
Cryptomathic is a software company specializing in the area of cryptography for e-commerce security systems. The company develops secure software for the financial and governmental industries. It focuses especially on developing back-end solutions using hardware security modules. Cryptomathic has its headquarters in Aarhus, Denmark. The company was founded in 1986, by three professors from University of Aarhus, among them Peter Landrock and Ivan Damgård. It now operates world-wide with offices in Cambridge, UK; Munich, Germany; San Jose, California, US and Sophia Antipolis, France. Cryptomathic has collaborated in research projects with the Isaac Newton Institute for Mathematical Sciences to develop Cryptomathic's systems for securing messaging between hardware security modules (HSMs). With Bristol University, Cryptomathic conducted research on authenticated encryption between HSMs. Awards and recognition In 2002, Cryptomathic's chief cryptographer Vincent Rijmen was named one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)
